Junctions - 2008 Aris
-
Upload
amardeep-singh -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Junctions - 2008 Aris
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
1/34
Medical Cell and Tissue BiologyBMS 6110C
John P. Aris, PhD
Rm B1-8, 392-1873, [email protected]
Ross & Pawlina, 5th Edition, Chapter 5
Cell Junctions
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
2/34
Cell Junctions
Anchoring - mediate cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesions;linked to cytoskeleton to transmit and distribute stress
Occluding - form seals between epithelial cells; block orregulate (paracellular) permeability between cells
Channel-forming - allow diffusion of small molecules
Signal-relaying - ligands on or released from cell transmit
signals to receptors on adjacent cell (e.g., synapses)
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
3/34
Cell Junctions in Epithelia
Junctions perform multiple functions in epithelia
MBoC5 Fig 19-3
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
4/34
Cell Junctions
Cell-cellSymmetrical - same proteins on different cells interact
Tight junction
Zonula adherens
Desmosome
Gap junctions
Cell-matrix
Asymmetrical - cell proteins interact with matrix
Hemidesmosome
Focal adhesion (actin-linked cell-matrix adhesion)
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
5/34
Cell Adhesion Molecules
Transmembrane proteins with elaborate extracellulardomains that mediate cell-cell or cell-matrix adhesions
Intracellular domains may bind adaptor proteincomplexes that bind and regulate attachment to the
cytoskeleton Attachment to cytoskeleton distributes mechanical stress
Number and activity are regulated (e.g., cells can "let go")
Junctional - proteins clustered into specific structures
Non-junctional - proteins distributed in plasma membrane
Anchoring junction proteins
Calcium dependent - cadherins and selectinsCalcium inde endent - I famil CAMs and inte rins
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
6/34
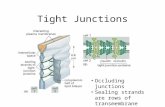
Tight Junctions
Occluding junction (encircles epithelial cells) Barrier to diffusion between cells (paracellular pathway) Separates apical and basolateral plasma membranes
Ross Fig 5-12
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
7/34
Tight Junctions
Tight junction blocks diffusion of soluble tracer molecules
added to either the apical or basolateral compartment
MBoC5 Fig 19-24
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
8/34
Tight Junction
TEM: TJ is closest to apical surface in epithelium
Freeze fracture of TJ reveals ridges in membranes thatcorrespond to sites of contact between cells
Ridges are linear arrays of occludin and claudin proteins
Ross Fig 5-10
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
9/34
Tight Junction Permeability
Some claudins and occludins have pores (A, B, and C) thatallow selective (paracellular) movement of ions or solutes
Hereditary hypomagnesemia results from mutated claudin
proteins that fail to resorb of Mg++ across renal epithelia
Side view Top view
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
10/34
Tight Junction Proteins
Occludins and claudins are transmembrane proteinsthat interact across the intercellular space to form TJs
ZO (zonula occludens) proteins 1-3 link occludin andclaudin to each other, to JAMs, and to actin filaments
JAMs - Ig family adhesion molecules (CAMs) in TJs
Ross Fig 5-11
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
11/34
Immunoglobulin
(Ig) CAMs
Diverse adhesion functions, all calcium independent Single transmembrane domain glycoproteins Extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain(s) NCAM (neural), ICAM (intercellular), VCAM (vascular)
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
12/34
Zonula
Adherens Anchoring junction
(encircles the cell)
AKA adhesion belt,belt junction, orbelt desmosome
Located "under"tight junction inepithelial cells
Connected to actinmicrofilaments that
join terminal web
MCB6 Fig 19-9
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
13/34
Zonula Adherens
Cadherin proteins attach to crosslinked actin filaments
Mechanical support - ZA and actin filaments transmit and
distribute stress throughout cell and to neighboring cells
Ross Fig 5-14
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
14/34
Cadherins
Calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecule Single transmembrane domain glycoproteins
Extracellular domain binds Ca++ and associates withextracellular domains of cadherins on adjacent cells
(homotypic binding interactions) Cytoplasmic domain associates with cytoskeleton
Many cadherins (>40) with tissue-specific distribution:E-cadherin (epithelial)N-cadherin (neural)P-cadherin (placenta)
Important in embryogenesis and cell differentiation
Often misregulated in disease (e.g., cancer)
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
15/34
Cadherins and Calcium
Calcium binding causes extracellular domains of cadherins
to adopt extended conformation capable of interacting
MBoC5 Fig 19-9
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
16/34
Cadherins and
Cytoskeleton Catenins are adaptor proteins
that form links to cytoskeleton
Catenins also regulate theadhesiveness of cadherins
F-catenin complex links classiccadherins to actin filaments
(e.g., in zonula adherens) K-catenin (plakoglobin)
complex links non-classicalcadherins to intermediate
filaments (e.g., in desmosome)
MBoC5Fig 19-14
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
17/34
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions
AKA macula adherens
Function as "spot
welds" to join cells Located along lateral
plasma membranes ofcolumnar epithelialcells or on processesof squamous cells
Intermediate filamentsassociate with plaqueproteins in cytoplasm
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
18/34
Desmosomes
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
19/34
Desmosomes
Non-classical cadherins interact across intercellular space Adaptor proteins form a dense plaque that interconnects
cadherins and binds them to intermediate filaments
MBoC5 Fig 19-17
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
20/34
Desmosomes
Desmoglein and desmocollin are non-classical cadherins
Adaptor proteins such as K-catenin (plakoglobin) and
desmoplakin link cadherins to intermediate filaments
MBoC5 Fig 19-17
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
21/34
Gap
Junction
Channel-forming junction
Named for gap of regularwidth between cellsvisualized by TEM
Water-filled junctionstransport molecules
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
22/34
Connexin - protein subunit, six form a hexameric connexon Connexons - two align to form the gap junction channel Regulation - elevated calcium concentrations close channel
Ross Fig 5-17 Gap
Junction
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
23/34
Hemidesmosomes
Hemidesmosome - "half-desmosome" in appearance only Mediates attachment to basal lamina (extracellular matrix) Cytoplasmic plaque is attached to cytoskeletal elements
Ross Fig 5-31
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
24/34
Hemidesmosomes
Integrins - membrane protein that "integrates" cell into matrix
Ross Fig 5-31
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
25/34
Integrins
Mediate calcium-independent cell-matrix adhesion Function as dimers of two membrane proteins (E and F) Adaptor proteins link integrins to intermediate filaments in
hemidesmosomes or actin filaments in focal adhesions Integrins bind matrix proteins such as laminin or fibronectin
MBoC5 Fig 19-45
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
26/34
Focal Adhesions
Anchoring junction (AKA actin-linked cell-matrix adhesion) Growing fibroblasts form many focal adhesions (orange)
that serve as anchoring points for actin filaments (green)
See Ross Fig 5-30
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
27/34
Focal
Adhesions
Fibroblasts attach to extracellular matrix via focal adhesions
Integrins - membrane proteins link actin filaments and matrix
Ross Fig 5-30
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
28/34
Selectins
Calcium-dependent
Single transmembranedomain glycoprotein
Extracellular domain binds
carbohydrates (classified aslectins - proteins that bindcarbohydrates)
Lectin domain binds specific
sugars on protein or lipid Three major classes:
P-selectins (platelets)E-selectins (endothelial cells)
L-selectins (leukocytes)
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
29/34
Transepithelial extravasation is associated with inflammation
Regulated by P-selectin exocytosis and integrin activation
Extravasation
MCB6Fig 19-36
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
30/34
Adhesion Protein Interactions
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
31/34
Adhesion Protein Interactions
Cis interactions - between proteins on the same cell Trans interactions - between proteins on different cells
Combination of interactions promotes junction formation
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
32/34
Junction Proteins
JunctionMembrane
proteins
Cytosolic
proteinsCytoskeleton
TightOccludins,claudins
ZO proteinsActin
filaments
Zonula
adherens
Cadherins
(classical)
Catenins (EF),
vinculin, Eactinin
Actin
filaments
DesmosomeCadherins:desmocollindesmoglein
Desmoplakin,plakoglobin(K-catenin)
Intermediatefilaments
Focaladhesions
IntegrinsVinculin, talin,
E-actininActin
microfilaments
Hemi-
desmosomeIntegrins Plectin, BP230
Intermediate
filaments
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
33/34
Blistering Disease
Many mechanisms underlie blistering disorders of the skin
Pemphigus group - autoimmune disease in whichautoantibodies target desmogleins present in desmosomes
-
8/8/2019 Junctions - 2008 Aris
34/34
Pemphigus Histology
Acantholysis - separation of epidermal keratinocytes (H&E)