IV Catheterization VTHT 1491- Special Topics Ms. Liddell
description
Transcript of IV Catheterization VTHT 1491- Special Topics Ms. Liddell
PowerPoint Presentation
IV CatheterizationVTHT 1491- Special TopicsMs. Liddell CTVT: Chapter 20 (pg: 607-610) VTDRG: Chapter 8 (pg: 349-351)Learning Objectives Describe the procedure for placement and care of a peripheral intravenous catheter
Describe the indications and procedure for placement and care of a jugular catheter
List requirements for monitoring of patients with intravenous catheters
3IV Catheterization Used for:Temporary access for medications, fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy, or transfusion of blood products3IV Catheterization Catheter site selection depends on: Available vessels Condition of vessels Patient Expense Urgency of situation
5IV CatheterizationComplicationsPhlebitisLocal cellulitisSepticemia Collapsed veins or hematomas rendering veins unusable
Swelling, heat, pus, thick corded feeling, or appearance of fluid from catheter site are signs to watch for.56IV Catheterization Types Winged needle (butterfly) catheterPlastic wings on needle shaft facilitate placement and taping (if needed) Tubing extending from needle to syringe connector port allows maneuverabilityIs for short-term useUsed for:blood collection Administration of non-irritating medications Moves out of vessel easily because of needle6
IV Catheter Types Over-the-needle catheterUsed primarily for peripheral vein catheterizationCome in many different sizes (gauges) that coordinate (color) with needle sizes Needlepoint extends beyond catheter tip for entry into veinOnce catheter is placed, needle is withdrawn from insertion siteMOST COMMON IV CATHETER USED
10IV Catheter Types Through-the-needle Usually longer than over-the-needle catheters (8- to 12-inch) and are primarily used for jugular vein Once catheter is placed, needle is withdrawn from insertion site and a needle guard is placed over needleProtects needle from sticking animal and shearing catheter
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AxSCCwdN1nI10IV Catheter Types Multi-lumen catheter Have two to three separate lumens allowing simultaneous infusions at one catheter sitePlacement is usually completed per- cutaneously with a guidewireMore expensive than other catheters
Used primarily in Jugular catheterization
13Peripheral Catheterization Sites Dogs and catsCephalic, medial saphenous (cat) and lateral saphenous (dog)20-gauge, 22-gauge, and 25-gauge, 1- to 1.5-inch catheters20-gauge, 22-gauge, 23/25-gauge, ` 5/8 butterfly catheters 13Peripheral CatheterizationALWAYS REMEMBERStart on the distal portion of the limb and move proximal for all catheter placement15Peripheral Vein Butterfly Catheterization Supplies ClippersAntiseptic scrub and solutionsCatheterA syringe filled with flushheparinized salineSalineTape and/or non-absorbable suture (not always used)15Butterfly Catheter Placement Procedure Venipuncturist can hold the wing of the catheter up or down when placing catheterOnce in vessel, blood will flow back into the clear tubing Syringe can be attached to tubing end and blood can be pulled into syringe for blood drawDigital pressure required from restrainerSyringe can be attached to tubing end and medications or flush can be administered through tubing Release of digital pressure required from restrainer
Butterfly Catheter Placement http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qsTAKiA3Uf0
18Peripheral Vein Catheterization Supplies ClippersAntiseptic scrub and solutionsCatheterA syringe filled with flushheparinized salineSalineInjection cap or T-connectorTape and/or non-absorbable sutureBandage material1819Peripheral Vein Catheterization Procedure Shave area of insertion site Surgical prep with antiseptic scrub and solutionAseptic technique is important to prevent infectionA relief hole may be made with a #11 blade or 20-gauge needle to reduce frictionIndicated in severely dehydrated patients or patients with tough skinOcclude vein proximal to insertion site with tourniquet or an assistant
19
21Peripheral Vein Catheterization Procedure cont..Grasp distal portion of leg and extend it to help immobilize the vein With bevel up, insert catheter through skin or relief hole at approximately 15-degree angleAdvance catheter into vessel; when blood flashes in (hub), needle and catheter are advanced together as a unit for an additional 1-4 mm21
23Peripheral Vein Catheterization Procedure cont..Hold needle still and advance the catheter ONLY into vessel Cap catheter with an injection cap or T-connector and flush catheterSecure catheter with tape wrapped around hub of catheter and then around leg
23
Taping in of Peripheral Catheters Taping techniques vary from person to persona and hospital to hospitalThere is not one right way to tape a catheter inAlways remember to:Secure the catheter hub and injection port Never secure tape to tightly Be sure patients leg is dry prior to applying tape
Peripheral Catheter Placement http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wt_K1beUZEI
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pUdJqaEe4Fw
29Jugular IV CatheterizationProcedure Site chosen is shaved and surgically preppedWipe or spray with betadine solution, left to dry on2-5 ml of lidocaine given ID over and above insertion site Create sterile field by opening sterile gloves, and laying opened catheter on glovesOther items are either placed on sterile field or in cold sterilization traySterile gloves are worn 2930Jugular IV CatheterizationHold catheter in dominant handother gloved hand occludes jugular Insert catheter into skin at approximately 45-degree angle, toward heartFlash of blood in hub indicates vessel is hit, advance centimeter moreHold needle still, sliding catheter into vessel; remove needle Check to make sure vein is still catheterized by applying digital pressureAttach a PRN or T-port and suture catheter into placeSome animals require skin to be cut or pilot hole to be drilled because of thick skin.
30
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AxSCCwdN1nI
Multi-Lumen Catheter Placement http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RGXP-FSjih8
36Jugular IV CatheterizationApply small amount of antibacterial ointment before placing wrap over catheterWrap neck or apply stents over catheters to stabilize them and to prevent them from getting rubbed out
Rotate ointments if catheter will be staying in long termprevents resistant Staphylococcus infections.
36
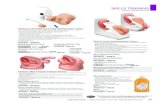
Examples of four types of IV catheters. Catheter A is a butterfly; catheter B is an OTN; catheter C is a multilumen (Triple-lumen); and catheter D is a through-the-needle.
39IV Catheter MaintenanceIf any of these things occur, remove catheter and place a new one in a different location:PhlebitisInfectionThrombosisLeaking at insertion site by itself or during a flushPain upon injection Any portion of the catheter is exposedPerformed every 48 hours or on an as-needed basisDressing should be removed and site inspected twice daily.Phlebitis may include erythema, swelling, tenderness upon palpation, and an apparent increase in skin temperature over vein.Infection is characterized by redness, local increase in temperature; may include a purulent dischargeThrombosis is characterized by vein that stands up without being held off and thick cord-like feeling to vein.
3940IV Catheter MaintenanceIf catheter site looks good, then clean with iodophor or chlorhexidine solutionRecommended not to leave a catheter in place longer than 72 hoursIf bandage gets wet, reason should be identified and bandage changedSwelling distal to catheter usually indicative of tight bandage.Swelling proximal to the catheter may be due to infiltration.
4041IV Catheter MaintenanceIf patient is chewing at bandage, reason should be investigatedCatheters not continuously used should be flushed with 4 U/ml of heparinized saline (1000 units/ 250 ml normal saline) every 4 hoursBags of heparinized saline are discarded every 12-24 hours to minimize risk of contaminationNEVER flush concentrated heparin solution into patient.Clearly label catheter to avoid inadvertent flushing of concentrated heparin into patient.
41