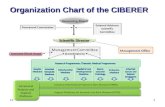
IT Services Organization Chart
description
Transcript of IT Services Organization Chart

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 1
IT Services Organization ChartIT Services Organization Chart

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 2
Authentication: SUNet IDsAuthentication: SUNet IDs
Stanford University Network IDentifier• 3-8 character identifier• Permanent – cradle to grave – but aliases allowed!• Not private and not anonymous• Your “golden key” to online services• Password – change every 180 days• http://sunetid.stanford.edu
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 3
Authentication: Workgroup ManagerAuthentication: Workgroup Manager
Workgroup Manager Web application Defines groups of community members for use on
restricted web pages or applications
Workgroups are:• Lists of members in a group• Identified by their SUNet IDs• Given a name that uniquely identifies them. • Replicated into the Active Directory (AD) – more on AD
later!
A workgroup may also contain subgroups!
• http://mais.stanford.edu/applications/workgroup/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 4
Authentication: Types of WorkgroupsAuthentication: Types of Workgroups
3 types of workgroups:
1. System-maintained workgroups:stanford:student (students) stanford:academic (faculty and students)stanford:faculty (faculty)stanford:administrative (staff and faculty)stanford:staff (staff) stanford:stanford (students, faculty, and
staff)
2. Department workgroups (often identified by the department’s assigned stem)
organization:businessaffairs_its gsb:affiliates helpdesk:consultants
3. Individual workgroups (identified by the owner’s SUNet ID preceded by a tilde ~)
~jdoe:book_exchange ~instr:friends ~santa:naughty_children
Using workgroups (with Webauth, for example) in a .htaccess file:AuthType WebAuth AuthType WebAuth AuthType WebAuthrequire privgroup stanford:staff require privgroup its:directors require privgroup
~instr:friends
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 5
Authentication: KerberosAuthentication: Kerberos
Kerberos:• A network authentication system for use on physically
insecure networks. • The heart of Stanford’s campus-wide network security
infrastructure.• Prevents eavesdropping or replay attacks.• Provides for data stream integrity (detection of
modification) • Prevents unauthorized reading of data using
cryptography systems such as the Data Encryption Standard.
• Is the official method for authentication at Stanford(see Admin Guide 64)
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 6
Authentication: Establishing Kerberos CredentialsAuthentication: Establishing Kerberos Credentials
Windows: • Network Identity Manager (NIM) • Stanford Desktop Tools• http://www.stanford.edu/services/ess/pc/docs/kerberos/
Macs: • Kerberos for Macintosh (runs in the background) • Stanford Desktop Tools• http://www.stanford.edu/services/ess/mac/docs/kerberos/
Unix: • kinit• http://unixdocs.stanford.edu/loggingin.html
How does it work?1. User runs NIM (Windows) or Stanford Desktop Tools (Windows/Mac) or
kinit2. User logs in with valid SUNet ID and corresponding password3. Kerberos credentials are established!
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 7
Authentication: Web Authentication (WebAuth)Authentication: Web Authentication (WebAuth)
Open-source web-based system for authenticating users (developed here!)
Protects web sites on the main Stanford web servers Can be used with other Apache-based web servers How does it work?
1. User visits a protected website2. Login screen appears and user enters SUNet ID and password3. User’s identity and Kerberos ticket carried in a cookie
https://weblogin.stanford.edu/help.html http://webauth.stanford.edu
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 8
Authentication: Web Login (WebAuth continued)Authentication: Web Login (WebAuth continued)
2 keys are given to you when you log in: 1. a key to the specific web site or service you visited, 2. and a "master" key that opens other protected web sites.
The keys last until you quit your browser program, or until they expire – up to 10 hours later.
Be sure you have "turned in your keys" by quitting your browser before you leave your computer. • Otherwise other people can access websites as though
they are you!
Note:• Using a protocol called SPNEGO, supported browsers can access
protected web sites using Kerberos credentials obtained from your computer login instead of using the WebLogin screen.
• For details, go to https://weblogin.stanford.edu/config.html
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 9
Authentication: ShibbolethAuthentication: Shibboleth
http://www.stanford.edu/services/shibboleth/
Lets you access secured non-Stanford sites (only those who have joined a common federation) using your SUNet ID.
Lets Stanford web servers authenticate users from those non-Stanford institutions using their local authentication credentials.
Example: COManage – Internet2 Project• Still in development…• COManage is the Collaborative Organization Management Platform
developed by the Internet2 Middleware Initiative. It is intended as a demonstration of the capabilities offered by tying together federated identity management (Shibboleth), groups management (Grouper), and (coming soon) privilege management into a cohesive support infrastructure for a variety of collaborative applications.
• http://middleware.internet2.edu/co/• http://comanage-dev.stanford.edu/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 10
Authentication: Guest AccountsAuthentication: Guest Accounts
Based on email address Uses Shibboleth as authentication A Stanford Guest Account allows you to view specific
Stanford web pages that normally require Stanford-Affiliated SUNet identification. A Guest Account might allow you to view and interact with web-authenticated department, individual, and group pages. The owner of the restricted pages can allow you to access them via your Guest Account.
Note: A Guest Account cannot be used to access any restricted data including HIPAA, FERPA, or PCI-regulated data.
http://www.stanford.edu/service/guest/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 11
Distributed File Systems – AFS (Andrew File Distributed File Systems – AFS (Andrew File System)System)
Stanford’s campus-wide file system Allows users to efficiently share files across local and
wide area networks System is backed up nightly University’s main web site and linked files hosted on
AFS
http://www.stanford.edu/services/afs/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 12
Distributed File Systems – AFS disk space quota Distributed File Systems – AFS disk space quota
1 GB of disk space per users, group, or department
Can be used to store web pages, text files, computer programs, pictures and other digital data
Learn more:http://www.stanford.edu/services/disk-space/
Request group/dept space or increase quota:http://tools.stanford.edu/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 13
Distributed File Systems – OpenAFSDistributed File Systems – OpenAFS
Lets you access AFS space on a desktop computer as a shared drive
http://www.stanford.edu/services/openafs/
Computing Services
Mac Windows

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 14
Distributed File Systems – Copying Files to AFSDistributed File Systems – Copying Files to AFS
For step-by-step instructions on copying files to AFS, visit http://filetransfer.stanford.edu/• OpenAFS• SFTP (Fetch/SecureFX)
WebAFS is a new, web-based method to easily copy files to AFS• http://afs.stanford.edu/• http://www.stanford.edu/services/afs/webafs/userguide/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 15
Distributed File Systems – Workgroup IntegrationDistributed File Systems – Workgroup Integration
Workgroups can be integrated with AFS, Mailing Lists, and the Active Directory
https://tools.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/workgroup-admin
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 16
Distributed File SystemsDistributed File Systems
Common Internet File System (CIFS)• CIFS (Common Internet File System) = “file servers”
• Also known as “Server Message Block”• Also known as the “Windows File Sharing”
• At Stanford, we use the CIFS protocol to provide access to a central file service.
• Can be used to share and store files for groups and departments.• Authentication is via Kerberos and NTLM version 2 (Windows NT LAN
Manager)
http://www.stanford.edu/services/storage/lowcost/cifs/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 17
Backup, System Security, and Anti-VirusBackup, System Security, and Anti-Virus
Backing Up:• Desktop/laptops (e.g., Mozy, Iron Mountain (BaRS being deprecated))
• Basically outsourced with a Stanford rate - CRC can help if part of a CRC contract
• Servers (e.g., AFS) - Using TSM (looking at disk to disk backup solutions)
System Security:• BigFix – http://www.stanford.edu/services/bigfix/
An OS patch management service which distributes critical security updates to Windows PCs and Macintoshes.
• PC Security Self-Help - http://www.stanford.edu/group/security/securecomputing/
• OS Updates• Windows: http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com/• Apple: http://support.apple.com/• Linux/Unix
Anti-Virus: Sophos (Stanford site-licensed anti-malware software, providing protection from both viruses and adware/spyware)• http://ess.stanford.edu/pc/sophos.html• http://ess.stanford.edu/mac/sophos.html
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 18
Business Applications SupportBusiness Applications Support
Support for ITS internal business apps and campus-wide enabling applications
Pinnacle (Billing), OrderIT, MyITServices
General Enterprise/IT Support Systems• Remedy/HelpSU - tickets; reporting• CMDB (Configuration Management DataBase) – at Stanford, we use BMC
Remedy
Calendaring• Zimbra information: http://www.stanford.edu/services/emailcalendar/
Docushare• A content and document management system• http://docushare.stanford.edu
Infra • Change Management system used to create, approve, schedule, and provide
notification of change requests related to IT systems hardware and software• http://changemanagement.stanford.edu
Stanford Answers (also Client Support): http://answers.stanford.edu
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 19
Business Applications Support (continued)Business Applications Support (continued)
Support for ITS internal business apps and campus-wide enabling applications
ACES (Access Control Enterprise Systems) – Card access to buildings
• Lenel
• CS Gold
eCommerce – a suite of services that enables Stanford's schools, centers, and departments to establish themselves as merchants, and market and sell products and services on the web. Managed by the Controller’s Office.
SMARTS – monitoring tool to monitor and respond to alerts from networks (phone, switch, data, VOIP, Net-to-Switch/Jack), door security, and environmental systems in the data centers
Unanet – time tracking tool that IT Services uses internally to track staff work time
Jira – tool used to track bugs and other issues in enterprise software used at Stanford
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 20
Departmental compute serversDepartmental compute servers
Remote access to high-speed, high-power computing resources to support large jobs and provide support for core curriculum and research
Support for departmental or course-specific computing needs.
Specific compute services that don't scale to an enterprise level.
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 21
Database Services – MySQLDatabase Services – MySQL
IT Services provides consulting and assistance with databases and database vendors, as well as hosting and support.
MySQL service• Popular open source database management system• With PHP programming language, used to build dynamic,
interactive Web sites. • Available for Stanford departments and official University
groups and services• https://www.stanford.edu/services/sql/• http://mysql.stanford.edu
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 22
Database Services – Microsoft SQL and OracleDatabase Services – Microsoft SQL and Oracle
Microsoft SQL• Microsoft’s implementation of SQL• IT Services offers support for departments who have
implemented Microsoft SQL Oracle
• IT Services provides consulting and assistance with databases and database vendors, as well as hosting and support.
• Note: No Oracle DBAs in-house For-fee services - supported via Ntirety
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 23
Directory Services (Registries)Directory Services (Registries)
OpenLDAP (Open Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)• http://www.stanford.edu/services/pubsw/package/network/
openldap.html• http://www.stanford.edu/services/directory/• http://www.openldap.org/
Active Directory• http://windows.stanford.edu/Public/Infrastructure/Services/
Directory.html Whois / StanfordWho
• http://stanfordwho.stanford.edu/ StanfordWhat
• http://stanfordwhat.stanford.edu/ Workgroup Manager
• http://workgroup.stanford.edu/ StanfordYou
• http://stanfordyou.stanford.edu/ Printed Directory (ASSU)
• http://assu.stanford.edu/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 24
Directory Services (Registries)Directory Services (Registries)
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 25
Technical Facilities (TFAC)Technical Facilities (TFAC)
Provides operational management and support for:• IT Services production systems• Infrastructure supporting these systems• Data Centers
• Forsythe, Sweet Hall, the 12 ECH (Electronic Communication Hub) facilities, and the Auxiliary Data Center in Livermore, CA)
Responsible for:• Space Planning• Vendor/Customer Coordination• System Hardware Installation• Cabinetry• Low Voltage Cabling and Branch Circuit Distribution• Tracking all equipment in the data centers, IT Services,
Administrative Systems, and the CFO’s office (Property Administration)
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 26
Storage ManagementStorage Management
IT Services provides solutions to data storage needs for all levels — individual, departmental, and institution-wide (enterprise). • 1 GB of AFS storage space is provided at no charge• Three additional tiers of fee based storage, each priced per
gigabyte for maximum flexibility. This service provided by block-level, or file-level storage
with multiple available protocols (SAN, NAS, iSCSI, CIFS, AFS, etc).
For interconnection, fiber channel and iSCSI is recommended
http://www.stanford.edu/services/storage/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 27
Unix/Linux/Windows System AdministrationUnix/Linux/Windows System Administration
Unix/Linux System Administration• Plan, manage and operate development and production
servers in Forsythe Data Center, Sweet Hall, and West ECH, East ECH, and Press ECH.
• http://www.stanford.edu/services/unixcomputing/
Windows System Administration• Addresses the need to move closer to single sign-on• Provides location-independent access to resources,• Provides manageability and security for the Microsoft
Windows platform• http://windows.stanford.edu/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Web Services – Infrastructure StuffWeb Services – Infrastructure Stuff
ITS web services allow clients control over the collection (database) and presentation (web) of information using various tools.
Virtual Host:• Lets you have a shorter web address (URL – Uniform Resource
Locator)• Learn more: http://virtualhosting.stanford.edu/• Request or update existing: http://tools.stanford.edu/
Scheduling Service:• Lets you schedule Unix commands to be run at a particular time.• Request or update existing: http://tools.stanford.edu/
Log Dump Request:• Lets web administrators manage site’s logging information• Using AWStats, can view statistics about activity on their site• Request or update existing: http://tools.stanford.edu/
Web Searching: • http://search.stanford.edu/• http://www.stanford.edu/services/websearch/google/
Web Space: http://www.stanford.edu/services/web/page 28
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Web Services – DatabasesWeb Services – Databases
MySQL• Popular, free, open-source relational database
management system known for its speed, reliability, and ease of use.
• http://www.stanford.edu/services/sql/• http://mysql.stanford.edu• Request a database: http://tools.stanford.edu/
Microsoft SQL• Microsoft’s implementation of SQL• IT Services offers support for departments who have
implemented Microsoft SQL via Ntirety support (for-fee service)
page 29
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 30
Web Services – Forms and CGIWeb Services – Forms and CGI
CGI (Common Gateway Interface): Lets you run programs on the Web – providing dynamic
content, collecting user input, and offering services Ruby, Python, PHP and Perl languages are supported http://cgi.stanford.edu/ Request CGI service: http://tools.stanford.edu/
Form Builder: Build, publish, and manage web forms on the Stanford
servers http://formbuilder.stanford.edu http://www.stanford.edu/services/webforms/
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Web Services – Content Management Systems Web Services – Content Management Systems (CMS)(CMS)
Content Management Systems (CMS):• Drupal installation: http://tools.stanford.edu/• Stanford look and feel templates:
http://web.stanford.edu/design/templates/modern/• SharePoint: http://www.stanford.edu/services/sharepoint/
Other systems will work, but aren’t necessarily supported. Your mileage may vary!
Note: These products are evolving. Stay tuned for new developments!
page 31
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Web Services – BlogsWeb Services – Blogs
Blogs:• MovableType installation: http://software.stanford.edu/• WordPress installation: http://tools.stanford.edu/• Drupal installation: http://tools.stanford.edu/• Stanford look and feel templates:
http://web.stanford.edu/design/templates/modern/• SharePoint: http://www.stanford.edu/services/sharepoint/
Other systems will work, but aren’t necessarily supported. Your mileage may vary!
page 32
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Web Services – WikisWeb Services – Wikis
Wikis:• MediaWiki installation: http://tools.stanford.edu/• Drupal installation: http://tools.stanford.edu/• Stanford look and feel templates:
http://web.stanford.edu/design/templates/modern/• SharePoint: http://www.stanford.edu/services/sharepoint/
Other systems will work, but aren’t necessarily supported. Your mileage may vary!
page 33
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Web Services – SharePointWeb Services – SharePoint
Fee-based service Offers tools for managing content on the Web Contains wikis, blogs, discussion forums, event
calendars, announcements, task lists, etc. built-in Workflow tools help manage and automate business
processes (approvals/publishing) http://www.stanford.edu/services/sharepoint/
page 34
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 35
Email at StanfordEmail at Stanford
Email at Stanford: http://email.stanford.edu/
Antivirus / SPAM (Sophos PureMessage): http://email.stanford.edu/antispam
Bulk email: Send email to large numbers of Stanford users for official, approved Stanford administrative purposes.
Mailing list services (Mailman): http://mailman.stanford.edu
Secure email: http://secureemail.stanford.edu/T
his service is for off-campus secure communication
(extra hurdles for data security)
Support for Microsoft Exchange servers
ITS is running a BES server for Blackberry devices
Computing Services

STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
page 36
Stanford Collaboration Tools (Email/Calendar/IM)Stanford Collaboration Tools (Email/Calendar/IM)
Integrated Email and Calendaring (IEC) web site: http://iec.stanford.edu
Stanford Email and Calendar services web site: http://www.stanford.edu/services/emailcalendar/
IEC solution• Webmail: http://webmail.stanford.edu/• Webcal: http://webcal.stanford.edu/• Desktop tools (Outlook, iCal, Apple Mail, Thunderbird):
http://www.stanford.edu/services/emailcalendar/desktop
Email Service Tools: http://tools.stanford.edu
Stanford Instant Messaging• http://im.stanford.edu/• Centrally-funded instant messaging service provided free-of-charge to
the Stanford community, using kerberos, SSL, and the jabber (XMPP) protocols
• A safe and secure way to conduct confidential Stanford business online, real-time. (Messages are secure only when sent between Stanford accounts.)
Computing Services