Introduction to the Six Kingdoms. Archaeabacteria Type of cell: Prokaryotes Number of Cells: ...
-
Upload
susanna-cummings -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Introduction to the Six Kingdoms. Archaeabacteria Type of cell: Prokaryotes Number of Cells: ...
Type of cell: Prokaryotes
Number of Cells: Unicellular
Structures: Have cell walls
Food/Energy: Can be autotroph, chemotroph, or heterotroph:
Chemotroph - makes food from chemicals instead of sun Reproduction:
Mostly asexual reproduction Movement:
Passive; no locomotion Habitat:
Live in extreme environments Ex: Can live without oxygen
Archaebacteria Members Examples:
Methanogens Produce fuel (ex:
methane gas) Halophiles – “salt –
lovers” Thermophiles –
“heat-lovers”
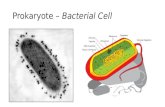
Type of cell: Prokaryote
Number of cells: Unicellular
Structures: Cell wall
Food/Energy: Heterotrophs, Chemotrophs,
and Autotrophs Reproduction:
Mostly asexual reproduction Binary fission
Reproduces very quickly Movement:
Flagella Habitat:
They can be found everywhere
The more common bacteria
Three main shapes: Round, Rod, Spiral
Can be: Harmful
Many cause illness Ex: TB, strep, tetanus, food poisoning
Helpful Decomposers (recycling) Used in making food Produce fuel Environmental cleanup
E. coli
Lactobacillus(used in yogurt)
Streptococcus
The miscellaneous “junk drawer” kingdom
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Number of cells: Mostly unicellular; a few
multicellular Structures:
Cell wall and/or chloroplasts in some groups
Food/Energy; Autotrophs & Heterotrophs
Reproduction: Mostly asexual reproduction
(binary fission) Locomotion:
Flagella, pseudopod, cilia Habitat:
Live in moist environments
Plant-like: Autrotrophs
Ex: Euglena, diatoms, & algae Animal-like:
Heterotrophs Ex: Amoeba, Paramecium
Fungus-like: Decomposers Ex: Slime mold, downy mold
Type of Cell: Eukaryote
Number of Cells: Mostly Multicellular; One
unicellular Structures:
Cell wall, hyphae, fruiting bodies Food/Energy:
Heterotrophs & Decomposers Reproduction:
Mostly sexual reproduction (spores)
Some asexual (budding) Locomotion:
None Habitat:
Moist, warm environments Not direct sunlight
Cell Type: Eukaryote
Number of Cells: Multicellular
Cell Structures: Cell wall, chloroplasts, large
vacuole Food/Energy:
Autotrophs Reproduction:
Mostly sexual reproduction Locomotion:
None
300,000 have been found…including trees, flowers, grasses, mosses etc.
Mosses Ferns Flowering Plants Grasses Conifers
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Number of cells: Multicellular
Structures: No cell walls Invertebrate & Vertebrate
Food/Energy: Heterotroph Reproduction:
Mostly sexual Some asexual
Movement: Walk, swim, fly, crawls, etc.
Habitat: Everywhere
Over a million identified species. 97 percent have no backbone 3% are vertebrates..Mammals ,birds,
reptiles, amphibians, fish
Cnidarians
Sponge and coral Worms
Mollusks
Arthropods