Introduction to the river valley civilizations
-
Upload
akshay-jasani -
Category
Education
-
view
52 -
download
6
Transcript of Introduction to the river valley civilizations

HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE & THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT -I
LECTURE-4
Introduction to the River Valley Civilizations
Comparative study of different manifestations with reference to location,materials and techniques, socio-cultural influences and other contextual factors
1st Semester B .Arch, August - December 2013

Unit-I
• Definition and scope of Architecture. Interdependence of various components of the builtenvironment. Need for a holistic approach.
• Man’s early/prehistoric attempts to colonise and personalize space. Examples of earlyshelters, Stonehenge, tumuli, etc. as expression of man’s physical and spiritual needs
• Determinants of Built Form - geo-physical, societal, political and technological, etc.Global examples of vernacular architecture.
• Introduction to the River Valley Civilizations. Comparative study of differentmanifestations with reference to location, materials and techniques, socio-culturalinfluences and other contextual factors
Unit-II
• Egyptian Civilization: Concept of the Royal Necropolis, locational context and architecturalcharacteristics of public buildings, e.g. mastabas, pyramids and temples(rock-cut &structural) -one example of each type to be chosen. Worker’s settlement- city of Kahun.
• Mesopotamian Civilization; the urban context and architecture of public buildings(ziggurats and palaces). Examples of the city and Ziggurat of Ur, city and palace and ofKhorsabad.
Unit-III
• Indus Valley Civilization: Form of the Harappan City, location and role of public buildings.• Architecture of the typical Harappan dwelling, Granary and Bath.• The Vedic Village, Building typology and construction
HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE & THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT -I

What is the meaning of civilization
The most advanced stage of human development
People were NOMADIC
People became SEDENTARY
Domestication of AnimalsStart Growing own foodThey built hutsThey start living is settlements
Neolithic Revolution
They sheltered incaves
Relying on hunting
Neolithic to civilizations
Beginning of civilization
• Settlements need rules/lawto maintain order
• Rules and laws needed toregulate irrigation
• Threat of outside invasionmade it necessary to haverules who could provideprotection

CIVILIZATION
Civilization is a human society which is more populated where people, share andspread a common culture.

CIVILIZATION
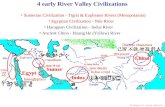
The civilizations occurred first near the River valley because conditions there weremost conducive for living and agriculture.They could fish in the rivers and hunt the animals that came there to drink.Annual floods spread silt- tiny bits of rocks and dirt from the river bottom- across thevalleys. silts made the valleys fertile, which is good for crops to grow in. This allowedfarmers to grow more food than they needed for themselves and their families.
Extra food also let some people living in river valleys do jobs other than farming.

CIVILIZATION
They began developed, systematically agriculture and domesticate animals andthey learned the secret of reproducing abundance in plants and animals throughcontrolled implantation of the seed.

CIVILIZATION Cities served as administrative centers Had a political system on control of a defined territory rather than kinship
connections Monumental building Major advances in science and technology Long distance trade System for keeping permanent records

EARLY RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATION

EARLY RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATION

EARLY RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Made lasting contributions to civilizations.

EARLY RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Impact of geography (location) on the origin of civilizationReligion, beliefs Social structureWriting Government

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
Egyptian civilization began along Nile river

The land of Egypt was protected by naturalbarriers on all sides.
It was very hard for an outsides to even enterEgypt.
The Mediterranean Sea
The Red Sea
Western Desert
Eastern Desert
Egypt’s natural isolation and material self-
sufficiency fostered a unique culture that for
long periods had relatively little to do with other
civilizations.
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION

• The Nile River was the most important thing to ancient Egyptians• It rises and falls at the same time every year• When the water recedes, it leaves fertile soil along its banks, which was very
good for agriculture.• Egyptian agriculture depended upon the floods.• Floods were regular, and this inspired the Egyptians to view the universe as a regular
and orderly place.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION

The climate was good
for agriculture, but
with little or no
rainfall, farmers had
to depend on the river
for irrigation by
constructing canals to
carry water out into
the valley.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION

The Nile provided the perfect waterway for trade.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
RELIGION, BELIEFS
• Egyptians believed in reincarnation, or, life after death• This belief was influenced by the rise and fall of the Nile, which represented a
cycle of life and death• They believed every person had double life force• This force fled the body at death and returned to join with the deceased in the
afterlife• Their belief in re-birth after death became their driving force behind their funeral
practices ‘ mummification’.• Mummification is a 70 day process that would preserve a person’s soul for after
life.• The priest would remove all of the organ from the deceased, dry them out with
spices and salt and place them in canopic jars which had spells written on them.• Like the organs, the body was also dried out with spices and salt to keep from
rotting.• The body was then wrapped with bandages and a death mask was places on his
head.• The wrapped body would be placed in a sarcophagus along with cloths,
jewellary, fruits that he could use in his afterlife.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
RELIGION, BELIEFS
• The King, or pharaoh, was a supreme ruler in the earliest period of Egyptianhistory and became a god after he died.
• The dead were buried in monumental tombs: Pyramid, mastabas. The amountand quality of tomb goods and the form of the tombs themselves reflect thesocial status of the deceased.
Pyramid Mastabas

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
RELIGION, BELIEFS
They also worshipped natural elements (Nile river, earth)and some animals thatwere considered sacred: crocodile, cat , beetle.Egyptian religion was ‘polytheistic’, that is ,they believed in various gods andgoddesses and The lineage of the gods extended to the pharaoh himself.The deities had a half human appearance and half animal.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
RELIGION, BELIEFS
Temple of Khons,Karnak

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
SOCIAL STRUCTURE
• The population of ancient Egypt was divided into groups of people with differentjobs and responsibilities to society.
• These social classes were structured as a pyramid .• This social pyramid shows the levels of each social class in terms of importance.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
SOCIAL STRUCTURE

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
Workers settlement – Kahun town
SOCIAL STRUCTURE

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
GOVERNMENT
• Earlier ,Egyptians lived in farming villages. Each village had its own rituals ,gods.
• Around 2000 B.C. lower and upper Egypt weredivided into one. This beginning the old kingdom.
• Pharaohs, were the center of Egypt's government.
• Theocracy- A type of government in which a ruleris a divine figure ; ruled Egypt
• People believed that it was the pharaoh whocaused the sun to rise, the Nile to flood and thecrops to grow.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
GOVERNMENT
• Viziers were responsible for the registrations ofpeople and property for tax purposes. Thesepeople recorded transactions dealing mostlywith land.
• The government structure included: viziers,army commanders, chief treasures, theminister of public works and tax collectors.
• Taxation was paid for mostly through labour andgoods . People were drafted to serve in thearmy if necessary and were forced into labor topay labor tax.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
GOVERNMENT
• Laws in Egypt were based on the crimes being committed. Some punishmentswere lenient like caning or some as dismemberment and executions.
• Buildings the pyramids , it showed that the dynasties had developed thestrength to support government organization to carry them out.
CaningDismemberment Executions.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
WRITING
The Egyptians invented a form ofwriting called hieroglyphics.Hieroglyphs are little pictures . Somestand for an object

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
About 2500 BC, the time when pyramids were rising in Egypt , the first Indiancivilizations were forming in Indus river valley.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
The Indus Valley civilization flourished in the western part of South Asia, in what today is Pakistan and western India. Natural borders consisted of mountains and the Arabian Sea, sheltering thecivilization from attack and disease.
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)

Himalaya, Hindu Kuch mountains provides a continuous source of water for theIndus and its tributariesThese mountain ranges also provided important timber, animal products andminerals , gold, silver , tin and some precious stones that were traded throughoutthe Indus valley .
Water from the river fertilized and irrigated crops. Proximity to the river allowedboats to become a viable transportation option.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)

Seasonal winds known as monsoons bring rain every summer. This valley was
dependent upon monsoons to grow their crops.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
Monsoons were unpredictable andled to famine or floods anddestruction

RELIGION, BELIEFS
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Sun was regarded as one of the greatest gods. People believed in magic andsuperstitions also and wore amulets for some protection.No temples found.Terra-cotta figures found for sacrificial purposes

RELIGION, BELIEFS
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Discrete cemeteries and burial grounds .Human figures in yoga position with ornaments and headdresses symbolizesfertility god.

RELIGION, BELIEFS
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Geometric symbols show beliefs in cosmology.‘Shiva seals’ show a man seated in yoga position surrounded by animals representreligious views .Various deities were worshipped and their images can be found on the seals.Evidences have also established the practice of several religious ceremonies andrituals. Although, no remains of any monument have been excavated but numerousterracotta statues of Mother Goddess have been found suggesting that MotherGoddess had been worshipped extensively by these people which symbolizingfertility
Mother Goddess Shiva seals Religious ceremonies

SOCIAL STRUCTURE
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
The caste system was a majorimpact on the social structurewithin Indus River Valleycivilization. It consisted of avariety of levels displaying socialstatus.

GOVERNMENT
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Indus government was well organized, had powerful leaders (Priest-Kings),and that the government promoted skills in mathematics and surveying tolay out the cities so precisely.
Indus Priests were in charge of government and were rulers as well. Therulers governed through trade and religion, instead of military strength.
Religion had an immense impact on government

WRITING
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Unlike other civilizations the language of ancient Indus valley civilization cannotbe deciphered. Our knowledge of this civilization is based almost entirely onvarious physical remains.
The Indus people used the pictorial script.In additions to the pictorial signs, the seals and amulets often containsiconographic motifs, mostly realistic pictures of animals apparently worshipped assacred, and a few cultic scenes, including deities and worshippers.

• The most characteristic feature of the Indus valley Civilization was its
urbanization.
• The cities show evidence of an advanced sense of planning and
organization.
• Each city was divided into the citadel area where the essential institutions of
civic and religious life were located and the residential area where the urban
population lived.
Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro the two main cities.
Both were carefully planned out.
CITY PLANNING
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION

CITY PLANNING
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
The regularity of plan and construction suggests agovernment with organization.
citadel area
Residential area

CITY PLANNING
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
A high degree of standardization in city planning architecture

CITY PLANNING
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
Indus river was used, in order to maintain and develop urban society

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
Mesopotamia is a flat plain between the two rivers, Tigris and Euphrates in SW Asia.Because of this region’s shape and the richness of its soil, it is called the FertileCrescent.

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
Environmental Challenges
1. Unpredictable flooding during periods of little rain / dry summer monthsDug irrigation ditches… brought water to fields

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
2. No natural barriers for protection- small villages lying in open plain were defenseless
Built walls around cities

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
3. Limited natural resources,especially building materials
- stone, wood, metal
Trade

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
Lacked building materials
Used Mud bricks

RELIGION, BELIEFS
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
Polytheistic religion i.e. believe in so many god, goddesses and demigods
They believed it wastheir duty to servethe gods. If thegods were nothappy then theywould be punishedby a flood or naturaldisaster. Theflooding of the Tigrisand Euphratesrivers wasunpredictable andso these peoplelived in constantfear.

RELIGION, BELIEFS
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
• Deities were in human forms and represent some natural phenomenon.• Gods were worshipped at huge temples called ziggurats.
They werebelieved to behomes for godsand goddesses.Only priests werepermitted on theziggurat and it wastheir responsibilityto care for thegods and attend totheir needs. As aresult, priests werevery powerfulmembers ofsociety.

RELIGION, BELIEFS
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
• They believe that the gods influenced much of what happened to them in their lives.
• They also believed in demons created by the gods, which could be good or evil.
• Cities and kingdoms were believed to be protected by individual gods and it was
the duty of the ruler to act on the god’s behalf , building temples and performing
ceremonies to gain the god’s blessings
• They thought world as a sphere , one half occupied by living , the other by the
dead.
• Souls of the dead wandered in the land of no return

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
SOCIAL STRUCTURE
Responsible for creating the laws of each city-state.
They were the closest to the gods
Priest
Kings and Government Officials
Soldiers and ScribesThe soldiers were proud members of a city-state. In the same social class as the soldiers were the scribes (writers).
They usually spent their day creating items to send to other places, selling goods, or trading with neighboring city-states.
When one city-state conquered another, they usually brought back prisoners to work as slaves for the upper class

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
GOVERNMENT
Politics:The political system was a Theocracy – Religious authority by divine rulers
Divine Rulers – Kings who got their power to rule from gods and therefore hadgod-like powers themselves; kings were aided by priests
There was no central government. Mesopotamia was divided into independentcity-states, which often fought for control of land and water.
Sumer- southern partAkkad- northern partBabylonia- these two regions were unifiedAssyria- Assyrian Empire

GOVERNMENT Although all the cities shared the same culture . Each city had its own government ,rulers, warriors. It’s own patron god and functioned like an independent country.At the center of each city was the temple called ziggurat.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
UrBabylon

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- MESOPOTAMIAN CIVILIZATION
WRITING
They invented a form of writing called Cuneiform that means wedge shaped
It’s a Pictograms form of writing i.e. a pictureused to symbolize a word or phrase .
They wrote on wet clay tablets with thepoint of a reed, then dried in the sun tomake a tablet

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION
Chinese civilization grew up in the river valley of the Huang He River (i.e. theYellow River) and the Yangzi River.
Huang He or Yellow River
Yangzi River Huang He or Yellow River
Yangzi River
The yellow soil particles inthe river give it its name“Yellow”

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (LOCATION)
The mountains, deserts, jungles and other geographic features have isolatedChinese culture. Having little contact with others , the Chinese believed their culturewas the center of the earth.

China’s natural resources include timber, stone, and metals.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION

• Early Chinese peoplewere polytheistic, andprayed to many Godsand nature spirits.
• They also looked todead relatives to helpthem in daily life andto help them pleasethe Gods.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION
RELIGION AND BELIEF

Ying and Yang
• Many Chinese alsobelieved that theuniverse held a delicatebalance betweenopposing forces.
• The Ying and Yang mustbe in balance forprosperity andhappiness to occur inone’s life.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION
RELIGION AND BELIEF

RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION
GOVERNMENT
• Mandate of Heaven says that the gods allowed a dynasty to rule until that dynasty got old & corrupt
• New dynasty was given new Mandate of Heaven to over throw old• This changing of dynasties is called the Dynastic Cycle
New Dynasty
•Brings peace
•Builds roads
•Land to peasants
•Protects people
•Too many taxes
•No protection
•Unfair treatment
•No building
Old Dynasty
• Floods
• Quakes
• Revolts
• Invaders
Problems


• The Chinese civilizations made achievements in early writing systems thatinclude both pictographs and ideographs and is now as one of the earliestwriting systems.
RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS- CHINESE CIVILIZATION
WRITING
![[PPT]RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS - Belton Independent … · Web viewRIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS WARM-UP Title your map “River Valley Civilizations” Locate the 4 River Valley Civilizations](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5acd72367f8b9aa1518d7c48/pptriver-valley-civilizations-belton-independent-viewriver-valley-civilizations.jpg)