INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL - Mrs. Roderick
Transcript of INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL - Mrs. Roderick
What is a cell?
•A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
Who discovered cells? •Robert Hooke (by looking at a piece of cork under a microscope
What is a theory? •An explanation, supported by many observations and experiments, that can be used to accurately explain related occurrences.
●A theory is the work of MANY scientists. It is a work in progress that may be supported by evidence, but NOT necessarily proven.
What is the cell theory?
1. All living things are composed of cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
3. Cells are produced from other existing cells.
•Prokaryotic Cells have NO nucleus.
•Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus.
Example: A Bacterial Cell
Examples: Animal Cell and Plant Cell
ORGANELLE
MAINTAINS HOMEOSTASIS
BY (FUNCTION):
“NICKNAME”
NUCLEUS Controls ALL cell
Activities
-Contains DNA (genetic material that directs all development)
Brain
NUCLEOLUS Site of ribosome production
Little Nucleus
CYTOPLASM Jelly-like material that allows other organelles to
travel throughout cell
RIBOSOME Site of protein synthesis
(where proteins are MADE)
●
●●
NUCLEAR MEMBRANE
Regulates the passage of
materials into and out of the
nucleus
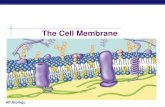
CELL MEMBRANE (PLASMA
MEMBRANE)
Regulates the passage of
materials into and out of the
cell
-Outer LIVING
barrier
Gatekeeper
MITOCHONDRIA Site of cellular respiration
(energy (ATP) is made here)
Mighty Mitochondria
or Powerhouse
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Tubular transportation system for proteins
ER
Vacuole Stores food, water, and
waste
Storage Tank
CHROMOSOME Thick rod-like structures found in the
nucleus that direct growth and development
(Contain DNA)
CELL WALL Provides support and structure
(made of cellulose-a complex starch)
-is a NON-LIVING structure
CHLOROPLAST Site of photosynthesis
(contain chlorophyll-a green liquid NOT an organelle)
Food factory
LYSOSOME Digests old cell parts
Clean up Crew
Or
Suicide Sacs
-Animal cells have a round shape/ Plant cells have a square shape -Plant cells have a cell wall/Animal cells DO NOT -Plant cells have a larger vacuole -Plant cells have chloroplasts (therefore plant cells can make their own food!)/Animal cells DO NOT -Animal cells have a lysosome/Plant cells DO NOT
-They are BOTH Eukaryotic cells (have a nucleus) -They BOTH have a cell membrane -They BOTH have mitochondria and ribosomes -They BOTH have a cytoplasm and ER
NUCLEAR MEMBRANE
MITOCHONDRIA
NUCLEOLUS
NUCLEUS
RIBOSOMES
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
LYSOSOME CHROMOSOME
VACUOLE
CELL MEMBRANE
CYTOPLASM
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
CYTOPLASM
RIBOSOMES
CELL MEMBRANE VACUOLE
CHLOROPLAST
MITOCHONDRIA
NUCLEOLUS NUCLEUS
NUCLEAR MEMBRANE
CHROMOSOME
CELL WALL
The Animal Cell has ALL of the above organelles EXCEPT:
The plant cell has ALL of the above organelles EXCEPT:
-Aids the mitochondria by instructing it to make ATP
-Aids the ribosome by providing the DNA to make proteins
-Aids the cell membrane by telling it what to let in and what to let out
Cell Membrane
-Regulates what enters and leaves the cell
-Homeostasis
-Transport -Excretion
-Regulation
-Aids the mitochondria by allowing in the materials needed for cellular respiration
-Aids the ribosome by allowing in the materials needed to make proteins
-Aids the vacuole by allowing wastes to exit the cell
Cytoplasm
-Jelly-like material that allows other organelles to travel throughout the cell
-Homeostasis
-Transport
-Metabolism
-Site of many chemical reactions
-Provides the energy (ATP) for ribosomes to make proteins
-Provides the energy (ATP) for the cell membrane To allow materials to pass through
-Aids the cell membrane by storing materials that need to be released from the cell
-Aids the chloroplast by storing water needed to carry out photosynthesis
-Works with the nucleus to make the proteins coded for by DNA
-Provides the proteins for all cell structures (organelles)