Introduction to FM
Transcript of Introduction to FM
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
1/16
Introduction toIntroduction to
Financial ManagementFinancial Management
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
2/16
Financial ManagementFinancial Management
Financial Management is thatFinancial Management is thatmanagerial activity which ismanagerial activity which is
concerned with planning andconcerned with planning andcontrolling of the firms financialcontrolling of the firms financialresources so that organizationalresources so that organizationalobjectives can be achieved.objectives can be achieved.
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
3/16
DEFINITION OF FINANCIALDEFINITION OF FINANCIAL
MANAGE
ME
NTMANAGE
ME
NTFinancial Management is theFinancial Management is the
management of fund in such a waymanagement of fund in such a way
that funds are procured at minimumthat funds are procured at minimumcost and they are utilized in bestcost and they are utilized in bestopportunitiesopportunities
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
4/16
Financial DecisionsFinancial Decisions
Financing DecisionsFinancing Decisions
(Capital Structure Decision)(Capital Structure Decision)
Long term Investment DecisionLong term Investment Decision(Capital Budgeting Decision)(Capital Budgeting Decision)
Short Term Investment DecisionShort Term Investment Decision
( Liquidity Decision )( Liquidity Decision )Dividend DecisionDividend Decision
(Distribution Decision)(Distribution Decision)
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
5/16
Function/ Role of a FinanceFunction/ Role of a Finance
ManagerManager Funds RaisingFunds Raising
Funds AllocationFunds Allocation
Profit PlanningProfit Planning
Understanding Capital Market & BusinessUnderstanding Capital Market & Businessenvironmentenvironment
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
6/16
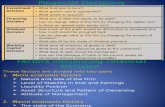
Objectives of FinancialObjectives of Financial
ManagementManagement
66
Profit maximization (profit after tax)Profit maximization (profit after tax)
Maximizing earnings per shareMaximizing earnings per share
Wealth maximizationWealth maximization
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
7/16
Profit MaximizationProfit Maximization
77
Maximizing the rupee income of firmMaximizing the rupee income of firmResources are efficiently utilizedResources are efficiently utilized
Appropriate measure of firm performanceAppropriate measure of firm performance
Serves interest of society alsoServes interest of society also
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
8/16
Objections to ProfitObjections to Profit
MaximizationMaximization
8
44It is VagueIt is Vague
44It Ignores the Timing of ReturnsIt Ignores the Timing of Returns
44It Ignores RiskIt Ignores Risk44In new business environment profitIn new business environment profit
maximization is regarded asmaximization is regarded as UnrealisticUnrealistic
DifficultDifficult InappropriateInappropriate
ImmoralImmoral
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
9/16
EPS MaximizationEPS Maximization
99
MaximisingMaximising EPSEPS meansmeans maximizingmaximizingprofitprofit (( earningearning )) perper shareshare
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
10/16
Objections to EPS MaximizationObjections to EPS Maximization
1010
MaximisingMaximising EPSEPS doesdoes notnot maximisemaximisethethe economiceconomic welfarewelfare of of thetheownersownersMarketMarket valuevalue isis notnot aa functionfunctionofof EPSEPS..
IgnoresIgnores timingtiming andand riskrisk of of thetheexpectedexpected benefitbenefit
MaximizingMaximizing EPSEPS impliesimplies thatthat thethe firmfirmshouldshould makemake nono dividenddividend paymentpaymentsoso longlong asas fundsfunds cancan bebe investedinvested atatpositivepositive raterate ofof returnreturnsuchsuch aa policypolicymaymay notnot alwaysalways workwork..
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
11/16
Shareholders WealthShareholders Wealth
MaximizationMaximization
1111
MaximizesMaximizes thethe netnet presentpresent valuevalue ofof aacoursecourse ofof actionaction toto shareholdersshareholders..
AccountsAccounts forfor thethe timingtiming andand riskrisk ofofthethe expectedexpected benefitsbenefits..
BenefitsBenefits areare measuredmeasured inin termsterms ofofcashcash flowsflows..
FundamentalFundamental objectiveobjectivemaximizemaximizethethe marketmarket valuevalue of of thethe firmsfirmssharesshares..
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
12/16
Agency CostAgency Cost
(Managers Vs. Shareholders Goals)(Managers Vs. Shareholders Goals)The decision taking authority in largeThe decision taking authority in large
companies lie in the hands ofcompanies lie in the hands ofmanagers.managers.
Shareholders as owners of theShareholders as owners of thecompany are the principals andcompany are the principals andmanagers are their agents.managers are their agents.
In theory, managers should act in theIn theory, managers should act in thebest interest of shareholders; that isbest interest of shareholders; that istheir actions and decisions should leadtheir actions and decisions should lead
to Shareholder's wealth Maximization.to Shareholder's wealth Maximization.
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
13/16
In practice, managers may not necessarilyIn practice, managers may not necessarilyact in the best interest of shareholders, andact in the best interest of shareholders, and
they may pursue their own personal goals atthey may pursue their own personal goals atthe cost of shareholders.the cost of shareholders.
Further, a company is a complex organizationFurther, a company is a complex organizationconsisting of multiple stakeholders such asconsisting of multiple stakeholders such as
employees, debt holders, consumers,employees, debt holders, consumers,suppliers, government and society.suppliers, government and society.
Managers in practice may, thus , perceiveManagers in practice may, thus , perceivetheir role as reconciling conflicting objectivestheir role as reconciling conflicting objectivesof stakeholders.of stakeholders.
This stakeholders' view of managers role mayThis stakeholders' view of managers role maycompromise with the objective of SWM.compromise with the objective of SWM.
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
14/16
Overview of FinancialOverview of Financial
ManagementManagement
1414
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
15/16
INTERFACE (RELATION) BETWEENINTERFACE (RELATION) BETWEEN
FINANCE
AND
OTHE
R FUNCTIONFINANCE
AND
OTHE
R FUNCTION MARKETINGMARKETING-- FINANCE INTERFACEFINANCE INTERFACE
PRODUCTIONPRODUCTION-- FINANCE INTERFACEFINANCE INTERFACE
PERSONNELPERSONNEL FINANCE INTERFACEFINANCE INTERFACE
TOP MANAGEMENTTOP MANAGEMENT-- FINANCE INTERFACEFINANCE INTERFACE
-
8/3/2019 Introduction to FM
16/16
ThanksThanks