Integument Skin and its appendages. Skin functions ProtectionProtection against water, bacteria,...
-
Upload
clemence-cunningham -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
2
Transcript of Integument Skin and its appendages. Skin functions ProtectionProtection against water, bacteria,...

IntegumentIntegument
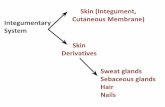
Skin and its appendagesSkin and its appendages

Skin functionsSkin functions• ProtectionProtection against water, bacteria, sunlight, mechanical
forces, dehydration, cold, etc.• Retaining body fluidsRetaining body fluids (protects against dehydration)• Temperature regulationTemperature regulation by varying peripheral blood flow,
sweating, hair elevation, insulation by adipose tissue under the skin
• Food storageFood storage and fat metabolism in the subcutaneous hypodermis
• Vitamin DVitamin D formation by the action of ultraviolet light• Sensory appreciationSensory appreciation of the environment by nervous
receptors• Friction surfaceFriction surface for motor tasks involving grasping,
rubbing, scratching etc.• Display and communicationDisplay and communication:: social, sexual and diagnostic

Skin and its appendagesSkin and its appendages

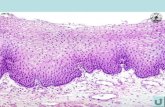
EpidermisEpidermis
Canadian Ladies Give Superb BackrubsCanadian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs

““Thick” skinThick” skin
http://www.med.uiuc.edu/histo/medium/atlas/image/b87a/40a8.htm

Stratum basale or germinativumStratum basale or germinativum• Columnar to cuboidal• Basophilic• Mitotic activity
– Proliferate to replace
lost surface cells
• Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
• Many tonofibrils• Free nerve endings
– pain

Stratum spinosumStratum spinosum• Cuboidal/flattened• TonofilamentsTonofilaments/”spines”
– Keratin bundles
• Malpighian layerMalpighian layer– Both basal and spinosum layers
– mitosis
Shrinkage during processing makes themlook pricklyprickly

Stratum granulosum/lucidumStratum granulosum/lucidum• GranulosumGranulosum
– 3-5 layers
• Keratohyalin granulesKeratohyalin granules– Coarse, basophilic
– Packed tonofilaments convert the cells to soft keratin
• Lamellar granulesLamellar granules– Lipid bilayers
– Eventually act as barrier
• LucidumLucidum– 2-3 layers, seen in thick skin
– Translucent ,eosinophilic
– No organelles or nuclei

Stratum corneumStratum corneum
• 15-20 layers• Flattened• Non-nucleated• Abundance of keratin
This is thin skinthin skinLucidum is missingOften granulosum ismissing

Keratinocyte life cycleKeratinocyte life cycle
• 2-3 weeks

MelanocytesMelanocytes• Basal layer• Appear paler
– No tonofilaments or desmosomes
• Synthesize melanin– Golgi participates in production
of melanosomes
• “injected” into keratinocytes
1 in 4 to 1 in 10 of basal layer cells

Langerhan’s cellsLangerhan’s cells
• Present in all layers• Easily seen in spinosum• Bone marrow derived• Pale nucleus• Pale cytoplasm• Cell processes (long
dendrites)• Antigen presenting cell
– Tissue macrophage
– Poorly phagocytic

Merkel CellMerkel Cell• Sensory cells with
vesicles• In or near basal layer• Clear nuclei/multilobed• No tonofilaments• Sensory nerve endings
– Mechanoreceptors
– Attach to disc shape endings of some axons that penetrate the epithelium

DermisDermis• Collagen and elastin
– Elastin gives skin elasticity but makes wounds gape
• Fibroblasts, other ct cells• Papillary dermisPapillary dermis
– Superficial, thin
– Fine collagen fibers
– Blood vessels, lymphatics
– Sensory nerve endings
• Reticular dermisReticular dermis– Coarse, irregular fibers
– Blood vessels, nerves

HypodermisHypodermis• Fatty layer• Looser connective tissue• Beneath dermis

Taking care of WrinklesTaking care of Wrinkles• Alpha lipoic acidAlpha lipoic acid
– Antioxidant
– Fat and water soluble
– Enhances capacity to heal
– Good for scars and wrinkles
• Retinoic acidRetinoic acid– Decreases fine lines
– Stimulates blood flow
– Even pigmentation
• Free radical damage– Use antioxidants
– Vitamins A,C, E
• Sloughing process slows as we age– Alpha Hydroxy Acids
• UV exposure– Inflammation
– Inflexible collagen and elastin
– Damages blood vessels
• Smoking– Decreases circulation

Arrector pili muscleArrector pili muscle
• Smooth muscle fibers• Inserts to hair follicle
beneath sebaceous gland
• “goose bumps”

Sebaceous glandSebaceous gland• Associated with hair
follicles– Except where there is no
hair!
• Sebum has weak antibacterial properites
• Mitosis in basal layer• Cells lost by holocrine
secretion

AcneAcne• Proprionibacterium acnesßProprionibacterium acnesß• Retin A, tretinoinRetin A, tretinoin,
– Increases cell turnover
– Allows sebum to be released more easily
• AccutaneAccutane– Inhibits sebum production
• Benzoyl peroxideBenzoyl peroxide– Produces oxygen
– Suppresses bacterial growth
• SulfurSulfur– Antibacterial and drying

Sweat glandsSweat glands• Merocrine (eccrine)Merocrine (eccrine)
– Exocrine glands with ducts
– Simple cuboidal
– Covers most skin
– Myoepithelial cells
• ApocrineApocrine– Axillae, breasts, genital
– Secretions with bacteria create odor

HairHair• VellusVellus
– Fine, pale hair
• TerminalTerminal– Coarser hair
• Shape of bulb determines texture of hair
• Overlapping layers of keratin

Hair in skinHair in skin
• http://www.pantene.com/haircare/hair_twh_5.htm• Everything you ever wanted to know!• Information on website is not needed for exam

Hair bulb and follicle structureHair bulb and follicle structure• Dermal PapillaDermal Papilla
– Vascular
– Cells covering papilla are source
of shaft
• MedullaMedulla– 2-3 layers cuboidal cells
– Vacuolated, air (may be absent)
• CortexCortex– Largest region
– Keratinized cells with melanin
• CuticleCuticle– Peripheral layer of hair
– Flat, scale like, clear anucleate cells
Hair bulb

Hair bulb and follicleHair bulb and follicle
• Inner Root SheathInner Root Sheath– Comes out when hair is
plucked
• Outer root sheathOuter root sheath– source of new
epidermal cells during wound healing
– Comes out when hair is ready to fall out 1. Hair we see sticking out of head
2. What we see when pluck hair
3. What we see when hair falls out (white)

Bulb ultrastructureBulb ultrastructure
*
**
*

Hair growthHair growth• Cyclical, not constant
• Cells near dermal papilla source of growth
• AnagenAnagen– Active growth phase– Hair resistant to falling out
• CatagenCatagen– Relatively short– regeneration
• TelogenTelogen– Resting– Long phase

AlopeciaAlopecia
• Alopecia AndrogenicaAlopecia Androgenica– Increases cell turnover (short anagen)– Allows sebum to be released more easily– MinoxidilMinoxidil and tretinoin spraytretinoin spray
• Increase size of hair follicle
• Prolong growth phase (anagen phase)
• Increase blood flow to skin
• Alopecia areataAlopecia areata– Unknown origin, pathologic

Skin cancersSkin cancers
• Basal cellBasal cell– Slow growing, rarely metastasize
• MelanomaMelanoma– Incredibly malignant, spreads to bone, lung
Basal cell carcinomaBasal cell carcinoma malignant melanomamalignant melanoma

ApligrafApligraf
• Approved by FDA for venous ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers– Very successful
• Shelf life of 5 days• Obtained from human
foreskin
Organogenesis, Inc. files for bankruptcyhttp://www.capecodonline.com/cctimes/archives/2002/sep/27/artificialskin27.htm

Side by side comparisonSide by side comparison


Type I hypersensitivityType I hypersensitivity
• Immediate• Anaphylactic • Wheal and flare
– urticaria
• Edema of papillary layer
**

Type III hypersensitivityType III hypersensitivity
• Can be hemorraghic• Immune complex mediated
– Antibodies already present in system
– Antibody/antigen complexes
• Many PMNs• Darker red is blood in dermis• Serum sickness• Artery has enlarged tunica media
– Fibroid necrosis
**

Type IV blister
• From poison ivy• Notice blister in
epidermis• Lymphocytes in
papillary layer of dermis
**

Type IVType IV
• T cell mediated• Mantoux reaction
– TB tine test
• Cell mediated• Transplant rejection
**