Injuries to Muscles, Bones, and Joints Chapter 8.
-
Upload
camron-lawrence-johnson -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
2
Transcript of Injuries to Muscles, Bones, and Joints Chapter 8.

Injuries to Muscles, Injuries to Muscles, Bones, and JointsBones, and Joints
Chapter 8Chapter 8

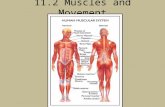
MusclesMuscles
Muscles are soft Muscles are soft tissues.tissues.
The body has over The body has over 600 muscles, most 600 muscles, most are attached to are attached to bones by strong bones by strong tissues called tissues called tendonstendons..
Electrical ImpulsesElectrical Impulses-- tiny jolts of electricity tiny jolts of electricity that cause muscles that cause muscles to contract and relax.to contract and relax.

BonesBones
The body has The body has 200 bones. 200 bones.
Humans are born Humans are born with 275 bones.with 275 bones.
Bones are filled Bones are filled with blood and with blood and nerves.nerves.

What are the functions What are the functions of our Skeleton?of our Skeleton? Provide shape and support.Provide shape and support. Enable movementEnable movement Protect internal organsProtect internal organs Produce Red blood cellsProduce Red blood cells Store nutrients for use.Store nutrients for use.

JointsJoints
The ends of two or more bones The ends of two or more bones coming together at one place coming together at one place form a joint.form a joint.
They are held together by They are held together by ligaments.- strong, tough bands.ligaments.- strong, tough bands.

How are they Injured?How are they Injured?
FracturesFractures DislocationsDislocations StrainsStrains SprainsSprains
They can happen in a variety of They can happen in a variety of ways.ways.

Fractures Fractures
A fracture is a A fracture is a complete break, complete break, chip, or crack in a chip, or crack in a bone.bone.
Usually happens Usually happens from a fall or blow from a fall or blow to the bone. to the bone.
Twisting Twisting movements could movements could also cause also cause fractures.fractures.

DislocationsDislocations
DislocationDislocation – the movement of bone at – the movement of bone at a joint away from its normal position.a joint away from its normal position.
Caused by a violent force tearing the Caused by a violent force tearing the ligaments that hold the bone in place.ligaments that hold the bone in place.
When the bone is no longer in place When the bone is no longer in place the joint cannot function.the joint cannot function.
Often leaves a bump, ridge, or hallow.Often leaves a bump, ridge, or hallow.

DislocationsDislocations

Ridge Created from Ridge Created from Dislocation.Dislocation.

SprainsSprains
SprainSprain- the tearing of ligaments at a joint.- the tearing of ligaments at a joint. Mild sprains may swell but heal quick.Mild sprains may swell but heal quick. If someone ignores swelling and pain they If someone ignores swelling and pain they
risk re-injury or making the injury worse.risk re-injury or making the injury worse. Severe sprains can involve fracture, Severe sprains can involve fracture,
dislocation.dislocation. Joints most commonly sprained are the Joints most commonly sprained are the
ankle, knee, wrist, and fingers.ankle, knee, wrist, and fingers.

Sprained AnkleSprained Ankle

StrainsStrains
StrainStrain- the stretching and tearing - the stretching and tearing of muscles or tendons.of muscles or tendons.
Often caused by lifting a heavy Often caused by lifting a heavy object or working the muscles too object or working the muscles too hard.hard.
Typically occurs in the neck, back, Typically occurs in the neck, back, thigh, or the lower leg.thigh, or the lower leg.

Back StrainBack Strain

Caring for Muscle, Caring for Muscle, Bone, or Joint injuries. Bone, or Joint injuries. (RICE)(RICE) RRest est - Do not move or straighten - Do not move or straighten
the injured area.the injured area. IImmobilize mmobilize - Stabilize the injured - Stabilize the injured
area in the position it was found. area in the position it was found. Splint the injured part only if the Splint the injured part only if the person must be moved and it will person must be moved and it will not cause them more painnot cause them more pain

R.I.C.E. (continued)R.I.C.E. (continued)
CCold old - Fill a plastic bag or wrap - Fill a plastic bag or wrap ice with a damp cloth and apply ice with a damp cloth and apply ice to the injured area for 20 min ice to the injured area for 20 min periods. Keep a thin barrier periods. Keep a thin barrier between ice and the skin.between ice and the skin.
EElevate levate - Do Not elevate the - Do Not elevate the injured part if it causes more injured part if it causes more pain.pain.

What can we do to What can we do to stabilize the injury?stabilize the injury? Use a splint to immobilize the injured area.Use a splint to immobilize the injured area. Only use a splint when you have to move Only use a splint when you have to move
or transport someone requiring more or transport someone requiring more medical attention, and it will not further medical attention, and it will not further harm them.harm them.
Check for circulation before and after Check for circulation before and after splinting.splinting.
Splint both the bone and joints if you are Splint both the bone and joints if you are unsure of the injury.unsure of the injury.

Types of splintsTypes of splints
Anatomic Anatomic Soft Soft Rigid Rigid The GroundThe Ground

Head, Neck, and Back Head, Neck, and Back InjuriesInjuries Mostly caused by Motor Vehicle Mostly caused by Motor Vehicle
crashes. (50%) crashes. (50%) Falls, sports accidents, acts of Falls, sports accidents, acts of
violence.violence. Only X-rays, CAT scans, and MRIs Only X-rays, CAT scans, and MRIs
can show the severity of injuries can show the severity of injuries they should always be treated as they should always be treated as serious injuries.serious injuries.

The Spine.The Spine.
The The spinespine is a strong, flexible is a strong, flexible column of small bones that column of small bones that support the head and trunk.support the head and trunk.
The spinal cord runs through The spinal cord runs through circular openings of these bones circular openings of these bones called called vertebraevertebrae. .
The vertebrae are separated from The vertebrae are separated from each other by cushions called each other by cushions called disksdisks..

Possible Injuries.Possible Injuries.
Fracture VertebraeFracture Vertebrae Damage NervesDamage Nerves Tear ligamentsTear ligaments Vertebrae can shift Vertebrae can shift
and squeeze the and squeeze the spinal cord.spinal cord.
Sometimes leaves Sometimes leaves people paralyzed.people paralyzed.

When should you suspect When should you suspect a person of a head, neck a person of a head, neck or back injury?or back injury? Was involved in a motor vehicle crash.Was involved in a motor vehicle crash. Was injured as a result of a fall from Was injured as a result of a fall from
greater than a standing height.greater than a standing height. Complains of neck or back pain.Complains of neck or back pain. Has tingling or weakness in the Has tingling or weakness in the
extremities.extremities. Is not fully alert.Is not fully alert. Appears to be intoxicated.Appears to be intoxicated. Appears frail or over 65 years old.Appears frail or over 65 years old.

How do we take care How do we take care of these injuries?of these injuries? Call 9-1-1.Call 9-1-1. Minimize the person’s head movement Minimize the person’s head movement
by placing your hands on both sides of by placing your hands on both sides of the person’s head. Gently hold the head the person’s head. Gently hold the head in the position in which you found it.in the position in which you found it.
Never remove a helmet or headwear Never remove a helmet or headwear unless it restricts air flow for breathing.unless it restricts air flow for breathing.
If unconscious, keep checking for If unconscious, keep checking for breathing and circulation.breathing and circulation.

Other Injuries.Other Injuries.
Chest Injuries- Sit the person so Chest Injuries- Sit the person so they can breathe easier. Sometimes they can breathe easier. Sometimes chest injuries go with back injuries. chest injuries go with back injuries. You can wrap the persons arm to the You can wrap the persons arm to the injured side for support.injured side for support.
Pelvic injuries- Keep the person lying Pelvic injuries- Keep the person lying flat. Watch for signs of internal flat. Watch for signs of internal bleeding. Minimize shock.bleeding. Minimize shock.