Initial Evaluation of the HIAPER Cloud Radar Doppler Velocity Measurements
description
Transcript of Initial Evaluation of the HIAPER Cloud Radar Doppler Velocity Measurements

Initial Evaluation of the HIAPER Cloud Radar Doppler Velocity Measurements
S. M. Ellis, J. Vivekanandan, P. Tsai, E. Loew, C. Burghart, M. Dixon, J. Emmett, M. Strong and
W.C. Lee

HIAPER Cloud Radar
• NSF deployment pool instrument– Requestable community resource• http://www.eol.ucar.edu/• Contact Vivek, [email protected]• Contact Scott Ellis, [email protected]
– Presentation: Requestable NSF Lower Atmospheric Observing Facilities for Scientific Research and Project-based Education - Tuesday, 17 September 2013 6-7:30pm in Colorado Ballroom V

HCR System Overview
• Deployable on NCAR GV, High-performance Instrumented Airborne Platform for Environmental Research (HIAPER)– Pod-based (under wing)– Other aircraft that can support large pod
• Deployable on ground – Vertical pointing– Container houses both HCR and HSRL
• Coincident radar/lidar facilitates particle size estimates in liquid and ice (e.g. Donovan et al, 2001; Tinel et al. 2005; Eloranta et al. 2007; Delanoe and Hogan, 2008)
• Dual-polarization– Currently LDR mode

HCR System Overview• W-band• Scanning in azimuth– Mechanical scanning nominally 30 deg/sec but up to
60 • In-flight, real-time aircraft attitude adjustment

High-performance Instrumented Airborne Platform for Environmental Research (HIAPER)
• 5,600 pounds (2,540 kilograms) Payload– For example: HCR, HSRL and microphysics/chemistry probes
• Max altitude 51,000 ft (less with full payload)• Range of about 7,000 miles (11,265 kilometers)

HCR System OverviewParameter Specification
Antenna 0.3m, Cassegrain
Antenna gain 46.2 dB
Antenna 3 dB beam width 0.7 degrees
Transmit frequency 94.4 GHz
Transmitter Klystron
Peak power 1.6 kW
Pulse width 0.2 – 1.0 ms
PRF 1 – 10 kHz
System noise power -106 dBm
Range resolution 30 – 150 m
Sensitivity -39.6 dBZ at 1 km

Simulations of Performance
• Developed program to estimate measurement errors for different operating parameters– Navigation correction accuracy
• Pitch• Roll• Drift
– Pointing accuracy– Measurement variance
• Dwell time• Spectrum width
– Unknown winds not at flight level
Wind

Calibration and Ground Tests
• Engineering calibration• Comparisons with Wyoming
Cloud Radar (WCR)• Real-time system monitoring• For details see poster #305
Thursday at 1:30PM by Pei-Sang Tsai
WCR Power, dBm
HCR
Pow
er, d
Bm

Navigation Correction• C-Migit INS/GPS system – Located at reflector for negligible moment arm– Size fits in the pod– Performance is quite good
• 100 Hz data• Accurate to about 0.01 deg
• Real-time correction of pointing angle– Keeps antenna pointing in desired direction– Helps mitigate the cross wind errors
Wind

Time Series Recording
• The HCR records the I and Q time series data for all flights– Enables investigation of advanced signal processing– Benefits data quality
• Spectral display tool has been developed

Test Flights Completed - SAANGRIA• Test flights completed in February and March 2013• EMI tests• Radar ran reliably
– Pressure leak • Antenna fixed at near nadir • Flight patterns for pointing calibration performed based on
Haimov and Rodi (2013)– Uses ground echoes – need flat terrain, with no forest, no water – Straight and level upwind/downwind– Straight and level cross wind– Left and right circles with roll angles ~ 20 to 30 deg
• Calibrated pointing following Haimov and Rodi (2013)• Corrected radial velocity for aircraft motion following Lee et al.
(1993)• Analyzed ground echo velocity on other data sets

Test Flights Completed - SAANGRIA
Ground echoes:
Mean Vr = 0.001 m/sStd dev Vr = 0.086 m/sVar Vr = 0.0074 m/s
(10 minutes of data over level ground)

Test Flights Completed - SAANGRIA
• Verified sensitivity - ongoing• Spectra checked for spurious artifacts

Test Flights Planned- IDEAS IV
• Beginning this week! (delayed by floods)• First implementation of real-time pointing
correction• First test of scanning capability• Correction of issues identified during
SAANGRIA– Pressure vessel leak– EMI

Future Plans• Continue testing and verification of data quality– Calibration – Dual-pol– Navigation correction and pointing
• Deploy for CSET– Study stratocumulus clouds between California and
Hawaii – Funded for summer of 2015
• Add second wavelength– Beam- and resolution-matched Ka-band – Funding dependent

Thank YouQuestions?
HCR pod
Dropsonde
Various probes

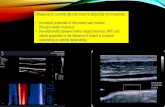
CSU-CHILL Comparison
CHILL Data HCR DataGV Skin Paint
Radius, km (approximate distance GV traveled in 60 sec)
Time, seconds060 30
Altit
ude
AGL,
km