IATROGENIC ORTHOPAEDIC INJURIES IN CHILDHOOD Injuries - Neil Price.pdf · Post LP intraspinal...
Transcript of IATROGENIC ORTHOPAEDIC INJURIES IN CHILDHOOD Injuries - Neil Price.pdf · Post LP intraspinal...

IATROGENIC ORTHOPAEDIC
INJURIES IN CHILDHOOD
NEIL PRICENEIL PRICE
St George’s HospitalSt George’s Hospital

Definition
IatrogenicIatrogenic = = iatrosiatros Gr. PhysicianGr. Physician
= = gennangennan Gr. to produceGr. to produce
"Any effect, usually adverse, resulting from "Any effect, usually adverse, resulting from
the activity of a physician or surgeon "the activity of a physician or surgeon "
Dorland's Medical Dictionary 20th Ed.Dorland's Medical Dictionary 20th Ed.

IATROGENIC ORTHOPAEDIC
INJURIES IN CHILDHOOD
ORTHOPAEDIC ORTHOPAEDIC
INJURIESINJURIES
•• Fracture TreatmentFracture Treatment
•• Paediatric orthopaedic Paediatric orthopaedic
treatmenttreatment
•• RadiotherapyRadiotherapy
NON NON -- ORTHOPAEDIC ORTHOPAEDIC
INJURIESINJURIES

Plaster casts
•• SoresSores
•• Compartment syndrome Compartment syndrome
•• BurnsBurns
•• Cast syndromeCast syndrome

Plaster casts - burns
•• Exothermic reaction on settingExothermic reaction on setting
•• Reports of partial & full thickness burnsReports of partial & full thickness burns
•• Burn if 50Burn if 50oo
c for 5c for 5--15min15min
•• Heat sinkHeat sink
PrecautionsPrecautions
•• Thinnest possible that will do jobThinnest possible that will do job
•• Wet thoroughly with tepid waterWet thoroughly with tepid water
•• Do not wring dryDo not wring dry
•• Do not wrap with bandage until dryDo not wrap with bandage until dry

Plaster casts - cast syndrome
•• Persistent vomiting in patients treated in Persistent vomiting in patients treated in
hyperextension body jackets post fracture hyperextension body jackets post fracture
or operationor operation
•• Due to obstruction of third part of Due to obstruction of third part of
duodenum by superior mesenteric vesselsduodenum by superior mesenteric vessels
•• Split /remove castSplit /remove cast
•• Avoid excessive extensionAvoid excessive extension
Nelson et al Nelson et al Postgrad. Med Postgrad. Med 42:42:457457--61 195761 1957

Skin Traction
•• Skin resists compression better than Skin resists compression better than
shearshear
•• Avulsion of superficial layers if >8lbs Avulsion of superficial layers if >8lbs
applied for any length of timeapplied for any length of time
Tourniquet effect of bandagesTourniquet effect of bandages

Bryant’s (Gallows) Traction for
femoral fracture
•• Bryant 19th century advised:Bryant 19th century advised:
•• Against use in children older than 3 years Against use in children older than 3 years
of ageof age
•• Use of splint on legs to prevent knee Use of splint on legs to prevent knee
hyperextension hyperextension
Volkman’s contracture reported 1950Volkman’s contracture reported 1950

Gallows Traction - Volkman’s ischaemia Nicholson et al JAMA 1955Nicholson et al JAMA 1955
Causative factors Causative factors
•• Reduction in hydrostatic pressure in lower Reduction in hydrostatic pressure in lower
limbs when held overhead proportional to limbs when held overhead proportional to
length of limb length of limb
•• Excessive traction (proportional to weight)Excessive traction (proportional to weight)
•• Tight bandagingTight bandaging
•• ShockShock
•• Hyperextension of kneeHyperextension of knee
•• Ischaemia from compartment syndrome or Ischaemia from compartment syndrome or
vascular injuryvascular injury

Gallows Traction & Volkman’s
ischaemia Prognosis - Mubarak & Carroll
JBJS 61B 1979
•• 9 children (10 limbs)9 children (10 limbs)
•• 2 cases on non2 cases on non--fractured side !fractured side !
Retrospective review showed:Retrospective review showed:
•• all diagnosed lateall diagnosed late
•• head injury delayed recognitionhead injury delayed recognition
•• Poor long term functional result once Poor long term functional result once
establishedestablished

Prevention
•• Should Should not not be used for child be used for child >2yrs>2yrs
>30lbs>30lbs
•• Care wrapping legCare wrapping leg
•• Avoid knee hyperextensionAvoid knee hyperextension
•• Frequent neurovascular checksFrequent neurovascular checks

Skeletal Traction pin
•• Growth plate damage by heat if power Growth plate damage by heat if power
drilleddrilled
•• Tibial pin Tibial pin >> 2 finger breadths 2 finger breadths distal distal to tibial to tibial
tuberositytuberosity
•• Deep peroneal nerve at riskDeep peroneal nerve at risk
•• Angle over muscle onto tibia avoiding Angle over muscle onto tibia avoiding
penetration of muscle (Nicol)penetration of muscle (Nicol)

Skeletal Traction pin
•• Recommended method of insertion angling over Recommended method of insertion angling over
muscle & neurovascular bundlemuscle & neurovascular bundle

Supracondylar Fractures - closed
pinning
Royce et al JPO 11: 191Royce et al JPO 11: 191--4 19914 1991
•• Ulnar nerve injury in 4/143 due to use of Ulnar nerve injury in 4/143 due to use of
medial pinmedial pin
Two types of palsy:Two types of palsy:
•• ImmediateImmediate due to direct damage by pindue to direct damage by pin
•• DelayedDelayed due to nerve contusion, oedema due to nerve contusion, oedema
or stretch of nerve over pinor stretch of nerve over pin

Supracondylar Fractures - closed
pinning
•• Recommend medial Recommend medial incisionincision and placing and placing
drill guide onto bonedrill guide onto bone
•• Replace pins showing malposition on IIReplace pins showing malposition on II
•• Direct damage should be treated by Direct damage should be treated by
exploration to remove pin from nerveexploration to remove pin from nerve
•• All four palsies recovered after 6 monthsAll four palsies recovered after 6 months

Proximal Tibial Osteotomy
•• Apophyseal or growth plate damage Apophyseal or growth plate damage
therefore more distaltherefore more distal
•• Iatrogenic fracturesIatrogenic fractures
•• Compartment syndromeCompartment syndrome
•• Peroneal palsyPeroneal palsy
•• Vascular injuriesVascular injuries
Neurovascular complication rate 3.3 Neurovascular complication rate 3.3 -- 18%18%

Proximal Tibial Osteotomy
Aetiology of peroneal palsyAetiology of peroneal palsy
•• Anterior tibial A. compromise (Steele 1971)Anterior tibial A. compromise (Steele 1971)
•• Anterior compartment syndromeAnterior compartment syndrome
•• Traction injury during exposure or correctionTraction injury during exposure or correction

Proximal Tibial Osteotomy
Technical recommendationsTechnical recommendations
•• Meticulous haemostasisMeticulous haemostasis
•• Prophylactic fasciotomyProphylactic fasciotomy
•• NonNon--constrictive splints/bandagesconstrictive splints/bandages
•• DistalDistal fibular resectionfibular resection
Slawaski et al JPO 1994 4.3% (255)Slawaski et al JPO 1994 4.3% (255)

Peroneal Palsy - Slawaski et al JPO 1994
Predisposing factors:Predisposing factors:
•• Older childrenOlder children
•• Increased blood loss & tourniquet timeIncreased blood loss & tourniquet time
•• Difficulty in exposureDifficulty in exposure
•• Angulatory > rotationalAngulatory > rotational
•• Recovery in all cases between 3 days and Recovery in all cases between 3 days and
six months ( two required exploration)six months ( two required exploration)

AVN post treatment of DDH
•• Classification & Classification &
natural history of natural history of
iatrogenic AVNiatrogenic AVN
•• Pavlik HarnessPavlik Harness
•• Closed reduction & Closed reduction &
splintagesplintage
•• Open reductionOpen reduction

Severity & Prognosis of AVN
•• Kalamchi & MacEwen JBJS 62A 1980Kalamchi & MacEwen JBJS 62A 1980
•• 119 patients with AVN post treatment119 patients with AVN post treatment
•• F/U 0.5F/U 0.5--27 (Av 9) years27 (Av 9) years
•• 8/79 (~ 10%) unilateral cases developed 8/79 (~ 10%) unilateral cases developed
AVN in the AVN in the normalnormal hiphip
•• Physeal Physeal involvement rather than of ossific involvement rather than of ossific
nucleus dictated outcomenucleus dictated outcome
•• Classification systemClassification system

Severity & Prognosis of AVN - Group I
Changes affecting the Changes affecting the
ossific nucleusossific nucleus
•• Delay in appearance of Delay in appearance of
ossific nucleusossific nucleus
•• MottlingMottling
•• Flattening & Flattening &
fragmentationfragmentation
•• Head spherical no Head spherical no
changes in neckchanges in neck

Severity & Prognosis of AVN - Group II
Lateral physeal damageLateral physeal damage
Head changes like Gp I but Head changes like Gp I but
in addition :in addition :
•• Lateral ossificationLateral ossification
•• Physeal irregularity & Physeal irregularity &
bridgingbridging
•• Lateral epiphyseal Lateral epiphyseal
notchingnotching
•• Lateral metaphyseal Lateral metaphyseal
defectdefect

Group II - late effects
•• Age 9Age 9--10 develop valgus neck deformity10 develop valgus neck deformity
•• Directs most of articular surface out of Directs most of articular surface out of
acetabulumacetabulum
•• Overgrowth of greater trochanterOvergrowth of greater trochanter
•• Early OAEarly OA

Severity & Prognosis of AVN - Group III
Central Physeal DamageCentral Physeal Damage
•• Central metaphyseal defectCentral metaphyseal defect
•• Central bridgingCentral bridging
•• Eventually short neck Eventually short neck
without alteration of neckwithout alteration of neck--
shaft angle (leg length shaft angle (leg length
discrepancydiscrepancy
•• GT overgrowth (GT GT overgrowth (GT
epiphyseodesis)epiphyseodesis)

Severity & Prognosis of AVN - Group IV
Total damage to head & Total damage to head &
physisphysis
•• Early femoral head Early femoral head
irregularityirregularity
•• Coxa magnaCoxa magna
•• Irregular, wide, short Irregular, wide, short
neck with medial beakneck with medial beak
•• Varus neckVarus neck
•• Acetabular dysplasiaAcetabular dysplasia

Outcome after iatrogenic AVN
Cooperman et al JBJS 1980Cooperman et al JBJS 1980
•• 25 patients @ 39 year follow up25 patients @ 39 year follow up
•• Av age 42yrAv age 42yr
•• in 96% radiographic signs of OAin 96% radiographic signs of OA
•• 80% disabling symptoms80% disabling symptoms
Iatrogenic AVN very grave prognosisIatrogenic AVN very grave prognosis

Iatrogenic Problems with Pavlik
Harness
•• Excessive flexionExcessive flexion
–– obturator obturator
dislocationdislocation
–– femoral nerve femoral nerve
neuropraxianeuropraxia
•• Excessive abductionExcessive abduction
–– AVNAVN
•• Brachial plexus palsyBrachial plexus palsy

AVN with Pavlik Harness
•• Incidence higher when treating Incidence higher when treating
Dislocation as compared to subluxationDislocation as compared to subluxation
•• PavlikPavlik 2.8%2.8%
•• TonnisTonnis 15%15%
•• KalamchiKalamchi 0%0%
•• Excessive abduction causes pressure on Excessive abduction causes pressure on
posterior vessels against posterior lip of posterior vessels against posterior lip of
acetabulumacetabulum
•• Human rather than frog positionHuman rather than frog position

Closed reduction & splintage
Higher incidence of AVN associated with: Higher incidence of AVN associated with:
•• Older age Older age
•• Reductions performed without GAReductions performed without GA
•• No preNo pre--op traction?op traction?
•• Eccentric reduction or persistent Eccentric reduction or persistent
dislocationdislocation
•• Splintage in excessive abductionSplintage in excessive abduction

Open Reduction of DDH
•• Choice of approachChoice of approach
Most commonly used is the anterior Most commonly used is the anterior
approach (2 approach (2 --15% AVN)15% AVN)
•• Medial Ludloff approach in younger Medial Ludloff approach in younger
childrenchildren
•• Recent reported that late results show Recent reported that late results show
>50% satisfactory results at 19yr follow up >50% satisfactory results at 19yr follow up
•• Eccentric reduction & AVN of 43% (mostly Eccentric reduction & AVN of 43% (mostly
Gp II)Gp II)
Koizumi et al JBJS 78B Nov 1996Koizumi et al JBJS 78B Nov 1996

SUFE - chondrolysis
•• Necrosis of articular cartilage of hip (6%)Necrosis of articular cartilage of hip (6%)
•• Unrecognised Unrecognised pin penetration proposed pin penetration proposed
as a cause ( 51% )as a cause ( 51% )
•• Animal studies show changes worse the Animal studies show changes worse the
longer the duration of penetrationlonger the duration of penetration
•• Can also occur in untreated slipsCan also occur in untreated slips
•• ImmunologicalImmunological
•• Genetic predisposition Genetic predisposition

Chondrolysis with SUFE
•• No direct evidence to support the theory No direct evidence to support the theory
that that transienttransient pin penetration alone pin penetration alone
causes chondrolysis causes chondrolysis
•• Zionts Zionts JBJS (US) 1991 JBJS (US) 1991 followed 14 cases followed 14 cases
of transient pin penetration for 3yr of transient pin penetration for 3yr -- no no
cases of chondrolysiscases of chondrolysis
•• However should be avoided if possibleHowever should be avoided if possible

Radiotherapy in childhood
•• Effects noted by Perthes’ 1903Effects noted by Perthes’ 1903
•• As more children survived malignacy the As more children survived malignacy the
magnitude of the effect was realisedmagnitude of the effect was realised
•• Most obvious effect is on growthMost obvious effect is on growth
•• Mediated by:Mediated by:
–– SystemicSystemic endocrine effect of endocrine effect of
hypothalamic irradiationhypothalamic irradiation
–– Local Local effect on growth plate & boneseffect on growth plate & bones

Radiotherapy - pathological effects
Effects seen in all components of growing Effects seen in all components of growing
bone:bone:
•• PhysisPhysis arrested chondrogenesisarrested chondrogenesis
decreased chondrocytesdecreased chondrocytes
•• MetaphysisMetaphysis deficient resorption of deficient resorption of
calcified bone & cartilagecalcified bone & cartilage
•• DiaphysisDiaphysis altered periosteal activityaltered periosteal activity

Radiotherapy - pathological
effects
Late effectsLate effects•• Small & medium vessel damageSmall & medium vessel damage
•• Reduced healing capacityReduced healing capacity
•• Reduced blood supply to unirradiated Reduced blood supply to unirradiated
bone less possibilty for compensatory bone less possibilty for compensatory
growthgrowth
•• Reduction in bone strength Reduction in bone strength -- increased increased
propensity to fracturepropensity to fracture

Radiotherapy - pathological
effects
•• Growth PlateGrowth Plate•• End result is End result is suspension suspension
or or retardationretardation of of
chondrogenesis & chondrogenesis &
osteogenesis with osteogenesis with
premature closure of premature closure of
growth platesgrowth plates
•• Termination or Termination or
suspension of bone suspension of bone
growthgrowth

Clinical effects
•• Axial shortening of long bones Axial shortening of long bones -- limb length limb length
discrepancydiscrepancy
•• Hypoplasia of flat bonesHypoplasia of flat bones
•• Scoliosis (bony wedging & soft tissue Scoliosis (bony wedging & soft tissue
“bowstring”)“bowstring”)
•• Joint degenerationJoint degeneration

Factors
•• Patient age Patient age effect effect worse at times of worse at times of
growth spurtgrowth spurt (<6yr or (<6yr or
during adolescenceduring adolescence
•• Radiation doseRadiation dose >>2000cGy dose 2000cGy dose
dependant thereafterdependant thereafter
•• Radiation energyRadiation energy newer megavoltage newer megavoltage
therapy absorbed less therapy absorbed less
by boneby bone

Radiotherapy - prognosis
•• Growth effects months or years after Growth effects months or years after
irradiationirradiation
•• Growth may resume if low dose therapyGrowth may resume if low dose therapy
•• Muscle atrophy associated with Muscle atrophy associated with
underdeveloped bone eg sarcomaunderdeveloped bone eg sarcoma

Prevention
•• Megavoltage linear acceleratorsMegavoltage linear accelerators
•• Modified dose regimesModified dose regimes
•• Other modalities of treatment Other modalities of treatment eg Ewingseg Ewings
•• Hyperbaric oxygenHyperbaric oxygen
•• Growth factorsGrowth factors

Non Orthopaedic injuriesNon Orthopaedic injuries
•• UAC leading to vascular UAC leading to vascular
occlusionocclusion
•• Extravasation injuriesExtravasation injuries
•• Fibrous bands in deltoid & Fibrous bands in deltoid &
quadricepsquadriceps
•• Post LP intradural dermoidsPost LP intradural dermoids
•• Osteomyelitis from punctureOsteomyelitis from puncture
•• Intraosseous infusion needlesIntraosseous infusion needles
•• Birth injuriesBirth injuries

UAC leading to vascular thrombosisUAC leading to vascular thrombosisFarrar et al JBJS 78B Oct 1996Farrar et al JBJS 78B Oct 1996
Usually severely ill neonates Usually severely ill neonates -- hypercoagulable hypercoagulable
Birth asphyxia, Rhesus Disease, sepsis & Birth asphyxia, Rhesus Disease, sepsis &
maternal diabetes can initiate intravascular maternal diabetes can initiate intravascular
coagulationcoagulation
Umbilical artery catheters can also precipitate Umbilical artery catheters can also precipitate
vascular disturbancevascular disturbance
Blanching in 32% during infusion Blanching in 32% during infusion -- stop infusionstop infusion

UAC leading to vascular thrombosisUAC leading to vascular thrombosisStringel et al 1985Stringel et al 1985
•• 100 neonates with 100 neonates with
UAC'sUAC's
•• 32% developed 32% developed
blanching of lower blanching of lower
limbs during infusionslimbs during infusions
•• 2 cases of frank 2 cases of frank
gangrenegangrene

UAC leading to ischaemia
•• Primary treatment is Primary treatment is
heparin infusion heparin infusion + +
thrombectomythrombectomy
•• Surgery alone Surgery alone
ineffectiveineffective
•• Conservative Conservative
management for management for
established gangreneestablished gangrene

Lessons
•• High index of suspicion on the part of High index of suspicion on the part of
NICU staffNICU staff
•• Early manipulation of coagulation system Early manipulation of coagulation system
++ surgical thrombectomysurgical thrombectomy
•• With established gangrene With established gangrene avoid the avoid the
temptation to perform early surgery.temptation to perform early surgery. Wait Wait
until demarcation well established as until demarcation well established as
usually more distal than first expected usually more distal than first expected

Extravasation injuriesExtravasation injuries
•• Result of intravenous cannula being or becoming Result of intravenous cannula being or becoming
misplaced with escape of irritant fluid into the misplaced with escape of irritant fluid into the
subcutaneous tissues subcutaneous tissues
•• VesicantsVesicants -- subcutaneous inflammation + necrosis subcutaneous inflammation + necrosis
with skin loss and ulceration with skin loss and ulceration -- Calcium solns, Calcium solns,
cytotoxics, radiographic contrast agentscytotoxics, radiographic contrast agents
•• IrritantsIrritants -- inflammatory reactions but rarely lead to inflammatory reactions but rarely lead to
necrosis necrosis -- albumin, blood products, MTXalbumin, blood products, MTX
•• InnocuousInnocuous -- absorbed without apparent damageabsorbed without apparent damage

Extravasation injuriesExtravasation injuries
•• Compartment syndromeCompartment syndrome
1 case of Volkman’s contracture due to 1 case of Volkman’s contracture due to
intravenous into leg intravenous into leg
Mubarak & Carroll JBJS 61B 1979

Extravasation injuries Extravasation injuries -- management management Loth & Eversman Loth & Eversman Clin Orth Clin Orth 272272 19911991
•• VolumeVolume
•• Host factorsHost factors
•• Type of agentType of agent
•• Necrosis intervalNecrosis interval-- time between escape & time between escape &
irreversible tissue damageirreversible tissue damage
•• Conservative treatment Conservative treatment --compressive compressive
dessing, elev, observation dessing, elev, observation

Extravasation injuries Extravasation injuries -- managementmanagement
•• Patients seen Patients seen after the necrosis intervalafter the necrosis interval
are best treated nonare best treated non--operativelyoperatively
•• Surgery Surgery --decompression, drainage decompression, drainage
irrigation, therapeutic liposuctionirrigation, therapeutic liposuction
•• RehabilitationRehabilitation
•• ReconstructionReconstruction

Fibrous bands in deltoid & quadricepsFibrous bands in deltoid & quadriceps
•• Due to multiple intramuscular injectionsDue to multiple intramuscular injections
especially tetracyclineespecially tetracycline
•• Post injection fibrosis in deltoid, quadriceps & Post injection fibrosis in deltoid, quadriceps &
gluteal musclesgluteal muscles
•• In deltoid fibrosis abduction contracture In deltoid fibrosis abduction contracture
described where child unable to approximate described where child unable to approximate
forearmsforearms
•• Patellar subluxation described in lateral Patellar subluxation described in lateral
quadriceps bandquadriceps band

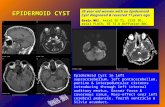
Post LP intraspinal epidermoid Post LP intraspinal epidermoid
tumourstumours
•• Intraspinal epidermoid tumours are rareIntraspinal epidermoid tumours are rare
•• 41% are iatrogenic in origin following LP, 41% are iatrogenic in origin following LP,
injections, etc.injections, etc.
•• Due to implantation of skin fragments Due to implantation of skin fragments
within spinal canalwithin spinal canal
•• Intradural, extramedullaryIntradural, extramedullary
•• Present with longstanding progressive Present with longstanding progressive
LBP, radicular pain, hamstring spasm, gait LBP, radicular pain, hamstring spasm, gait
abnormalitiesabnormalities

Post LP intraspinal epidermoid Post LP intraspinal epidermoid
tumourstumours
•• Investigation of choice MRI enhanced with Investigation of choice MRI enhanced with
GdGd--DTPADTPA
•• Non operative treatment brought almost Non operative treatment brought almost
no reliefno relief
•• Good prognosis if removedGood prognosis if removed
Caro et al Caro et al JPOJPO 1111: 288: 288--293 1991293 1991

Birth Injuries
•• Less common nowadays with advances in Less common nowadays with advances in
obstetric practiceobstetric practice
–– especially LSCS for delivery of breech especially LSCS for delivery of breech
presentationpresentation
–– better assessment of fetal maturitybetter assessment of fetal maturity
•• Most commonly clavicular fracture or mild Most commonly clavicular fracture or mild
brachial plexus palsybrachial plexus palsy

Birth Injuries - incidence
Incidence has fallen steadilyIncidence has fallen steadily
1930’s1930’s 20 / 100020 / 1000
1950’s1950’s 7 / 10007 / 1000
1990’s1990’s 22--3 / 10003 / 1000
Clavicle > Brachial plexus > Humerus & Clavicle > Brachial plexus > Humerus &
femurfemur

Birth Injuries - aetiology
Risk factorsRisk factors
Birth wt > 4.5kg (maternal diabetes)Birth wt > 4.5kg (maternal diabetes)
Wickstrom et al 1988Wickstrom et al 1988
Breech deliveryBreech delivery

Birth Injuries - aetiology
•• Cervical spinal cord injury due to Cervical spinal cord injury due to
excessive traction to deliver arrested excessive traction to deliver arrested
shoulder or forceful rotation of head from shoulder or forceful rotation of head from
OO--P to anteriorP to anterior
•• Femoral fractures from groin traction in Femoral fractures from groin traction in
extended breech extended breech
•• Humeral fractures shoulder dystocia in Humeral fractures shoulder dystocia in
breech breech

Birth Injuries - clavicular fractures
•• Most common Most common
•• Account for 40Account for 40--50% of all birth injuries50% of all birth injuries
•• Usually greenstick mid third fracture (may Usually greenstick mid third fracture (may
be complete, oblique or transverse)be complete, oblique or transverse)
•• Risk factors large birth weight and Risk factors large birth weight and
shoulder dystocia but most follow vertex shoulder dystocia but most follow vertex
deliveries.deliveries.

Birth Injuries - clavicular fractures
•• Present with “pseudoparalysis” and pain Present with “pseudoparalysis” and pain
on handlingon handling
•• May not be apparent if greenstick until May not be apparent if greenstick until
callus palpablecallus palpable
•• 5% of neonates with clavicular fracture 5% of neonates with clavicular fracture
will have brachial plexus palsywill have brachial plexus palsy
Oppenheim et al 1990Oppenheim et al 1990

Differential diagnosis
•• Upper humeral osteomyelitisUpper humeral osteomyelitis
•• Separation of proximal humeral epiphysisSeparation of proximal humeral epiphysis
•• Congenital pseudarthrosis of clavicleCongenital pseudarthrosis of clavicle
–– if unilateral on opposite side to the if unilateral on opposite side to the
heartheart
–– no callus or tendernessno callus or tenderness
–– smooth bone ends on Xsmooth bone ends on X--rayray

Clavicular fractures - treatment
•• SymptomaticSymptomatic
•• Careful handlingCareful handling
•• Sling if very displacedSling if very displaced

Proximal humeral epiphyseal separation
•• Physis is a weak point which fails before Physis is a weak point which fails before
ligaments and joint capsuleligaments and joint capsule
•• Shoulder dislocations are rareShoulder dislocations are rare
•• Most apparent Shoulder dislocations are Most apparent Shoulder dislocations are
epiphyseal separationsepiphyseal separations
•• Any doubt resolved by U/S or Any doubt resolved by U/S or
arthrographyarthrography
•• Treat by immobilisation in IR for 2Treat by immobilisation in IR for 2--3 weeks3 weeks
periosteal new bone by 6periosteal new bone by 6--10 days10 days

Distal humerus & elbow
•• Dislocation extremely uncommonDislocation extremely uncommon
•• XX--ray’s suggest posteromedial dislocation ray’s suggest posteromedial dislocation
but proximal radius & ulna too close to but proximal radius & ulna too close to
distal humerusdistal humerus
•• Treatment realigment and splintage in Treatment realigment and splintage in
posterior slabposterior slab
•• Prognosis Prognosis -- full or virtually full recovery full or virtually full recovery
in most casesin most cases

Humeral & femoral shaft fractures
UsuallyUsually mid third, transversemid third, transverse
completecomplete
HumerusHumerus 22--3 weeks immobilisation 3 weeks immobilisation
across chestacross chest
FemurFemur Bryant’s traction Bryant’s traction ++ spicaspica
<< 4040oo
angulation will correctangulation will correct

Proximal femur
•• Fracture separation of FCEFracture separation of FCE
•• Mild flexion & ERMild flexion & ER
•• XX--ray ray -- ? DDH or proximal femoral ? DDH or proximal femoral
deficiencydeficiency
•• Normal acetabulum (index <30Normal acetabulum (index <30oo
))
•• U/S or arthrogramU/S or arthrogram
•• MUA + Spica or Bryants tractionMUA + Spica or Bryants traction
•• Possible late coxa vara or femoral Possible late coxa vara or femoral
retroversionretroversion

THANK YOUTHANK YOU
&&
GOOD LUCK! GOOD LUCK!
















![Epidermoid and dermoid cysts of the head and neck region · Sahalok et al. Epidermoid and dermoid cyst removal 348 cyst in the oral cavity, lower lip, or upper lip.[7] Giant epidermoid](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5f0d065f7e708231d4384dcd/epidermoid-and-dermoid-cysts-of-the-head-and-neck-region-sahalok-et-al-epidermoid.jpg)
