SESSION 3 MIND AND MOVEMENT Alternative Care for the Mind and Body Jennifer Kitchen July 3, 2013.
Hypertension A Case Study Jennifer Kitchen July 19, 2013.
-
Upload
gwendolyn-clark -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of Hypertension A Case Study Jennifer Kitchen July 19, 2013.

HypertensionA Case Study
Jennifer Kitchen
July 19, 2013

Overview
• Vicki, a patient just diagnosed with Hypertension (HTN)• What is Hypertension?• Appropriate Treatment Prognosis (including therapies,
medications, etc.) • Patient Teaching• Potential Barriers to Therapy

Vicki
• 42 years old • African American• Married to her high school sweetheart, Robert, for 20 yrs.• Self-employed, successful insurance agent • Busy lifestyle, travels often and eats at fast food
restaurants for most meals• Blood pressure, 145 over 94

What is Hypertension?
• Hypertension (HTN) is…• High Blood Pressure (BP)• A major cause of strokes and heart attacks
• 1 in 4 adults have high BP • An estimated 5-10 million people have HTN but are
unaware of it• HTN contributes Directly or Indirectly to almost 800,000
deaths a year• (Moser, 2012)

Normal Blood Pressure
What is Hypertension?
• Normal BP is about 120/80 • Systolic pressure- pumping pressure• Diastolic pressure- resting pressure• (ACP, 2004).

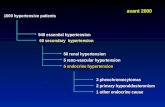
Stages of Hypertension
What is Hypertension?
(Foex, 2004)
Table 1: Stages of hypertension
Stage Systolic DiastolicOptimal <120 <80Normal 120–129 80–84High-normal 130–139 85–89HTN stage 1 140–159 90–99HTN stage 2 160–179 100–109HTN stage 3 >180 >110
Systolic and diastolic pressures given in mm Hg.

Treatment Prognosis
• HTN is not curable• Can be controlled with…• Medication (drug therapy)• Diuretics, Beta-adrenergic blockers, Vasodilators, Calcium
channel blockers, Angiotension-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and Angiotension receptor blockers (ARBs)
• Lifestyle changes• Limit sodium intake, Reduce and maintain a healthy weight,
Manage a healthy diet, Exercise, Reduce stress, and Quit smoking
• (Frazier and Drzymkowski, 2009)

Patient Teaching
• Cause of HTN is Unknown, but many factors may contribute to HTN…• Age, Smoking, Heredity, Obesity, Sedentary lifestyle, Poor
diet and nutrition, and Hyperactive (type A) personality
• Stress is considered a Major Factor!• (Frazier and Drzymkowski, 2009)

Patient Teaching
• Living with HTN…• Remember high BP cannot be Cured, only Controlled• Drug therapy is important in helping control HTN• Lifestyle changes are also important• BP must be monitored regularly• (Frazier and Drzymkowski, 2009)

Potential Barriers
• Making lifestyle changes• “Bad habits are hard to change.”
• Staying on medication• “If I can’t feel it, it must not be there.”
• Monitoring BP• “My blood pressure is always higher when I go to the
doctor’s office.”

Sometimes all we need is to take a break on the busy tracks of life.

References
American College of Physicians (ACP), (2004). ACP Special Report: Living With Hypertension. Retrieved from http://www.acponline.org/patients_families/pdfs/health/hypertension_report.pdf
Foex, P. and Sear, J.W., (2004). Hypertension: pathophysiology and treatment. Continuing Education in Anesthesia, Critical Care & Pain; 4:3. DOI 10.1093. Retrieved from http://ceaccp.oxfordjournals.org/content/4/3/71.full.pdf+html.
Moser, M. (2012). High Blood Pressure: lower it and live longer. Hypertension Education Foundation (HEF). Retrieved from http://www.hypertensionfoundation.org/PDinfo/HBP(HEF)120611.pdf
Frazier, M. S. and Dryzmkowski, J. W. (2009). Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions (4th Ed.). St. Louis, MO: Saunders Elsevier Inc.