【極秘】♂人類女体化計画♀wasadasan.com/repo/nyotaika2.pdf · 【極秘】♂人類女体化計画♀ Copyright ©2013 ♂人類女体化計画♀ @スザンヌみさき
Human Reproduction ♀ ♂. Reproduction BINGO Free Space and…. Cervix Clitoris Estrogen...
-
Upload
jared-kelley -
Category
Documents
-
view
231 -
download
0
Transcript of Human Reproduction ♀ ♂. Reproduction BINGO Free Space and…. Cervix Clitoris Estrogen...
Reproduction BINGOFree Space and….
• Cervix• Clitoris• Estrogen• Progesterone• Fertilization• Menstruation• Menstrual Cycle• Ova• Ovaries• Vagina• Fallopian Tubes• Ovulation• Urethra• Uterus• Endometrium
• Cowper’s Gland• Ejaculation• Epididymis• Penis• Prostate gland• Scrotum• Semen• Seminal Vesicles• Sperm• Testicles• Testosterone• Vas Deferens
• Both sexes have reproductive Both sexes have reproductive organs called GENITALS or organs called GENITALS or GENITALIA designed for the GENITALIA designed for the purpose of intercourse and purpose of intercourse and conception. conception.
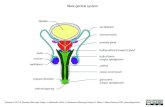
Female Reproductive SystemFemale Reproductive System
Female reproductive organs are for Female reproductive organs are for intercourse, reproduction, urinationintercourse, reproduction, urinationpregnancy and childbirth.pregnancy and childbirth.
9. Ovary (Ovaries)9. Ovary (Ovaries)
• Two solid egg-shaped structures Two solid egg-shaped structures • They are attached to the uterus by ligaments. They They are attached to the uterus by ligaments. They
are the counterpart of the male testicles.are the counterpart of the male testicles.• Ovaries have two main functions:Ovaries have two main functions:
#1-store and release the ova or female egg cell. Some of #1-store and release the ova or female egg cell. Some of the ova disappear; others are dormant until each is ripened the ova disappear; others are dormant until each is ripened and released after puberty.and released after puberty.
#2-produce female sex hormones ESTROGEN and #2-produce female sex hormones ESTROGEN and PROGESTERONE PROGESTERONE
8. Ova 8. Ova • The female reproductive cell. The female reproductive cell. • They are the largest cells in the They are the largest cells in the
female body. female body. (about the size of a grain of (about the size of a grain of sand.) sand.)
• The female baby is born with all The female baby is born with all the ova she will ever have the ova she will ever have (about (about 200,000 in each ovary). 200,000 in each ovary).
• About 400-500 ova mature and About 400-500 ova mature and are released over a lifetime are released over a lifetime
4. Estrogen 4. Estrogen
• Estrogen is responsible for the secondary sex Estrogen is responsible for the secondary sex characteristics and the sex drive in females. It characteristics and the sex drive in females. It spurs the onset of puberty and is responsible spurs the onset of puberty and is responsible for OVULATION. for OVULATION.
12. Progesterone12. Progesterone
• Progesterone builds up the lining of the Progesterone builds up the lining of the uterus called the endometrium in preparation uterus called the endometrium in preparation for the fertilized ovumfor the fertilized ovum
11. Ovulation11. Ovulation
• When the egg is released from the ovary.When the egg is released from the ovary.• At the age of pubertyAt the age of puberty• The ovum moves to the surface of the ovary in bursts The ovum moves to the surface of the ovary in bursts
outout• The ova falls into the fallopian tube and waits for The ova falls into the fallopian tube and waits for
fertilization fertilization • This happens every 28 days This happens every 28 days • It happens at about the 14It happens at about the 14thth day of the cycle day of the cycle
10. FALLOPIAN TUBES10. FALLOPIAN TUBES(oviducts)(oviducts)
• Two tubes attached on either side of the uterus. Two tubes attached on either side of the uterus. • They are about four inches long and 3/16 inch in They are about four inches long and 3/16 inch in
diameter (the size of a cooked spaghetti noodle). diameter (the size of a cooked spaghetti noodle). • The oviducts carry egg cells toward the uterus and sperm The oviducts carry egg cells toward the uterus and sperm
cells toward the egg cell. cells toward the egg cell. • Fertilization takes place in the upper third of the oviduct. Fertilization takes place in the upper third of the oviduct.
14. Uterus14. Uterus• A hollow, muscular organ (A hollow, muscular organ (shaped somewhat like an upside-down shaped somewhat like an upside-down
pear, about the size of a fist).pear, about the size of a fist). • The uterus is lined with endometrium The uterus is lined with endometrium (a blood lining.) (a blood lining.)
• The uterus has one main function—to protect and The uterus has one main function—to protect and nourish a fetus nourish a fetus
• The walls of the uterus have the ability to stretch to The walls of the uterus have the ability to stretch to the size of a small watermelon. the size of a small watermelon.
• After childbirth the uterus shrinks back to the After childbirth the uterus shrinks back to the original shape in 6-8 weeks, but it can take up to original shape in 6-8 weeks, but it can take up to nine months for the uterus to fully recover. nine months for the uterus to fully recover.
1. Cervix1. Cervix
• The neck or opening of the uterus. The neck or opening of the uterus. • A normal healthy cervix is the strongest muscle in A normal healthy cervix is the strongest muscle in
the body. the body. • It dips down about half an inch into the vagina. It dips down about half an inch into the vagina. • It is normally plugged by mucus. It stays tightly It is normally plugged by mucus. It stays tightly
closed during pregnancy, but thins and opens for the closed during pregnancy, but thins and opens for the delivery of the baby.delivery of the baby.
• How big does it need to dilate to for birth? How big does it need to dilate to for birth?
15. Vagina15. Vagina• Female organ used for intercourse, it is an Female organ used for intercourse, it is an
empty passageway leading from the vaginal empty passageway leading from the vaginal opening to the uterus. opening to the uterus.
• It is only 3-4 inches long, but will lengthen It is only 3-4 inches long, but will lengthen during arousal. during arousal.
• The vaginal walls are made of many small The vaginal walls are made of many small folds of membrane that stretch greatly to folds of membrane that stretch greatly to accommodate a baby during birth. accommodate a baby during birth.
• The vaginal wall also secrete a fluid that helps The vaginal wall also secrete a fluid that helps to make intercourse easier. to make intercourse easier.
2. Clitoris2. Clitoris
• A small, pea shaped bump at the front of the A small, pea shaped bump at the front of the labia. labia.
• It contains a small amount of erectile tissue. It contains a small amount of erectile tissue. • The clitoris increases sexual pleasure The clitoris increases sexual pleasure
3. ENDOMETRIUM
• The lining of the uterus.• During menstruation, it is what sloughs off.• During pregnancy it thickens and provide the
place of implantation for the fertilized ova.
6. Menstrual Cycle and 7. 6. Menstrual Cycle and 7.
• Day 1 – Day 1 – MenstruationMenstruation begins (bleeding) begins (bleeding)• Day 1-5 – Bleeding Continues Day 1-5 – Bleeding Continues • Day 6-9 - Ovum is maturing and endometrium lining is thinDay 6-9 - Ovum is maturing and endometrium lining is thin• Day 10 – 14 - Endometrium lining thickens and hormones Day 10 – 14 - Endometrium lining thickens and hormones
rise. rise. – Around Day 14 – Ovum bursts out of the ovary Around Day 14 – Ovum bursts out of the ovary
• Day 15 – After 24 hours the egg is doneDay 15 – After 24 hours the egg is done
• Day 15-28 – Egg travels down to thickened lining and either Day 15-28 – Egg travels down to thickened lining and either is implanted or it dissolvesis implanted or it dissolves– Day 26 – In the absence of fertilization, hormone levels drop and Day 26 – In the absence of fertilization, hormone levels drop and
the endometrium lining breaks down the endometrium lining breaks down – Day 28 – Menstruation prepares to begin again. Day 28 – Menstruation prepares to begin again.
FEMALE TIME LINE:FEMALE TIME LINE:• Ages 9-12 Ages 9-12
– Secondary sex characteristics appearSecondary sex characteristics appear
• Ages 11-14Ages 11-14– Menstrual cycle beginsMenstrual cycle begins
• Late 20-30'sLate 20-30's– Peak sexual urgesPeak sexual urges
• Ages 45-55Ages 45-55– Menopause (cycle stops, but sex urge continues)Menopause (cycle stops, but sex urge continues)
5. FERTILIZATION / Conception
• The end purpose for the ova and the sperm• When the sperm penetrates the surface of the
ova and enters inside.• The 23 chromosomes from each sex cell
combine and begin to multiply to begin to form a new human being!!!
Male Reproductive SystemMale Reproductive System
Male reproductive organs are for intercourse, Male reproductive organs are for intercourse, reproduction and urinationreproduction and urination
Male vs. Female?
MALE TIME LINE:• Infancy
– Erections begin• Ages 11-14
– Secondary sex characteristics appear• Ages 13-16
– Sperm produced in adult amounts (puberty)• Late teens
– Peak sexual urges for boys• Throughout life
– If good health is present, there is the sex urge and ability to father children
6. Scrotum 6. Scrotum
• A sac-like pouch located behind the penis that A sac-like pouch located behind the penis that holds each testes and helps regulate holds each testes and helps regulate temperature for sperm production.temperature for sperm production.
10. Testicles or Testes10. Testicles or Testes• The two testes are small organs that lie in the scrotum and The two testes are small organs that lie in the scrotum and
produce sperm and the male hormone testosterone. produce sperm and the male hormone testosterone. • The testicles are the male sex gland. The testicles are the male sex gland. • The testicles are outside the body because the male sperm The testicles are outside the body because the male sperm
that is manufactured in the testes need cooler-than-body that is manufactured in the testes need cooler-than-body temperature for normal growth and development. temperature for normal growth and development.
• They are the counterpart to the female ovary. They are the counterpart to the female ovary. • Loss of one does not impair the function of the other.Loss of one does not impair the function of the other.• Four to five billion sperm cells are produced each month. Four to five billion sperm cells are produced each month.
11. Testosterone11. Testosterone
• The male reproductive hormone made by the The male reproductive hormone made by the testicles which causes the changes of puberty. testicles which causes the changes of puberty.
• This hormone causes secondary sex This hormone causes secondary sex characteristics, production of sperm and characteristics, production of sperm and sexual urge. sexual urge.
• It is produced in the testicles and enters the It is produced in the testicles and enters the bloodstream at a fairly constant rate. bloodstream at a fairly constant rate.
9. Sperm 9. Sperm • The microscopic cells produced by the male's The microscopic cells produced by the male's
testicles which can fertilize the female's testicles which can fertilize the female's ovumovum. .
• They are tiny, living cells 100 times smaller They are tiny, living cells 100 times smaller than a pencil dot. (the smallest cell in a mans than a pencil dot. (the smallest cell in a mans body body
• Enough sperm would fit on the head of a pin Enough sperm would fit on the head of a pin to re-populate the earth if each sperm to re-populate the earth if each sperm fertilized an egg. fertilized an egg.
• It is destroyed by warm body temperature, It is destroyed by warm body temperature, acidic environment. acidic environment.
• It can survive in a women’s body for 5-8 days. It can survive in a women’s body for 5-8 days. • Any sperm not ejaculated are passed in the Any sperm not ejaculated are passed in the
urine.urine.
3. Epididymis3. Epididymis
• The structure that forms a mass over the back The structure that forms a mass over the back and upper part of each testes.and upper part of each testes.
• Sperm are stored there for as long as six Sperm are stored there for as long as six weeks while they ripen to maturity. weeks while they ripen to maturity.
1. Cowpers Gland1. Cowpers Gland
• Two small pea-sized glands located beneath Two small pea-sized glands located beneath the prostate gland on both sides of the base the prostate gland on both sides of the base of the penis. of the penis.
• They secrete a clear, sticky fluid that helps to They secrete a clear, sticky fluid that helps to neutralize the acidity of the urethra.neutralize the acidity of the urethra.
12. Vas Deferens12. Vas Deferens
• two long, thin tubes that serve as a two long, thin tubes that serve as a passageway for sperm and a place for sperm passageway for sperm and a place for sperm storage. storage.
• The contraction of the vas deferens along with The contraction of the vas deferens along with the action of the cilia help transport the the action of the cilia help transport the sperm through the vas deferens.sperm through the vas deferens.
8. Seminal Vesicles 8. Seminal Vesicles
• two small glands that secrete a fluid that two small glands that secrete a fluid that nourishes and enables the sperm to move.nourishes and enables the sperm to move.
5. Prostate Gland 5. Prostate Gland
• surround the urethra beneath the bladder. surround the urethra beneath the bladder. The gland secretes an alkaline fluid that The gland secretes an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acid found in the male urethra neutralizes the acid found in the male urethra and the female reproductive tract. and the female reproductive tract.
• Without the action of the secretions of the Without the action of the secretions of the prostate gland, many sperm would die and prostate gland, many sperm would die and fertilization of an ovum would be impossible.fertilization of an ovum would be impossible.
13. Urethra13. Urethra• A dual purpose tube that both semen and urine pass A dual purpose tube that both semen and urine pass
through to leave the body. Semen and urine never through to leave the body. Semen and urine never mix. mix.
• Special muscles or sphincters surround the urethra. Special muscles or sphincters surround the urethra. • During urination, one sphincter will relax so that the During urination, one sphincter will relax so that the
pressure from the bladder will push urine out from pressure from the bladder will push urine out from the body. the body.
• During ejaculation, another sphincter will relax so During ejaculation, another sphincter will relax so that semen can flow through the urethra to the that semen can flow through the urethra to the outside of the body.outside of the body.
4. Penis4. Penis• The male organ for sexual intercourse, The male organ for sexual intercourse,
reproduction, and urination. reproduction, and urination. • The reproductive purpose of the penis is to deposit The reproductive purpose of the penis is to deposit
semen in the vagina during sexual intercourse. semen in the vagina during sexual intercourse. • The head of the penis or glans contains many nerve The head of the penis or glans contains many nerve
endings. At birth the glans is covered by a loosely endings. At birth the glans is covered by a loosely fitting skin called the foreskin. fitting skin called the foreskin.
• When the penis is erect it is 5-7 inches long An When the penis is erect it is 5-7 inches long An erection occurs when the sponge-like chambers in erection occurs when the sponge-like chambers in the penis fill with blood. the penis fill with blood.
7. SEMEN:7. SEMEN:
• a combination of fluid that is produced in the a combination of fluid that is produced in the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper's seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper's gland. This fluid nourishes and helps sperm gland. This fluid nourishes and helps sperm move through the urethra.move through the urethra.
2. EJACULATION2. EJACULATION
• the passage of sperm from the penis, a result the passage of sperm from the penis, a result of a series of muscular contractions.of a series of muscular contractions.
Birth Defect An abnormality of structure, function, or body metabolism which often results in a physical or mental handicap, a
shorter life span, or is fatal
• About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects. • The parents of one out of every 28 babies receive the frightening news
that their baby has a birth defect• There are over 4,000 known birth defects• Birth defects are the leading cause of death in the first year of life
What causes birth defects?• Both genetic and environmental factors can cause birth defect. However,
the causes of about 60% of birth defects are currently unknown.• A single abnormal gene can cause birth defects. Every human being has
about 100,000 genes that determine traits like eye color, hair, etc.
Lifestyle and EnvironmentMOM
• Lifestyle – STD’s substance abuse, alcohol, habits
• Age• # of kids
– spacing from prior pregnancy
• health / exercise / attitude– weight – Stress level
• Nutrition / Diet – caffeine– Folic Acid
• Medical History– immunizations and records
• Missing pregnancy check-ups (13 total)• Radiation• Toxins and pollution• Genetics
DAD• Nutrition / Diet
– Caffeine• Lifestyle
– STD’s substance abuse, alcohol, habits
• Health / exercise / attitude– weight – Stress level
• medical history• Radiation• genetics
Can birth defects be prevented?• While the causes of most birth defects are not known, there
are a number of steps a woman can take to reduce her risk of having a baby with a birth defect.– Visit a health care provider for a pre-pregnancy check up. Especially if
a woman has health problems– When pregnant take daily multivitamin containing 400 mg of the B-
vitamin folic Acid– Avoid alcohol, drugs, smoking, prescription or over-the-counter
medication with out checking with her health care provider.
• Genetic counseling is a form of medical care that helps couples to understand their genetic codes and how they might affect their children.
Can some birth defects be diagnosed before birth?
• Ultrasound– A technique that uses sound waves to show a picture of a baby (fetus)
in the womb.
• Amniocentesis – A small sample of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is removed and
examined to detect certain birth defects ( Rh disease, and strength of the lungs of the fetus)
• Chronic villus sampling– A prenatal test that takes a tiny tissue sample from outside the sac
where the fetus develops.
• Placenta Conditions
Results• Miscarriage – occurs prior to 20 weeks of pregnancy
– Most miscarriages occur when pregnancy is not developing normally. Natures way of expelling a baby incapable of surviving.
– 1st trimester- chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, hormonal problems, infections, and health problems of the mother.
– 2nd trimester – often caused by uterus problems. Misshaped uterus, weakened cervix that dilates prematurely, chromosomal abnormalities, immune system problems,
• Stillbirth – after 20 weeks of pregnancy– When the fetus appears to be developmentally normal, but for some
reason is born dead.– Most common causes: Placenta problems, Birth defects, Growth
restrictions, Infections• Baby will live and you will enjoy and adjust
Newborn Screening Tests• Before leaving the hospital certain newborn tests are giving to
eliminate certain birth defects
• Neonatal Death• In 1996 about 19,000 babies died in the first month of life• Most common causes• The baby was born with a birth defect – 25% of neonatal deaths• Heart defects – 1/3• Chromosomal abnormalities• Brain and central nervous system• Premature birth – 20% of neonatal deaths• Respiratory distress syndrome – immature lungs• Bleeding in the brain