Http:// The Nervous System.
-
date post
19-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Http:// The Nervous System.
The Nervous System
- General organization
- The basic units- the cells
- Neurophysiology
- Neural interactions
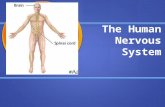
Brain, Spinal cord, Neuronal pathways, Special senses
Peripheral Nervous system
Central Nervous system
sensory motor
AutonomicSmooth and cardiac
muscles; Glands
Somatic
Skeletal muscles
Motor (Efferent)Sensory (Afferent)
Somatic (skin, skeletal muscle and joints)
Visceral (internal organs)
“As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose fluttering wings would someday—who knows?—enlighten the secret of mental life”
Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934)
Neurons“The Mysterious Butterflies of the Soul”
Neurons“The Mysterious Butterflies of the Soul”
Santiago Ramón y Cajal
Nobel prize in physiology and medicine 1906
• Whitish, fatty (protein-lipoid), segmented sheath around most long (NOT ALL) axons
• It functions to:- Protect the axon- Electrically insulate fibers from one another- Increase the speed of nerve impulse transmission
Myelin sheath
• Formed by Schwann cells in the PNS
• A Schwann cell:- Envelopes an axon in a trough- Has concentric layers of membrane that make up the myelin sheath
Myelin sheath
Axons are bundled together to form fascicles
CNS: axon bundles form tracts PNS: axon bundles form nerves
Astrocytes
- Support and brace neurons- Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies- Guide migration of young neurons- Control the chemical environment
MicrogliaThe “Immune System” of the CNS
- Small, ovoid cells with spiny processes- Turn into phagocytes upon inflammation
(monitor the health of neurons, in the absence of macrophages, due to the BBB)
Ependymal cells
- Ciliated epithelial cells lining the central cavities of the brain and spinal column
- Forming a permeable barrier between the CSF and nervous tissue
- Beating cilia helps circulating the CSF
CSF(cerebrospinal fluid)
Banizs et al. Development (2005)
What could happen in B?
B A
-Beating cilia helps circulating the CSF
Oligodendrocytes
- Insulators of the thick neurons of the CNS
- A single oligodendrocyte can form myelin sheaths around several axons
The supporting neuroglia in the PNS
- Schwann cellssurround and insulate axons (the “oligodendrocytes” of the PNS)- Satellite cellsSupport an nourish cell bodies (“astrocytes”
of the PNS)
Summary
Peripheral Nervous system
Central Nervous system
sensory motor
Autonomic
Smooth and cardiac muscles; Glands
Somatic
Skeletal muscles
Motor (Efferent)Sensory (Afferent)
Somatic (skin, skeletal muscle and joints)
Visceral (internal organs)
Neurophysiology
Opposite electrical charges attract each other
In case negative and positive charges are separated from each other, their coming together liberates energy
Thus, separated opposing electrical charges carry a potential energy
-- - - - ---
+ +++ +++
inside
outside
• Voltage (V)measure of differences in electrical potential energy
generated by separated charges• Current (I)the flow of electrical charge between two points• Resistance (R) hindrance to charge flow
Neurophysiology
-- - - - ---
+ +++ +++
inside
outside
--- - ----
+ ++
+ +++
inside
outside+++
-Current: ions
Resistance: membrane permeability
Voltage: potential across the membrane