HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
Transcript of HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
1/21
Lecture 2
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
2/21
OVERVIEW
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
3/21
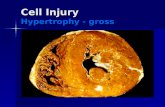
Cell Injury: an alteration in cellstructure or functioning that occurs whencells are . . .
severely stressed that they are nolonger able to adapt
exposed to inherently damaging agents
suffer from intrinsic abnormalities
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
4/21
General Principles of Cell Injury
The cellular response to injuriousstimuli depends on:
_______________________________.
The consequences of cell injury depend
on:_______________________________.
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
5/21
Causes of Cell Injury
Hypoxia
Physical Agents
Chemicals and DrugsMicrobiologic Agents
Immunologic Reactions
Genetic Defects
Nutritional Imbalances
Aging
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
6/21
PREDISPOSING FACTORS:
AgeGender
Nutritional status
GenesEnvironment
Pre-existing conditions
Immune-compromised
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
7/21
Morphologic Alterationsin Cell Injury
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
8/21
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
9/21
Reversible Cell Injury:1. Generalized swelling of the cell and its
organelles
2. Blebbing of the plasma membrane3. Detachment of ribosomes from ER
4. Clumping of nuclear chromatin
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
10/21
Irreversible Cell Injury:1. Increase swelling of cell
2. Swelling and disruption of lysosomes
3. Presence of large amorphous densities inswollen mitochondria
4. Profound nuclear changes:
-Pyknosis
-Karyorrhexis
-Karyolysis
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
11/21
NUCLEAR CHANGES
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
12/21
APOPTOSIS
Limits neoplasmic growth
does NOT stimulate inflammatoryresponse
Apoptotic stimuli:
1. Cell membrane damage
2. Mitochondrial damage
3. DNA damage
4. Viral infection
5. Immune-mediated attack
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
13/21
Feature Necrosis ApoptosisCell size Enlarged (swelling) Reduced (shrinkage)
Nucleus Pyknosis
karyorrhexiskaryolysis
Fragmentation into
nucleosome-size fragments
Plasmamembrane
Disrupted Intact; altered structure,especially orientation of
lipids
Cellularcontents
Enzymaticdigestion; may leakout of cell
Intact; may be released inapoptotic bodies
Adjacentinflammation
Frequent No
Physiologic orpathologic role
Invariablypathologic(irreversible)
Often physiologic, eliminatesunwanted cells; may bepathologic after DNA
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
14/21
TYPES OF NECROSIS: According to. . .
BASIC MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES :
Coagulation Necrosis
Liquefaction Necrosis
Fat NecrosisCaseous Necrosis
Gangrenous Necrosis
ACCORDING TO LOCATION OR EXTENT:
Focal
Massive
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
15/21
rapid coagulation of cytoplasm
Denaturation and precipitation of
cellular proteins
usually encountered when arterial
supply is cut off, producing Anemic orIschemic Infarction.
COAGULATIONNECROSIS
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
16/21
Enzymatic digestion of the cell by its own
hydrolytic lysosomal enzymes
Necrosis of tissues rich in liquid usually
induces them to absorb fluid, leading tosoftening & liquefaction
LIQUEFACTION NECROSIS
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
17/21
destruction of adipose tissue
Pancreatic lipase is released intosurrounding tissues splitting neutral fats intofatty acids & glycerol, w/o affecting cellmembrane.
FA combine w/ Ca to form soaps w/c are
replaced by phosphoric acid & carbonicacids, forming white precipitates of CaPO4& CaCO3.
FAT NECROSIS
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
18/21
CASEOUS NECROSIS
characterized by a collection of soft,whitish-gray debris resembling clumpedcheese
cells are converted into a granular,friable mass of coagulated CHON & fat,with total loss of cell detail.
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
19/21
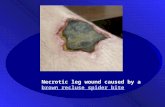
GANGRENOUSNECROSIS
massive tissue death due to ischemia &superimposed bacterial infection.
combination of coagulation &liquefaction necrosis.
2 TYPES:
A. DRY GANGRENEB. WET GANGRENE
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
20/21
DRY GANGRENE
Sterile necrosis Due to arterial occlusion, producing
ischemic necrosis & consequentdesiccation/ mummification.
sharp demarcation line
tissue discoloration is due to release
of blood pigments
-
7/31/2019 HPlec 2 Cell Injury-necrosis
21/21
WET GANGRENE
venous occlusion
Bactl. infxn. + ischemic injury= putrefaction.
Offensive, foul-odored fluid
liquefaction necrosis & toxemia
no sharp line of demarcation