How Plants Are Classified Part 2: Reproduction 6-2.3: Compare the characteristic structures of...
-
Upload
william-wilbanks -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of How Plants Are Classified Part 2: Reproduction 6-2.3: Compare the characteristic structures of...

How Plants Are Classified Part 2: Reproduction
6-2.3: Compare the characteristic structures of various groups of plants (including vascular or
nonvascular, seed or spore-producing, flowering or cone-bearing, and monocot or dicot).

Link• Five fast things you know about seeds

Essential Question
What are the main ways scientists classify plants?
You already know they are classified as vascular and non-vascular.
The following classification can also be used to group plants.
?

Seed Producing Plants• Seed-producing plants are plants that
reproduce through seeds. Seed plants make their own seeds.
• Seeds contain the plant embryo (the beginnings of roots, stems, and leaves) and stored food (cotyledons) and are surrounded by a seed coat. From those seeds, new plants grow.

Seed Producing Plants
• There are two major groups of seed-producing plants: cone-bearing plants (gymnosperm) and flowering plants (angiosperm).

Seed ProducersThe Cone-Bearing Plants
• Most cone-bearing plants are evergreen with needle-like leaves.
• Conifers never have flowers but produce seeds in cones. These seeds are said to be “naked”.
• Examples include pine, spruce, juniper, redwood, and cedar trees.

Seed Producers: The Flowering Plants
• Flowering plants differ from conifers because they grow their seeds inside an ovary, which is embedded in a flower.
• The flower then becomes a fruit containing the seeds.

Flowering Plants: Cont.
• Examples include most trees, shrubs, vines, flowers, fruits, vegetables, and legumes (beans).

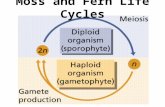
The Non-Seed Producers: Spore Producing Plants
• Spore-producing plants are plants that produce spores for reproduction instead of seeds.
• Spores are much smaller than seeds. • Almost all flowerless plants produce spores. • Examples include mosses and ferns.

Give 3 qualitative observations about fern spores?
See Fern Spores Video

Give 3 qualitative observations about moss spores?
See Moss Spores Video

Classify each picture as a seed producer or spore producer
1. 2. 3.
4. 5.

SummarizeFollow the teacher to create a diagram
comparing seed-producers to spore-producers.
Seed Producers Spore Producers

Answer EQ
• Define key terms.1. Seed2. Spore3. Conifer