Hormones and the Endocrine System
description
Transcript of Hormones and the Endocrine System

Hormones and the Endocrine System
Chapter 40

I. Hormones • chemical messengers inside a body
o relay a message from one part of body to anotherII. Endocrine System
• all cells, tissues, and organs involved in producing hormones III. Categories of Hormones
A. pheromones• act between two organisms, usually same species
B. endocrine hormones1. act within an organism, some distance away from where
produced2. endocrine glands vs. exocrine glands
C. paracrine hormones• act within an org., in cells adjacent to where they are
producedD. autocrine hormones• act within an org., in the same cells in which they are
produced

Three different categories of hormones

IV. Basic Facts About HormonesA. hormonal activity/control is much slower than neural
activity/controlB. transported in circulatory or lymphatic systemC. chemical nature of hormones
1. proteins • peptide hormones
2. lipidsa. sterols (4-ring structure) b. prostaglandins (linear)
D. hormones work in a very specific manner1. attach to receptor sites on their target cells • attachment is in a lock-and-key fashion
2. only affect their target cells• most cause powerful and important effects

Fig. 40.3 Target cell concept

E. rate of secretion determines short-term vs. long-term effects
1. quick bursts short-term effects2. slow, steady secretion long-term effects
F. hormone release • prompted by physical, chemical, and environmental cues
G. control of hormone secretion1. negative feedback 2. releasing and inhibiting hormones• releasing hormones often cause release of stimulating
hormoneso stimulate a target gland to release one or more of its
hormones3. other hormones with opposite effects• antagonistic hormones

Page 740 Some elements of hormone control

V. Hormones and the Target Cell
A. peptide hormones1. most interact with membrane
receptors on target cell• hormone on receptor (1st
messenger) activates 2nd messenger
o cAMP, cGMP2. 2nd messenger relays
message to nucleus by triggering an enzyme cascade
• series of reactions, each using its own enzyme
3. enzyme cascade releases an end-product causes an effect or response
Fig. 40.4 Peptide hormones

B. lipid hormones1. no 2nd messengers or
enzymes 2. directly effect gene action3. hormone diffuses through
membrane moves into nucleus joins with receptor proteins activates a gene gene synthesizes a protein protein carries out response
VI. Invertebrate HormonesA. source is often nervous systemB. involved in many aspects of life
1. molting• periodic shedding of
exoskeleton2. metamorphosis • egg larva pupa adult
Fig. 40.5 Lipid hormones

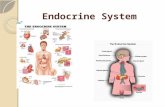
Fig. 40.2 An overview of the human endocrine system

VII. Human Endocrine SystemA. pituitary gland (hypophysis)
1. anterior pituitary• releases 7 different hormones o incl., gonadotropins
hormones that affect the gonads2. posterior pituitary
a. releases two categories of hormonesb. more directly controlled by nervous system
than ant.3. both halves controlled by hypothalamus
a. “hormone control center”b. releasing and inhibiting hormones

Fig. 40.6 Hypothalamus and the pituitary gland

B. thyroid gland and parathyroid gland1. parathyroid embedded within thyroid2. regulation of metabolism and Ca3. hyperthyroidism vs. hypothyroidism vs.
goiterC. pancreas
1. insulin vs. glucagona. great example of antagonistic
hormonesb. both affect blood glucose levels• insulin lowers; glucagon raises
2. diabetes mellitus
Fig. 40.10 Regulation of blood calcium level

Fig. 40.15 Regulation of blood glucose level

D.adrenal glands1. located on top of each kidney2. usually release hormones in response to
stress3. adrenal cortex• releases corticosteroidso long-term responses to stress
4. adrenal medulla• epinephrine (adrenalin) and
norepinephrineo short-term responses to stress

Fig. 40.11 Adrenal glands

E. ovaries• estrogen and progesterone
F. testes• testosterone
G. thymus gland• hormones involved in immune response
H. pineal gland1. located deep inside brain2. melatonin• helps regulate daily rhythms of sleep and
wakefulnesso circadian rhythms
3. some influence over hypothalamus and pituitary glands
I. prostaglandins1. lipid hormones of nonspecific origin2. aid in birth process, blood clotting, and
inflammation

Fig. 40.2 An overview of the human endocrine system