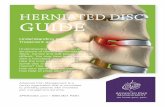
Herniated cervical disc
-
Upload
isnawan-widyayanto -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
553 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Herniated cervical disc

Herniated Cervical Disc
Lecturer :
Prof.dr.MI Widiastuti,PAK ,Sp.S (K),MScNeurology Dept Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro University
Isnawan Widyayanto

DefinitionIs a spine condition of the cervical segment that occurs when the gel-like center of a disc (nucleus pulposus) ruptures through a weak area in the tough outer wall (annulus fibrosus).

Anatomy
Spine is made of 24 movable bone called vertebrae.
The cervical (neck) section of the spine support the weight of the head and allows head to bend forward and backward, from side to side, and rotate 180 degreesThere are 7 cervical vertebrae numbered C1-C7


Vertebra
The vertebral body is a thin ring of dense boneConsisting of the body, pedicles and laminaeVertebral foramen is a whole in vertebral body that spinal cord runs through

Intervertebral Disc
Gel like Tissue between each vertebrafibro cartilaginous cushionsserve as the spine's shock absorbing systemprotect the vertebrae, brain, and other structuresThe discs allow some vertebral motion extension and flexion.

The disc is made up of 3 structures the (1) Nucleus pulposus, gelatinous center(2) Annulus Fibrosus. Its job is to contain the nucleus(3) Vertebral end plates that attach the disc to the vertebrae

Ligamentum
Weak point

Pathophysiology
•Herniated disc can occur when there is enough pressure from the vertebrae above and below•This can force some or all of the nucleus pulposus through a weakened or torn part of the annulus fibrosus.


The four stages to a herniated disc

Disc Degeneration: chemical changes associated with aging causes discs to weaken, but without a herniation.
1

The form or position of the disc changes with some slight impingement into the spinal canal. Also called a bulge or protrusion.
2

The gel-like nucleus pulposus breaks through the tire-like wall (annulus fibrosus) but remains within the disc.
3

The nucleus pulposus breaks through the annulus fibrosus and lies outside the disc in the spinal canal (HNP).
4

Cause Injury Improper lifting Aging Spontaneous

SymptomsSymptoms of a herniated disc can vary
depending on the location of the herniation and the types of soft tissue that become involved.
They can range from little or no pain if the disc is the only tissue injured, to severe and unrelenting neck that will radiate into the regions served by affected nerve roots that are irritated or impinged by the herniated material

•The two most common levels in the cervical spine to herniate are the C5 - C6 level (cervical 5 and cervical 6) and the C6 -C7 level. The next most common is the C4 - C5 level, and rarely the C7 - T1 level may herniate.
•Rarely, the herniated disc may put pressure on the spinal cord,causing problems in the leg.

Include dull or sharp pain in the neck or between the shoulder, pain that radiates down the arm to the hand or fingers, or numbness or tingling in the shoulder or arm. Certain positions or movements of the neck can intensify the pain.
Weakness in the arm muscles may accompany the dull pain in some cases

Most frequent segment C4 - C5 (C5 nerve root) - Can cause weakness in the deltoid
muscle in the upper arm. Does not usually cause numbness or tingling. Can cause shoulder pain.
C5 - C6 (C6 nerve root) - Can cause weakness in the biceps (muscles in the front of the upper arms) and wrist extensor muscles. Numbness and tingling along with pain can radiate to the thumb side of the hand. This is one of the most common levels for a cervical disc herniation to occur.
C6 - C7 (C7 nerve root) - Can cause weakness in the triceps (muscles in the back of the upper arm and extending to the forearm) and the finger extensor muscles. Numbness and tingling along with pain can radiate down the triceps and into the middle finger. This is also one of the most common levels for a cervical disc herniation
C7 - T1 (C8 nerve root) - Can cause weakness with handgrip. Numbness and tingling and pain can radiate down the arm to the little finger side of hand.

Rare C4 - C5 (C5 nerve root) - Can cause weakness in the
deltoid muscle in the upper arm. Does not usually cause numbness or tingling. Can cause shoulder pain.
C5 - C6 (C6 nerve root) - Can cause weakness in the biceps (muscles in the front of the upper arms) and wrist extensor muscles. Numbness and tingling along with pain can radiate to the thumb side of the hand. This is one of the most common levels for a cervical disc herniation to occur.
C6 - C7 (C7 nerve root) - Can cause weakness in the triceps (muscles in the back of the upper arm and extending to the forearm) and the finger extensor muscles. Numbness and tingling along with pain can radiate down the triceps and into the middle finger. This is also one of the most common levels for a cervical disc herniation
C7 - T1 (C8 nerve root) - Can cause weakness with handgrip. Numbness and tingling and pain can radiate down the arm to the little finger side of hand.

X-ray CT Scan MRI Electromyography (EMG) &Nerve
Conduction Velocity (NCV)
Investigation

Plain cervical spine radiographs evaluate chronic degenerative changes, metastatic disease,infection, spinal deformity, and stability. But can’t show herniation.
X-ray

CT-Scan
CT scan delineates cervical spine fracture and is used extensively in trauma cases.
Occasionally a CT scan with a myelogram may also be ordered, as it is more sensitive and can diagnose even subtle cases of nerve root pinching.

MRI
The single best test to diagnose a herniated disc is aMRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan.
A MRI scan can image any nerve root pinching caused by a herniated cervical disk.

EMG and NCVAn EMG is an electrical test that is done by
stimulating specific nerves and inserting needles into various muscles in the arms or legs that may be affected from a pinched nerve. If the muscles have lost their normal innervation, there will be spontaneous electrical activity.
These test can detect nerve damage and muscle weakness

Differential Diagnosis
Brachial Neuritis Cervikal Myofascial
Pain Cervikal Spondylosis Cervikal Sprain and
Strain Complex Regional Pain
Syndromes Fibromyalgia Neoplastic Brachial
Plexopathy Osteoarthritis Osteoporosis (Primary
and Secondary) Paget Disease Psoriatic Arthritis Radiation-Induced
Brachial Plexopathy Rheumatoid Arthritis Rotator Cuff Disease Scheuermann Disease Thoracic Outlet
Syndrome Traumatic Brachial
Plexopathy

Treatment
Nonsurgical- Self care : Rest and restrict activity- Medication- Physical theraphy and exercise- Bracing- Cervical traction
Surgical

Nonsurgical treatmentConservative non surgical treatment is the first step to recovery. Most cases of cervical pain do not require surgery and are treated using non-surgical methods.
In most case, the pain from herniated disc will get better within a couple days and completely resolve in 4 to 6 weeks.

MedicationNSAID, such as aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, etc
used to reduce inflammatory and relieve pain.Analgesic, such as Acetaminophen can relieve
pain but don’t have the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs.
Muscle relaxant such as methocarbamol may be presribed to control muscle spasm.
Steroid may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation of the nerves. Taken orally in tapering dosage over a-five day period
Steroid injection into the area of your herniated disc may performed if the pain is severe.

NSAID, such as aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, etc used to reduce inflammatory and relieve pain.
Analgesic, such as Acetaminophen can relieve pain but don’t have the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs.
Muscle relaxant such as methocarbamol may be presribed to control muscle spasm.
Steroid may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation of the nerves. Taken orally in tapering dosage over a-five day period
Steroid injection into the area of your herniated disc may performed if the pain is severe.

NSAID, such as aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, etc used to reduce inflammatory and relieve pain.
Analgesic, such as Acetaminophen can relieve pain but don’t have the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs.
Muscle relaxant such as methocarbamol may be presribed to control muscle spasm.
Steroid may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation of the nerves. Taken orally in tapering dosage over a-five day period
Steroid injection into the area of your herniated disc may performed if the pain is severe.

NSAID, such as aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, etc used to reduce inflammatory and relieve pain.
Analgesic, such as Acetaminophen can relieve pain but don’t have the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs.
Muscle relaxant such as methocarbamol may be presribed to control muscle spasm.
Steroid may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation of the nerves. Taken orally in tapering dosage over a-five day period
Steroid injection into the area of your herniated disc may performed if the pain is severe.

NSAID, such as aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, etc used to reduce inflammatory and relieve pain.
Analgesic, such as Acetaminophen can relieve pain but don’t have the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs.
Muscle relaxant such as methocarbamol may be presribed to control muscle spasm.
Steroid may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation of the nerves. Taken orally in tapering dosage over a-five day period
Steroid injection into the area of your herniated disc may performed if the pain is severe.

Physical therapy & Exercise Mckenzie exercises can be used to help
reduce the pain in the arm.
In the initial period a physical therapist may also opt to use modalities, such as heat/ice or ultrasound, to help reduce muscle spasm.

Bracing and Cervical traction
A cervical collar or brace may be recommended tohelp provide some rest for the cervical spine.

Surgical
For patient whose pain doesn’t improve with the nonsurgical treatment, surgery may be necessary.
The goal of surgery is to remove the portion of disc that is pushing on the nerve.
Surgical procedure to remove the disc called Discectomy

Surgery technique
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF)
Artificial disc replacementMinimally invasive microendoscopic
discectomyPosterior Cervical Discectomy

Discectomy

Thank You