HEREDITY CHAPTER 4. You have Characteristics or traits. Acquired Traits —Reading Skills Inherited...
-
Upload
augusta-fields -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
2
Transcript of HEREDITY CHAPTER 4. You have Characteristics or traits. Acquired Traits —Reading Skills Inherited...
- Slide 1
- HEREDITY CHAPTER 4
- Slide 2
- You have Characteristics or traits. Acquired Traits Reading Skills Inherited Traits eye color
- Slide 3
- In sexual reproduction, offspring produced, are NOT identical to their parents. Each parent contributes a cell that contains genetic information
- Slide 4
- Heredity is the passing of gene from parent to offspring. Most traits are not coded for by just one gene
- Slide 5
- Different forms of the same gene are called Alleles
- Slide 6
- There are 46 chromosomes in humans-23 Pairs X and Y are the sex chromosomes 1 X and 1 Y=Males 2X = females
- Slide 7
- Gregory Mendel is the man. He made important discoveries about heredity. He was monk and studies each trait on a pea plant separately. First Generation Second Generation
- Slide 8
- Alleles interact to produce traits Phenotype is what we see Dominate Recessive
- Slide 9
- Genotype is alleles an organism has. You might see them, you might not.
- Slide 10
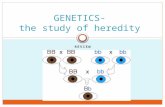
- PUNNETT SQUARES Patterns in Heredity can be predicated. Each parent has 2 alleles for a particular gene So Punnett Squares show one way alleles combine to make offspring
- Slide 11
- In the Punnett Square, each offspring would express the phenotype of dominate alleles.
- Slide 12
- Percentages and fractions can express the probability of an outcome. Probability is the likelihood of a specific outcome
- Slide 13
- The purpose of the Punnett Square is to show the probability of each combination of alleles for one offspring A Punnett square only indicates the probability of different outcomes.not specific ones!
- Slide 14
- There are two steps necessary for sexual reproduction: Meiosis I Meiosis II
- Slide 15
- Two cells combine for sexual reproduction: N N 2N OFFSPRING / Zygote / Diploid Gamete / Haploid Gamete / Haploid
- Slide 16
- Gametes are found in reproductive organs of plant and animals cells. Fertilization is the process that takes place when a sperm and egg combine.
- Slide 17
- DNA AND RNA DNA provides information to the cell to make proteins Remember Proteins: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Amino Acids
- Slide 18
- MOLECULES PROTEIN Molecules Some amino acids are small 129 Amino Acids Some amino acids are large 3685 Amino Acids DNA and RNA are made up of Nucleic Acids Molecules There are FOUR different types of nucleotides Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine
- Slide 19
- DNA Remember in Mitosis In Interphase the DNA replicates During replication each strand of DNA is used as a template to produce a copy of the other strand
- Slide 20
- RNA RNA uses DNAs sequences of bases to link amino acids (Protein Molecule) into chains that form proteins. RNA like DNA is made up of Nucleotides (Nucleic Acid Molecule )
- Slide 21
- 3 TYPES OF RNA tRNA: transfer RNA- it picks up Amino Acids and transfers them to where the chain begins mRNA: messenger RNA- forms a copy of DNA translates rRNA: ribosomal RNA- brings together the two other types of RNA to form a chain of Proteins ( amino acids)
- Slide 22
- RNA BASE PAIRS Cytosine Guanine Adenine Uracil
- Slide 23
- DNA Transcription (writing copying) mRNA RNA Translation tRNA Protein
- Slide 24
- PROJECT: DNA
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- ATOMS THAT MAKE UP DNA Hydrogen Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorus