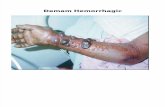
Hereditary hemorrhagic disorders. Taking histrory Is an essential part of the diagnostic process for...
-
Upload
roland-booth -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Hereditary hemorrhagic disorders. Taking histrory Is an essential part of the diagnostic process for...

Hereditary hemorrhagic disorders

Taking histrory
• Is an essential part of the diagnostic process for detecting disorders of bleeding. It is crucial in determining who should be given laboratory tests and is of importance for the determination of the extent of testing to be used if the screening tests are negative.
• A good history also allows the physician to classify the patients in to various groups

Taking history
• Spontaneous loss of blood (nose bleeds, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, vaginal loss, hematuria, rectal loss of blood/melanea, hemoptysis)
• Bleeding into tissue (bruises, small skin haemorrhages, muscle bleeding, deep hematomas, bleeding into joints)
• Reaction to trauma (tooth extraction, tonsillectomy, puerperal bleeding, operations, bleeding from cuts)
Ask for:

Taking history
• Medication
• Onset of complaints
• Family history
Ask for:

Spontaneous loss of blood
• Is not a specific sign of any special bleeding disorder but is found in general only in the more severe disorders. Nose and gingival bleeding are exceptions to this rule. Bleeding form these sites is observed more often in disturbances of primary hemostasis and may occur in patients with relatively minor hemorrhagic disease.
• Hemoptysis is not a sign of a general bleeding disorder.

Bleeding into tissues
• Bleeding into joints and muscles is observed in hemophilia and in severe deficiencies of humoral coagulation factors.
• Joint bleeding is rare, however, outside hemophilia.
• Superficial bleeding, especially petecchiae, is observed in thrombocytopenia and vascular disorders but not, or only seldom, with deficiencies of coagulation factors.

Medication• Several analgetics, especially aspirin, increase the
bleeding time. These drugs are often not considered as medication by the patient and their use should be asked specifically
• The onset of the symptoms may be important to distinguish between congenital and acquired disorders
• A congential disorder may express itself for the first time rather late in life especially when no challenge to the hemostatic mechanism has occured

Taking history • The family history is of eminent
importance for the diagnosis of diseases like hemophilia and von Willebrand’s disease

History and demography of hemophlia (with special reference to the situation in Sweeden)
• Hemophilia was described s a hereditary disease in the Talmud as early as the fifth century of our era
• Modern knowledge and research in hemophilia date from the 19th century (in 1803 American physician Otto reffered the victims as „bleeders”)- congenital bleeding disorder only affecting men and passed on by healthy women

History and demography of hemophlia (with special reference to the situation in Sweeden)
• The disease was described as manifesting itself in prolonged coagulation time and an abnormal bleeding tendency which appears early in childhood, the most typical bleeding symptom being joint bleeds
• In Germany the disease was given its original designation, Haemorrhaphilia, to denote a disease characterized by ‘love of bleeding’, the name subsequently being shortened to hemophilia.

History and demography of hemophlia (with special reference to the situation in Sweeden)
• Hemophilia was formerly thought to be uniform entity, but at the end of 1940s Pavlovsky in Argentina discovered the the coagulation defect in the blood of one hemophiliac could be normalized by infusion of blood from another hemophiliac
• In the 1950s it was fonud that there must be at least two types of hemophilia (deficiency of factor VIII- hemophilia A (typical), deficiency of factor IX – hemophilia B
• Hemophilia A and B are comparable in heredity, and are clinically indistinguishable

Degrees of severity in hemophilia
Coagulation activity Joint
VIII:C (%) IX: C (%) bleeds Hemophilia A Severe
Moderate
Mild
<1
1-4
5-25
100
100
100
+++
+
(+)
Hemophilia A Severe
Moderate
Mild
100
100
100
<1
1-4
5-25
+++
+
(+)

Occurrence of hemophilia in Sweden(1990)
Severe Moderate Mild Total
Hemophilia A 163 71 297 531
(80%)
Hemophlia B 38 20 77 135
(20%)
Total 201
(30%)
91
(14%)
374
(56%)
666

Changes in median life span among Swedish hemophiliac
1890-1990
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
1900 1940 1960 1990
healthy males
mild
moderate
severe

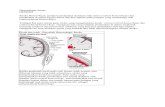
Heredity in hemophilia
Normal women Affected male
Gametes
Children
Parents
Trait-carrying Normal Trait-carrying NormalGirl boy girl boy

Heredity in hemophilia
Trait carrying women Normal male
Gametes
Children
Parents
Normal Normal Trait-carrying Affected girl boy girl boy

The structure and thrombin activation (thrombin cleavage site ) of circulating factor VIII
Circulating form of factor VIIIin complex with vWF
vWF
A1 A2 B
C2 C1 A3
vWF
Elimination of B domain
vWF
Ca++
Ca++
Ca++
Final activation

Factor VIII and vWF factor
• The concentration of factor VIII in plasma is only 150ng/ml whereas vWF is present at large excess, 5-10ug/ml
• vWF factor is thus the carrier protein which is required for adequate secretion of factor VIII and also protects the labile factor VIII from proteolytic degradation
• Moreover, since farctor VIII is associated with vWF, it is targeted to the exposed subendothelium and localized at its site of action in sufficient concentrations.

Synthesis of factor VIII, the v Willebrand factor and the factor VIII-vWF complex
Factor VIII Von Willebrand factor X-chromosome Chromosome 12
Liver sinusoidal cells Hepatocyte Endothelial cells
Megakarocytes Endothelial cells
Single chain form of factor VIII transforms into two-chain form
vWF subunit (Mr ~ 220kDa) combines into vWF protomer
Factor VIII, two-chain form, Mr ~280kDa
vWF multimer, Mr ~ 1-20 MDa
Factor VIII-vWF complex

Factor VIII• Synthesized by sinusoid cells in the liver• The gene of factor VIII is is located on the long
arm of the X chromosome• Plays a key part in the coagulation process as a
cofactor for factor IXa and thereby accelerates the activation of factor X
• Is inactivated by activated protein C important regulating mechanism

Factor IX• Is synthesized in the liver, and is a single chain
glycoprotein with molecular weight of 56 000• The plasma concentration is 3-5 ug/ml• The factor IX gene is located on the long arm of the
X chromosome • Together with a factor VIIIa and phospholipid, factor
IXa forms an enzyme complex in the presence of calcium ions tenase, then converts the zymogen factor X to the active enzyme factor Xa

von Willebrand factor• The vWF is a large adhesive glycoprotein present in both plasma,
the -granules of platelets, and the vessel wall• It is composed of a series of multimers ranging in molecular mass
from 800kDa to as much as 20 000 kDa (single subunit of 220 kDa)
• Plays an important part in the earliest phase of hemostasis by promoting the adhesion of platelets to the subendothelium exposed after vessel injury
• Serves as a carrier protein for factor VIII, thereby preventing the rapid removal of factor VIII from the circulation
• The high molecular weight multimers of vWF are the most hemostatically efficient (interaction with platelets and subendothelium)

Bleeding symptoms in hemofilia
• Mean age at diagnosis of hemophilia is about nine months in severe cases and 22 months in moderate cases
• The commonest symptoms at the onset are: - soft tissue bleedings (41%)- Bleeding in conjunction with puncture, injection or
surgery (16%)- Bleedings of the oral cavity (11%)- The bleedings into muscle and and joints that are
characteristic of the disease are not a rule seen at onset

Bleeding symptoms in hemofilia
• After negligible trauma, or even no trauma patients with severe hemophilia are afflicted with profuse and extensive bleeding into the soft tissue and muscles
• Its can be extremely painful and could leads to serious pressure defects as neural damage with consequent paresis, and even result in the formation of pseudotumors (blood-filled cysts)
• The slightest lesion (e.g. small cut) can result in uncontrolled bleeding that may last for weeks

Bleeding symptoms in hemophilia
• The most characteristic symptoms are joint bleeds, which appeared when the child is learning to walk
• Acute join bleeds usually develop without any known trauma
• Bleeds may affect almost any joint, the most commonly occur in the knees, ankles and elbows
• Bleeding into the shoulder or hip joints being more rare
• Spinal and wrist joints are very seldom affected, and usually only as a result of trauma

Bleeding symptoms in hemophilia
• After bleeds, the joint becomes stiff, swollen, warm and tender
• Generally the joint remains slightly flexed, all movement being inhibited by stiffness and pain
• Bleeding in the iliopsas muscle is not uncommon and is often misinterpreted as bleeding into the hip joint

Bleeding symptoms in hemophilia
• Cerebral hemorrhage has been the commonest single cause of death
• It can often be caused by minimal trauma, giving rise to exsanguinating hemorrhage, in time resulting in severe intracranial hemorrhage start prophilactic replacement therapy at the earliest opportunity

Bleeding symptoms in mild hemophilia
• Patients do not usually manifest either severe bleedings or joint bleeds
• Bleeding episodes occur first and foremost in conjunction with trauma and surgery, and they manifest renal and gastric bleedings
• Even in these patients life-threatening bleeding may result from dental extraction !

Hemophilic arthropathy• Isolated joint bleeding episodes are relatively innocuous
blood has been reabsorbed and the swelling has diminished, normal joint mobility and function are restored
• Repeated bleeding episodes damage of various joint components— arthropathy affecting both the joint capsule and cartilage as well as the adjacent bones and soft tissue fibrosis of the joint capsule and surrounding soft tissue, with markedly reduced joint mobility

Hemophilic arthropathy• The joint cartilage degenerates and is eroded after repeated
bleedings by the action of aggressive proteolytic enzymes and collagenases reduced cartilage stability
• Parallel with the cartilage degeneration, the underlying subchondral bone undergoes changes, becoming by turns osteoporotic (bone resorption) and sclerotic (ossification)
• Clinically, joint function is impaired, both extension and flexion being diminished, and the joint can become deformed by widening and various forms of malalignment.
• The surrounding musculature is affected atrophy

Replacement therapy in hemophilia A• Recent years have witnessed the development of several high purity
preparations (i.e. Containing > 10IU of factor VIII/mg protein) and several super-pure preparations (i.e. With a final specific activity of 1000-4000 IU VIII;C/mg protein)
• All preparations are virus-inactivated with methods that exclude the risk of HIV transmission
• Preparations purified with monoclonal antibodies, and these exposed to wet heat and steam treatment or chemical inactivation, also manifest a high degree of safety with regard to hepatitis C transmission
• In contrast to low or intermediate purity concentrates, the superpure concentrates have been found to have no immunosupressive effect

Factor VIII concentratesPreparation Manufacturing
procedure Virus
inactivation
Octanativ – M
(Pharmacia)
Affinity purified with monoclonal antibodies
against factor VIII
Solvent detergent technique
Hemate P
(Behring)
Cryoprecipitate+Al(OH)3 adsorption+PEG+Glycine
Wet heat treatment at 60C
for 10h
Recombinate (Baxter)
DNA technology
Kogenete (Bayer)
DNA technology

Properties of factor VIII concentrates
Preparation
VIII:C vWF:Ag Fibringogen Fibronectin Specific activity IU VIII:C/mg
protein
IU/ml ug/IU VIII:C
Octanativ – M
(Pharmacia) 96 1,6 <0.001 <0.001 37
Hemate P
(Behring) 28 71 0.09 0.07 5.7
Recombinate (Baxter)
50 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 5.2
Kogenete (Bayer)
169 < 0.001 <0.001 <0.001 42

Factor IX concentrates available Preparation Manufacturing
procedure Virus
inactivation
Prothromplex TIM4
(Immuno)
DEAE Sephadex Steam treatment at 60C for 10h
Nanotiv
(Pharmacia)
Chromatographic purification
Solvent detergent technique
Immunine (Immuno) „ Steam treatment at 60C for 10h
Mononine (Armour) Affinity purified with monoclonal
factor IX antibodies
Sodium thiocyanate

Biochemical properties of factor IX concentrates
Preparation IX:C II VII X PC PS Specific activity
IU IX:C/mg protein
Prothromplex TIM4
(Immuno)
55 86 3.9 44 2.3 7 1.9
Nanotiv
(Pharmacia)115 0.05 <0.01 0.03 0.17 0.74 278
Immunine (Immuno)
110 0.98 <0.05 0.21 0.002 0.04 195
Mononine (Armour)
98 0.25 0.03 0.02 0.14 0.06 236

Proposed therapy for severe bleeds in severe hemophilia A (serious hematoma, retroperitoneal bleeds, gastrointestinal bleeds,
intracranial bleeds)
Desired postinfusion factor VIII concentration
50-100% initially, then 20-40%
Duration of treatment 7-14 days until healing achieved
Factor VIII dosage50-70 IU/kg body weight at 6h intervals initially, then approx. 20IU/kg at 6-8 h inetrvals

Principles of relpacement therapy as cover for surgery
Hemophilia A Hemophilia B
Major Minor Major Minor Day of operation
- desired level (%)
- initial dose (IU/kg)
- maintenance dosage(IU/kg)
- interval (h)
50-100
50-60
25-30
4-6 h
40-50
25-40
20-30
4-8
50-150
60-70
30-40
8-12
40-50
30-40
20-30
8-12
Days 2-7 postoperatively
- desired level (%)
-maintenance dosage (IU/kg)
- interval (h)
40-60
20-40
4-6 h
30-50
15-20
6-12
40-60
30-40
12-24
30-50
15-20
24
Day 8 postoperatively
- desired level (%)
- maintenance dosage(IU/kg)
- interval (h)
15-25
10-15
12-24 h
15-25
10-20
24-48

Home infusion treatment • To prevent profuse bleedings by giving treatment
treatment immediately in the event of incipient bleeding• To save time and money in terms of transport to and
from hospital, waiting times, and days of treatment• To reduce absence from school or work due to sick
certification• To render the patients independent so that they can live
normal lives

Prophylaxis and home treatment(severe hemophilia patients)
Present age (years) 3-12 13-20 21-26 27-35
Age at start of treatment
Joint bleeds/year
Total annual dose of FVIII/IX per kg, Ux103
Orthopedic joint score
Annual absence from school/work, days
1-2
0.2
5.9
0
2.5
2.6
1.65.4
1.2
0.9
4.9
5.6
1.2 2.7
2.9
2.8
7.0
5.0
0.4 3.3
6.6
5.8
Twice a week tretment regimen – 800-2500 IU/kg body weight annualy 5400 IU factor VIII/IX per kg annually by Port –A-Cath system

Factor VIII/IX antibodies• Inhibitors develop at an early age, and usually after only a
few infusions of factor VIII or factor IX• In every case of hemophilia an inhibitor test be carried one
or twice a year, and before any form of surgical intervention
• In the treatment of hemophilacs with inhibitors, the aim is twofold:
- to control severe acute bleeding episodes or to prepare the patient for essential surgery
- to induce immune tolerance, or at least to convert a high responder into alow responder, by elimination of the antibodies

Management of acute bleedings in patients with low inhibitors titers (<10 BU)
Treatment Effect
Previous low immune responce (<10BU)
Factor VIII/IX concentrates- increased doses-
Maintained response possible
Previuos high immune response (>20BU)
Factor VIII/IX concentrates- increased doses-
Factor VIII/IX concentrates – increased doses + cyclophosphamide
PCC
APCC (Autoplex, Feiba)
Good initial response
Resistant after 4-6 days
Response 6-9 days
Beneficial effect in 40-60% of episodes

Management of acute bleedings in patients with high inhibitors titers (>10 BU)
Methods used or proposed Temporary reduction of the inhibitor:- extensive plasma exchange- immunoabsorption
Porcine factor VIII
Factor VIII inhibitor by-passing agents- PCC or APCC (Feiba, Autoplex)- Recombinant factor VIIa

Desmopressin (DDAVP) treatmentmanagement of mild or moderate hemophilia A and vWD
• Intravenous administration - 0,3ug/kg , the peak plasma concentrations of VIII:C and
vWF occur after about 30minutes
- the plasma concentration of VIII:C increases about 2-6 times and that of vWF about 2-4 times about the respective baseline levels
• Subcutaneous administration 0,4ug/kg
- the peak plasma concentrations of VIII:C and vWF occur after about 2h
- the plasma concentration of VIII:C increases about 2-5 times and that of vWF about 2 times about the respective baseline levels