Hemolytic Jaundice due to Anti-Mi a, Diagnosed by Management with An Hour-Specific Nomogram for...
-
Upload
candace-waters -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Hemolytic Jaundice due to Anti-Mi a, Diagnosed by Management with An Hour-Specific Nomogram for...

Hemolytic Jaundice due to Anti-Mia, Diagnosed by Management with An Hour-Specific Nomogram for Transcutaneous
Bilirubin (TcB) Values
Jun Kunikata1, Takashi Kusaka2, Saneyuki Yasuda2,
Shinji Nakamura2, Kosuke Koyano2, Satoshi Hamano1,
Hitoshi Okada1, Susumu Itoh1
1Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Japan2Maternal Perinatal Center, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Japan

Introduction
Hemolytic jaundice can develop in neonates born to mothers who have irregular antibodies in her blood.
All pregnant women are recommended to have irregular antibody screening test, but many irregular antibodies tend to be missed through routine prenatal screening tests.

Introduction
Low frequency antibodies are rare causes of hemolytic jaundice and there are no established management methods for these antibodies.
We experienced a case of hemolytic jaundice due to anti-Mia antibody that was diagnosed early by transcutaneous jaundice meter.

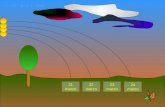
Transcutaneous jaundice meter (Konica Minolta, JM-103)
150 g

0
5
10
15
20
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60 66 72
Postnatal Age (hours)
Transcutaneous Bilirubin (TcB) Levels in the First 72 Hours
in a Normal Newborn Population in JAPAN
97.5%tileAverage2.5%tile
171
342
0
TcB
(m
g/d
L)
TcB
(µ
M)

Case Report
Patient : A male infant delivered by cesarean section at 38 weeks' gestation with a birth weight of 3148 g.
Anti-Mia had been found in his mother’s serum in a prenatal antibody screening test.
He showed no abnormal findings at birth and was admitted to a newborn nursery. But a transcutaneous jaundice meter (JM-103) showed 1.8 mg/dL (30.8 μM) one hour after birth, which were above the treatment line in our hour-specific nomogram.
So we admitted him to our NICU and started treatment.

Clinical course and management of jaundice
2 hours after birth
plasma total bilirubin 6.1mg/dL(104.3 μM)
1 hour after birthtranscutaneous jaundice meter (JM-103) showed 1.8 mg/dL (30.8 μM)

Laboratory data (2 hours after birth) WBC 2082
0/μl
RBC 373 /μl
Ht 38.1 %
PLT 33.2 ×104/μl
hemogram
stab 1.0 %
seg 31.0 %
eosinophil 13.5 %
basophil 0.5 %
lymph 41.5 %
mono 6.5 %
myelo 1.0 %
erythro 3.0 %
reticulo 7.91 %
Total protein 5.6 g/dl
albumin 3.8 g/dl
BUN 8.7 mg/dl
creatinine 0.7 mg/dl
uric acid 5.6 mg/dl
total bilirubin 6.3 mg/dl
direct bilirubin 0.6 mg/dl
indirect bilirubin
5.7 mg/dl
AST 25 U/L
ALT 6 U/L
ALP 643 U/L
LDH 422 U/L
γ-GTP 179 U/L
Blood type AB(+)
Mother’s Blood type B(+)
immunohematology test
direct Coombs test (+)
indirect Coombs test (+)
anti-A antibody (-)
anti-B antibody NT
Mia antigen (+)
Anti- Mia antibodies were separated from his red blood cells.

Clinical course and management of jaundice
Administration of γ-globulin
Diagnosis:Hemolytic jaundice induced by anti-Mia
antibody
Starting Photo therapy
Need no further treatmentafter Day 3
Jaundice was swiftly improved

About anti-Mia antibody
Anti-Mia is one of irregular antibodies that react with the Mi III phenotype.
Several studies have reported that Asians tend to have Mi III phenotype much more than Whites: 7.3% in Taiwan Chinese blood donors, 6.28% in Hong Kong Chinese blood donors, 9.7% in Thai blood donors and 0.0098% in Whites).
The frequency of Anti-Mia antibody among Chinese patients is 0.28%.1)
There are only a few reports of hemolytic disease caused by anti-Mia, so Mia antigen is not considered to be necessary to test red blood cells for irregular antibody screening test.
1) R.E.Broadberry and M.Lin, The incidence and significance of anti-”Mi” in Taiwan, TRANSFUSION 1994;34;349-352.

Hitosh Ohto:新生児溶血性疾患と母児免疫 .輸血学 (改訂第3版 ), Tokyo, Chugai-Igakusya, 2004,512-521 (III)

Antigen Profile of test red blood cells

Discussions
Difficulty in finding low frequency antibodies prevent us from predicting and treating hemolytic jaundice promptly.
We can use transucutaneous jaundice meter to predict hemolytic jaundice so that kernicterus or exchange transfusion will be prevented.

Conclusion
Transcutaneous jaundice meter and an hour-specific 97.5th percentile-based TcB nomogram is useful in the management of newborn jaundice as a non-invasive first-line examination.

Management of jaundice and treatment progress