Natalie was born with a heart defect Natalie needed a new heart.
Heart Defect PDF (1)
-
Upload
rosemarycastro -
Category
Documents
-
view
12 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Heart Defect PDF (1)

Nessa Osuna Cardiac Notes for Pediatrics test #3 Name Picture Signs and Symptoms Treatment Nursing Notes
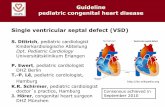
Ventral Septal Defect (VSD)
Most common! Abnormal connection between the R and L ventricles. Lowers Cardiac Output. Flow from L to R, pulmonary congestion. *Asymptomatic *CHF *Enlarged heart *Acyanotic
-‐Surgical repair -‐May close by 2 yrs old.
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Flow from L to R, pulmonary congestion. *Asymptomatic *CHF *Acyanotic
-‐Diuretics for CHF -‐Surgery
You can wait for surgery if asymptomatic bc it may resolve spontaneously. As the murmur gets louder, the hole is closing.

Nessa Osuna Cardiac Notes for Pediatrics test #3 Tricuspid Atresia
Absent tricuspid valve! The Foremen Ovale is used (remember the pressure causes this). HIGH right-‐sided pressure. Unoxygenated blood is shunted to L. atrium into the L. ventricle then to the body and lungs.
Increase pulmonary blood flow by using the patent ductus arteriosus with Prostiglandin *Surgery -‐glenn procedure -‐atrial septostomy -‐shunting -‐fontan procedure
There is currently NO way to replace an atrial valve
Patient Ductus Arteriosus
Left to right shunting. Fibers don’t respond to the increase in O2 after birth. *Continuous murmur below left clavicle *Asymptomatic or murmur *Bounding pulses *Widening pulse pressure of >20 (systolic-‐diastolic)
Indomethacin: *preterm only! *NSAID *prostaglandin inhibitor *only if no other defects & asymptomatic other option: -‐surgery
Dx: by echo or xray

Nessa Osuna Cardiac Notes for Pediatrics test #3 Atrio-‐ventricular Septal Defect
Severe left to right shunt. LUNGS ARE MOST EFFECTED *severely impaired Cardiac Output
See ASD & VSD See ASD & VSD
Aortic Stenosis
Not always the valve. Could be general area. *Hypertrophy of L. Ventricle *Enlarged heart
Meds can reduce symptoms (<BP) but cannot cure. Surgery: valve replacements and catheterizations
This is found to be one of the reasons for kids falling dead during sports.
Coarctation of the Aorta
Pinching/stricture of the aorta. High pressure behind and in front. *BP okay in hands/arms but low in lower limbs. *Bounding pulses in upper body but weak in lower.
*Prostaglandin E1 to open artery by relaxing the muscle. *Diuretics and inotropic drugs to treat s/s *Surgical Repair *Catheterization
Always check pulses both sides and upper and lower extremities!

Nessa Osuna Cardiac Notes for Pediatrics test #3 Transposition of the Great Arteries
Unoxygentated blood enters the R. atrium and R. Ventricle. Parallel circulation. *Initially appears normal *Cyanosis develops w/in a few hours of life
Prostiglandin immediately to keep PDA open. Surgery
This is NOT compatible with life. You WANT another defect to help. Can be detected by US if they receive prenatal care.
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Connection
*Cyanosis develops w/in a few hours to a few weeks of life depending on configuration *Tachypnea *Dyspnea *Snowman-‐figure 8 appearance on chest xray *R. Ventricular hypertrophy *Enlarged heart *Murmurs
Surgery to reconnect the pulmonary arteries to the left atrium and to close the (ASD) atrial septal defects
Sometimes can be detected in utero via ultra sound.

Nessa Osuna Cardiac Notes for Pediatrics test #3 Truncus Arteriosus
*Cyanosis develops w/in a week or two of life *CHF s/s *Hazy chest x-‐ray *Possible hepatomegaly *Poor feeding *Facial swelling or neck vein distention
Medicines such as diuretics and inotropic meds to manage signs/symptoms. Surgery: separating the pulmonary arteries from the truncus, closure of the septal defects, create connection from pulmonary arteries to the right ventricle.
Possibly not on exam
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Left ventricle is tiny and aortic stenosis is present. *O2 sats 70-‐80’s *Cyanosis *Poor feeding *Tachypnea *Dyspnea *Weak/rapid pulses *Lethargy *Cool/clammy skin *Dilated pupils/lackluster stare
*Heart transplant *3 step surgical process (70-‐80% survive; live in the hospital) *Do nothing
Not compatible with life

Nessa Osuna Cardiac Notes for Pediatrics test #3 Pulmonary Stenosis
*Central cyanosis *CHF s/s *Possible Right-‐sided hypertrophy *Back up pressure can open up Foreman Ovale
Prostiglandin given to keep PDA open Surgery: Percutaneous balloon vulvuloplasty
Tetralogy of Fallot
Combination of pulmonic stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, overriding aorta and VSD. Mixed blood is sent out to system. *Cyanosis *O2 sats 80-‐85’s *Tachypnea *Irritability
Treat symptoms: -‐Decrease venous return -‐Conservative O2 -‐Comfort and stop crying to minimize O2 consumption
Don’t want to put a lot of oxygen on them. Squat knee to chest to get O2 by restricting venous return and getting O2 to main organs. May be associated with chromosomal abnormalities