Estimation of Stapedius-Muscle Activation using Ear Canal ...
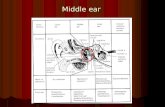
Hearing Anatomy. Ear Protection Middle Ear: –Contains 2 smallest striated muscles in the body-...
-
Upload
theodora-tracey-gray -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
1
Transcript of Hearing Anatomy. Ear Protection Middle Ear: –Contains 2 smallest striated muscles in the body-...

Hearing Anatomy

Ear Protection
• Middle Ear:– Contains 2 smallest striated muscles in the
body-• Tensor Tympani (stiffens ear drum)• Stapedius (draws stapes away from oval window)
– Contraction is the basis of Acoustic Reflex-• Protects against damaging loud sounds• Tune ear to respond to selectively high speech
frequencies• Protects us from our own voices when too loud

Ear Protection
• How does the acoustic reflex work?– Pits two auditory muscles against each other
(they pull on opposite ends of ossicular chain)
– Tensor tympani stretches ear drum tight; more resistant to large vibrations of sound
– Stapedius attaches to stapes (antagonist to tensor tympani)and stiffens ossicular chain and acts against transmission of loud sounds.
– At extremely loud sounds the stapedius changes axis around which the stapes vibrates

Stapes
Stapes Movement
Vestibular Canal
Tympanic Canal
Uncoiled CochleaCochlear Partition
(Basilar Membrane)
Incus*Stapes shifts to midline relieving pressure on inner ear

Inner Ear: Hydraulic System
• Cavern with 2 exits close together:– Oval and sealed with a movable door (footplate
of stapes)
– Round, sealed and flexible membrane (round window)
– Off to one side- Passageway that spirals upward for 2 1/2 turns before it ends (cochlea)
– Off in the other direction is the vestibular mechanism- organ which maintains balance & detects bodily movement.

Utr
icle
Sac
cule
Ves
tibu
le
Oval Window
Round WindowCochlea
Semicircular Canals
Vestibular Mechanism
Inner Ear:Bony Labyrinth
*Filled with perilymph

Inner Ear
• Oval Window: The opening in the inner ear to which the stapes fits
• Round Window: A membrane sealed opening in the inner ear that relieves pressure at the oval window by the vibratory movement of the stapes
• Semi-Circular Canals: 3 fluid filled canals by which turning movements of the head are detected
• Vestibular Mechanism: The acceleration and equilibrium mechanism

Inner Ear
• Vestibule: The central room into which the oval window opens that connects to both vestibular mechanism and auditory receptors
• Saccule: The membranous cavity in the vestibule that detects forward and sideways movement
• Utricle: The membranous cavity that opens into the semicircular canals and detects forward and sideways movement

Cochlea
Helicotrema
Cochlea Canals UncoiledRoundWindow
Reissner’sMembrane
Scala VestibuliCochlear Duct
Scala Tympani
Basilar Membrane

Cochlea
• Cochlea: The spiral-shaped organ of hearing in the inner ear
• Scala Vestibuli: The perilymph filled canal extending from vestibule to the apex of the cochlear spiral
• Scala Tympani: The perilymph filled canal extending from the apex of the cochlea to the round window
• Helicotrema: The isthmus of the apex of the cochlea through which perilymph can flow from scala vestibuli to scala tympani

Cochlea• Cochlear Duct: The portion of the membranous labyrinth,
containing the auditory sensory receptors, forms partition
between scala vestibuli and scala tympani
• Basilar Membrane: The partition tuned to different
frequencies along its length, on which the organ of Corti
rests, separates cochlear duct from scala tympani
• Reissner’s Membrane: Thin partition separating the
cochlear duct from the scala vestibuli

Membranous Labyrinth
Utr
icle
Membranous Labyrinth
Bony Labyrinth
Saccule
Cochlear Duct* Filled with endolymph

Inner Ear: Neural System
• Organ of Corti- Mounted on the basilar membrane along its entire length– Converts hydraulic energy into bioelectric
energy
– Immersed in the endolymph that fills cochlear duct
– Above is Reissner’s membrane, separating the sealed duct from the vestibular canals
– Below the basilar membrane, terminating at round window

Inner Ear: Neural System
• Basilar membrane:– Membrane stretched between outer wall of bony
labyrinth and the bony core around which the cochlear channels spiral
• Organ of Corti:– Between 15,000 & 20,000 auditory nerve receptors are
contained in the organ of Corti– Each receptor has its own hair cells arranged in four
rows:• one row of..Inner (3,000)
• three rows of...Outer (12,000)

Nucleus
Cilia
Basilar Membrane
Nerve Endings
PhalangealProcess
Hair Cells

Hair Cells
• Rests on phalangeal cells
• Each hair cell has a phalangeal cell
• Inner row and three outer rows of phalangeal cells– outer-Deiter’s cells
• Cilia is not nerve cell but movement generates neural response
• Each inner hair cell has 30-60 cilia
• Each outer hair cell has 75-100 cillia
• Organ of Corti may contain a million or more cilia

Hair Cell Support
• Any movement of the cilia generates a neural auditory signal– Hair cells are firmly buttressed
– No accidental movement of cilia (signals without sound)
– Inner row of cells- Border cells of Held
– Outer rows- Cells of Claudius & Cells of Hensen
– Between inner & outer rows are pillars of Corti

Reading/Assignments
• Seikel: Pgs.548-558
• Dickson: Pgs. 265-281








![[原著]A Study of Electrically Evoked Stapedius Reflex Owa ...okinawa-repo.lib.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/bitstream/20.500.12001/...ear could produce a sense of hearing has been well known since](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/60f778a6a6e1bf3633356823/ea-study-of-electrically-evoked-stapedius-reflex-owa-okinawa-repolibu-.jpg)