Head and Spinal Injuries. Scalp Wounds Bleed profusely because the scalp has a rich blood supply and...
-
Upload
stanley-briggs -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Head and Spinal Injuries. Scalp Wounds Bleed profusely because the scalp has a rich blood supply and...
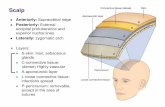
Scalp WoundsBleed profusely because the scalp has a rich
blood supply and the blood vessels there do not constrict
Severe scalp wounds may be accompanied by: Concussion
Skull fractureImpaled objectSpinal injury
Care for Scalp WoundsControl bleeding by gently applying direct
pressure with dry, sterile dressingIf you suspect a skull fracture- apply pressure
around edged rather than on the center of the wound
Keep head and shoulders slightly elevated to help control bleeding if no spinal injury is suspected
Seek medical care
Click to edit the outline text format
Second Outline Level
Third Outline Level Fourth Outline Level Fifth Outline Level Sixth Outline Level Seventh Outline
Level Eighth Outline Level
5/11/10
Scalp Wounds
Recognizing a Skull FractureDifficult to determine except by X-ray unless the
skull deformity is severe.Signs and Symptoms of a skull fracture include: Pain at the point of injuryDeformity of the skullBleeding from the ears or noseClear,pink,watery Cerebrospinal fluid leaking
from ear or nose. (halo sign) on white cloth will form pink ring around slightly blood-tinged center
Discoloration around eyes (raccoon eyes)Discoloration behind an ear (Battles sign)Heavy scalp bleeding if skin is broken- may expose
skull or brain tissue.
Click to edit the outline text format
Second Outline Level
Third Outline Level Fourth Outline Level Fifth Outline Level Sixth Outline Level Seventh Outline
Level Eighth Outline Level
5/11/10
Recognizing Skull Fracture
Care for Skull FractureMonitor the victim’s breathing and provide
appropriate careStabilize the victims neck to prevent movementSlightly elevate victims head and shoulders to
help control bleedingCover wounds with sterile dressingTo control bleeding, apply pressure around edges
of the wound.DO NOT:Stop the flow of blood from an ear or nose-could
increase pressure within the skullRemove impaled objectPress on fractured area
Brain InjuriesCauses short-and long-term problemsMost are a result of motor vehicle crashes and falls50,000 people die in the US of head trauma and 2x that
have brain injuries that leave them with permanent damage
Brain injuries are difficult first aid emergencies to handle, victim is often confused, or unresponsive making assessment difficult
Brain will swell from bleeding when its injuredUnlike other tissues, however the brain is confined in
the skull-interferes with brain functioningNerve cells of the brain and spinal cord unlike most
other cells in the body, are unable to regenerate-once dead, they are lost forever and can not be replaced.
3 Types of Common Occurring Brain Injuries
Concussion- temporary loss of brain function, usually without permanent damage
Contusion- bruising of brain tissue
Hematoma – localized collection of blood as a result of a broken blood vessel
Concussiontemporary loss of brain function, usually without
permanent damageNo bleeding in brain occursPerson can be unconscious or have amnesiaLonger the victim is unconscious, or the longer the
memory loss lasts, the more serious the concussionUnlikely-but can cause deathGrade 1- no loss of consciousness, symptoms or mental
status abnormalities resolve in less than 15 minutesGrade 2- no loss of consciousness, symptoms or mental
status abnormalities last more than 15 minutesGrade 3 – Any loss of consciousness
Concussion
Concussion
Football Concussion
Double KO
Care for Brain Injury1. Seek immediate medical care2. Stabilize the victims head - Suspect a spinal
injury in an unresponsive victim until proven otherwise
3. Grasp victims head over the ears and hold head and neck until EMS arrives
4. If long wait, kneel with victims head between your knees
5. Monitor victims breathing6. Control bleeding7. Brain-injury victims tend to vomit. Roll
victim onto his/her side while stabilizing neck
8. Monitor level or responsiveness- best indicator of neurologic function
Further CareSeveral signs appearing within 48 hours of a
head injury indicate a need to seek medical care
Headache lasting 1 or 2 days or increases in severity
Nausea, vomitingDrowsiness- wake victim every 2 hours to check
consciousness and sense of orientationVision problemsMobilitySpeechSeizures
Eye InjuriesPenetrating eye
injuries: sharp object, such as knife or needle penetrates eye
Care:Seek immediate
medical careStabilize object
Blows to the EyeBlows to the eye –
blood vessels around the eye rupture
CareApply ice or cold
pack for about 15 minutes
Seek medical care if there is double vision, or reduced vision
Cuts of the Eye or LidSigns:
Cut appearance of the cornea
Inner liquid filling of the eye
Lid is cutCare:
If eyeball is cut do not apply pressure
If only eyelid is cut, apply sterile dressing with gentle pressure
Bandage both eyes lightly
Seek medical care immediately
Eye AvulsionKnocking the eye from its
socketCare
Cover eye loosely with sterile dressing that has been moistened
Do not try to push eyeball back into socket
Cover undamaged eye with patch to stop movement
Seek medical care immediately
Eye Avulsion Injuries http://connect.in.com/orbital-
bone/photos-ecs70070f1-78af8f4e205936f4.html
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HX_5zIXxKEU&feature=related
Basketball Eye Avulsion http://www.youtube.com/
watch?v=0ANtDOk6FCk
Broken NoseSigns
Pain, swelling, and possible crooked appearance
Bleeding and difficulty breathing through nostrils
Black eyes appearing 1-2 days after injury
CareSeek medical care If bleeding is present
give care as for a nosebleed
Apply iceDo not try to straighten
Knocked-Out ToothCommon dental emergencyTo prevent tooth from
drying and protect ligament fibers from damage reimplantation needs to be done within 30 minutes
CarePlace rolled gauze pad in
socket where tooth came out to control bleeding
Place tooth in Milk if available. Preferably whole milk
Take victim and tooth immediately to dentist
Broken TeethFrequently broken
by falls or direct blows
CareGently clean dirt and
blood from injured area
Apply ice pack on the face in the area of the injured tooth
Seek immediate dental care
Spinal InjuriesSpine- column of vertebrae stacked on one
another from tailbone to base of the skullEach vertebra has a hollow center through which
spinal cord passes*If a broken vertebra pinches spinal nerves,
paralysis can resultA mistake in handling a spinal injury victim could
mean a lifetime of paralysis for the victimFallsDiving accidentsMotor vehicle crashes
Recognizing Spinal InjuriesPain radiating into arms or legsNeck or Back painNumbness, tingling weakness, burning, or
lessened sensation in the arms or legsLoss of bowel or bladder controlParalysis of the arms or legsDeformity: odd looking angle of victims head
and neck
Checking for Spinal InjuriesHave victim wiggle fingersSqueeze fingers and ask if they can feel
itSqueeze victims handAsk victim to wiggle toesHave victim push foot against rescuers
handPinch victims hand for response