Gout
description
Transcript of Gout
-
GOUT
Wayne Blount, MD, MPHProfessor,Emory Univ. S.O.M.
-
OBJECTIVESIdentify diagnostic criteria for gout
Identify 3 treatment goals for gout
Name the agents used to treat the acute flares of gout and the chronic disease of gout
-
Why Worry About Gout ?Prevalence increasingMay be signal for unrecognized comorbidities : ( Not to point of searching)
Obesity (Duh!)Metabolic syndromeDMHTNCV diseaseRenal disease
-
URATE, HYPERURICEMIA & GOUT
Urate: end product of purine metabolism
Hyperuricemia: serum urate > urate solubility (> 6.8 mg/dl)
Gout: deposition of monosodium urate crystals in tissues
-
HYPERURICEMIA & GOUT
Hyperuricemia caused byOverproductionUnderexcretion
No Gout w/o crystal deposition
-
THE GOUT CASCADE UrateOevrproductionUnderexcretion
Hyperuricemia
________________________________________
SilentGoutRenalAssociatedTissue manifestationsCV events &Deposition mortality
-
GOUT: A Chronic Disease of 4 stages
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Acute Flares of crystallization
Intervals between flares
Advanced Gout & Complications
-
ACUTE GOUTY FLARESAbrupt onset of severe joint inflammation, often nocturnal;Warmth, swelling, erythema, & pain;Possibly feverUntreated? Resolves in 3-10 days90% 1st attacks are monoarticular50% are podagra
-
SITES OF ACUTE FLARES90% of gout patients eventually have podagra : 1st MTP joint
-
SitesCan occur in other joints, bursa & tendons
-
INTERVALS SANS FLARESAsymptomatic
If untreated, may advance
Intervals may shortenCrystals in asx jointsBody urate stores increase
-
FLARE INTERVALSSilent tissue deposition & Hidden Damage
-
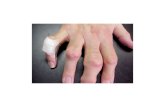
ADVANCED GOUTChronic Arthritis
X-ray Changes
Tophi Develop
Acute Flares continue
-
ADVANCED GOUTChronic ArthritisPolyarticular acute flares with upper extremities more involved
-
TOPHISolid urate deposits in tissues
-
TOPHIIrregular & destructive
-
TOPHI RISK FACTORS
Long duration of hyperuricemia
Higher serum urate
Long periods of active, untreated gout
-
RADIOLOGIC SIGNS
-
X-RAYS
-
X-RAYS
-
DIAGNOSING GOUT
Hx & P.E.
Synovial fluid analysis
Not Serum Urate
-
SERUM URATE LEVELSNot reliable
May be normal with flares
May be high with joint Sx from other causes
-
GOUT RISK FACTORSMalePostmenopausal femaleOlderHypertensionPharmaceuticals:Diuretics, ASA, cyclosporine
-
GOUT RISK FACTORSTransplantAlcohol intakeHighest with beerNot increased with wineHigh BMI (obesity)Diet high in meat & seafood
-
SYNOVIAL FLUID ANALYSIS (Polarized Light Microscopy)The Gold standard
Crystals intracellular during attacks
Needle & rod shapes
Strong negative birefringence
-
SYNOVIAL FLUID
-
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pseudogout: Chondrocalcinosis, CPPDPsoriatic ArthritisOsteoarthritisRheumatoid arthritisSeptic arthritisCellulitis
-
Gout vs. CPPD
Similar Acute attacks
Different crystals under Micro;Rhomboid, irregular in CPPD
-
Gout vs CPPD
-
RA vs Gout
Both have polyarticular, symmetric arthritis
Tophi can be mistaken for RA nodules
-
RA vs Gout
-
REDNECK MEDICAL TERMS
BENIGN : WHAT YOU BE AFTER YOU BE EIGHT
-
TREATMENT GOALS
Rapidly end acute flaresProtect against future flaresReduce chance of crystal inflammation
Prevent disease progressionLower serum urate to deplete total body urate poolCorrect metabolic cause
-
ENDING ACUTE FLARESControl inflammation & pain & resolve the flareNot a cureCrystals remain in jointsDont try to lower serum urate during a flareChoice of med not as critical as alacrity & duration EBM
-
Acute Flare Med Choices
NSAIDS
Colchicine
Corticosteroids
-
MED ConsiderationsNSAIDS : Interaction with warfarinContraindicated in:Renal diseasePUDGI bleedersASA-induced RAD
-
MED ConsiderationsColchicine :Not as effective late in flareDrug interaction : Statins, Macrolides, CyclosporineContraindicated in dialysis pt.sCautious use in : renal or liver dysfunction; active infection, age > 70
-
MED Considerations
Corticosteroids :Worse glycemic controlMay need to use mod-high doses
-
TREATMENT GOALSRapidly end acute flaresProtect against future flaresReduce chance of crystal inflammation
Prevent disease progressionLower serum urate to deplete total body urate poolCorrect metabolic cause
-
PROTECTION VS. FUTURE FLARESColchicine : 0.5-1.0 mg/dayLow-dose NSAIDS
Both decrease freq & severity of flaresPrevent flares with start of urate-lowering RX Best with 6 mos of concommitant RXEBM
Wont stop destructive aspects of gout
-
TREATMENT GOALSRapidly end acute flaresProtect against future flaresReduce chance of crystal inflammation
Prevent disease progressionLower serum urate to deplete total body urate poolCorrect metabolic cause
-
PREVENT DISEASE PROGRESSIONLower urate to < 6 mg/dl : DepletesTotal body urate poolDeposited crystals EBM
RX is lifelong & continuousMED choices :Uricosuric agentsXanthine oxidase inhibitor
-
PREVENT THIS
-
URICOSURIC AGENTSProbenecid, (Losartan & fenofibrate for mild disease)
Increased secretion of urate into urine
Reverses most common physiologic abnormality in gout ( 90% pt.s are underexcretors)
-
XANTHINE OXIDASE INHIBITORAllopurinol :Blocks conversion of hypoxanthine to uric acidEffective in overproducersMay be effective in underexcretorsCan work in pt.s with renal insufficiency
-
WHICH AGENT ?AllopurinolUricosuricIssue in renal disease X XDrug interactions X XPotentially fatal hypersen- sitivity syndrome XRisk of nephrolithiasis XMutiple daily dosing X
-
WHICH AGENTBase choice on above considerations & whether pt is an overproducer or underexcretor : Need to get a 24-hr. urine for urate excretion:< 700 --- underexcretor (uricosuric)> 700 --- overproducer (allopurinol)
-
NEW AGENTSRX gaps : Cant always get urate < 6AllergiesDrug interactionsAllopurinol intoleranceWorse Renal disease
-
URICASE ENZYMES (Stay Tuned)
Catabolize urate to allantoin:More soluble, excretable form
Currently approved for hypoeruricemia in tumor lysis syndrome
Some concerns: fatal immunogenicity & unknown long-term effects
-
CASE STUDIES
-
CASE J.F.80 YO W F c/o acute overnight pain & swelling in R kneePE: 51 & 180 lbsR knee swollen, warm & erythematousPMH : HTN x 5 yrsMeds: HCTZ (25 QD) & ASASH : 20 PY smoker; 5 wine drinks/wk
-
WHAT ARE J.F.s RISK FACTORS FOR GOUT ?A. HTNB. SMOKERC. HCTZD. ASAWINE CONSUMPTIONOBESITYAGEPOSTMENOPAUSAL
-
HOW WOULD YOU DX GOUT ?
A. HX & PE COMPATIBLEB. CHECK SERUM URATE LEVELASSESS SYNOVIAL FLUIDTRIAL OF COLCHICINECHECK X-RAYS
-
IF YOU DX GOUT, WHAT RX TODAY? (& Why?)
A. MOTRINB. INDOCINC. PREDNISONED. ALLOPURINOLE. PROBENECIDF. COLCHICINE
-
NEXT STEP FOR J.F. ?
A. Modify risk factorsB. Give refills to rx next flareC. Start colchicine to prevent flaresD. Check serum urate levelE. Start allopurinolF. Start probenecid
-
CASE M.B.
56 YO W M c/o hand stiffness & growthsPE : 62 & 205 lbsMultiple tophi; chronic arthritisPMH : DM x 8 yrs; gout x4 yrs, but no flares x 3 yrs, lost 20# on Atkins dietMeds: Glyburide; colchicine (0.6 mg TID)Labs: Creat.= 2.0; Urate = 11.4
-
IN WHAT STAGE OF GOUT IS M.B. ?
A. Doesnt have gout
B. ASX. Hyperuricemia
C. Interflare period
D. Advanced Gout
-
WOULD YOU CHANGE MDS RX ?
No Not goutNo No flare x 3 yrs.Yes - Increase colchicineYes Add allopurinolYes Add benemid
-
WHAT OTHER ISSUES WOULD YOU CONSIDER ?
Renal dysfunctionWeightDMGlyburideDiet
-
CONCLUSIONSGout is chronic with 4 stagesUncontrolled gout can lead to severe diseaseSeparate RX for flares & preventing advancementMany meds for flaresTreating the disease requires lowering urateGet a 24-hr urine for urate excretion
-
QUESTIONS