LK1 Peranan Radiologi pada Kasus Tumor Glomus Jugularis (6-11-2012).pdf
Glomus jugular tumor
-
Upload
gay-keller -
Category
Documents
-
view
58 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Glomus jugular tumor

Glomus jugular tumorGlomus jugular tumor
Chunfu Dai M.D & Ph.DChunfu Dai M.D & Ph.D

Background Background
Originate from chemoreceptor jugular veiOriginate from chemoreceptor jugular veinn
glomus jugulare tumor is arisen in the adveglomus jugulare tumor is arisen in the adventitia of the dome of the jugular bulbntitia of the dome of the jugular bulb
This tumor is part of the neuroendocrine sysThis tumor is part of the neuroendocrine system, these tumors are highly vascularized.tem, these tumors are highly vascularized.
Glomus tumors represent 0.6% of neoplasGlomus tumors represent 0.6% of neoplasms of the head and neckms of the head and neck

Pathology Pathology
All paraganglia are composed of chief cells (tAll paraganglia are composed of chief cells (type I cells, ie, chemoreceptive cells) and sustype I cells, ie, chemoreceptive cells) and sustentacular cells (type II cells, ie, supporting celentacular cells (type II cells, ie, supporting cells). Developmentally, both types of cells are ols). Developmentally, both types of cells are of neuroectodermal origin; specifically, they arif neuroectodermal origin; specifically, they arise from neural crest cellsse from neural crest cells
The vast majority of glomus tumors are benigThe vast majority of glomus tumors are benign and slow to grow with bone erosion.n and slow to grow with bone erosion.

Pathology Pathology
Glomus jugulare tumors are typically located just Glomus jugulare tumors are typically located just under the skull base, at the bulb of the internal juunder the skull base, at the bulb of the internal jugular vein. The tumors may spread superiorly intgular vein. The tumors may spread superiorly into the jugular foramen, causing CN IX, CN X, and o the jugular foramen, causing CN IX, CN X, and CN XI deficits. CN XI deficits.
The primary blood supply to jugulare tumors is viThe primary blood supply to jugulare tumors is via the ascending pharyngeal artery. In addition, ta the ascending pharyngeal artery. In addition, the occipital and posterior auricular arteries can che occipital and posterior auricular arteries can contribute to vascularization. ontribute to vascularization.
Intraoperatively ligation of external carotid artery Intraoperatively ligation of external carotid artery can significantly reduce the hemorrhagecan significantly reduce the hemorrhage

Symptoms Symptoms
Pulsatile tinnitus, Pulsatile tinnitus, Conductive hearing loss, aural blConductive hearing loss, aural bl
eeding, and aural discharge.eeding, and aural discharge. Sensorineural hearing loss, vertiSensorineural hearing loss, verti
go, aural pain and go, aural pain and Cranial neuropathy. Such as it cCranial neuropathy. Such as it c
an compress CN IX, X, and XI.an compress CN IX, X, and XI.

Symptoms Symptoms
Functioning tumors, which are rare, can inFunctioning tumors, which are rare, can increase risk of mortality. These active tumocrease risk of mortality. These active tumors secrete catecholamines, which can lead rs secrete catecholamines, which can lead to clinical manifestations of hypertension, to clinical manifestations of hypertension, headaches, palpitations, and tachycardiaheadaches, palpitations, and tachycardia

Signs Signs
Positive Brown’s sign.Positive Brown’s sign. Aural polypAural polyp Cranial nerves Cranial nerves
involvement involvement

Lab testsLab tests
Routine laboratory studies are not helpfulRoutine laboratory studies are not helpful In the rare patient with functioning lesions, In the rare patient with functioning lesions,
preoperative and postoperative catecholapreoperative and postoperative catecholamine measures may help confirm successfmine measures may help confirm successful resection of the lesionul resection of the lesion

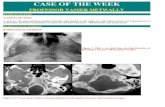
Image studyImage study
A combination of contrast-enhanced CT, A combination of contrast-enhanced CT, MRI, and angiography is ideal for proper diMRI, and angiography is ideal for proper diagnosis and localization of the tumors.agnosis and localization of the tumors. MRI MRI Contrast-enhanced CT Contrast-enhanced CT Angiography remains of paramount importancAngiography remains of paramount importanc
e if the diagnosis is obscure or if embolization e if the diagnosis is obscure or if embolization is planedis planed. .

CTCT
Glomus jugulare tumors are enGlomus jugulare tumors are enhancing soft-tissue masses at thancing soft-tissue masses at the skull base, but skull-base arhe skull base, but skull-base artifact can mask their presence. tifact can mask their presence.
These tumors are seen within tThese tumors are seen within the jugular foramen.he jugular foramen.
The demonstration of bone eroThe demonstration of bone erosion of the jugular foramen and sion of the jugular foramen and petrous apex is often a key finpetrous apex is often a key finding in the diagnosis. Careful rding in the diagnosis. Careful review of bone windows is neceeview of bone windows is necessary. ssary.

MRIMRI
It can show intense tumor enhancement, aIt can show intense tumor enhancement, and is a key finding in the diagnosis. nd is a key finding in the diagnosis.
A salt-and-pepper fine vascular pattern caA salt-and-pepper fine vascular pattern can be seen in the tumors; this finding is sugn be seen in the tumors; this finding is suggestive of intrinsic tumor neovascularity, pgestive of intrinsic tumor neovascularity, particularly on T2-weighted images. articularly on T2-weighted images.

MRIMRI
Images show that enhancing soft-tissue mImages show that enhancing soft-tissue masses protrude both intracranially and extrasses protrude both intracranially and extracranially at the skull base. acranially at the skull base.
Coronal imaging can show tumoral relationCoronal imaging can show tumoral relationships to the brainstem and skull base, and ships to the brainstem and skull base, and deep cervical soft-tissue structuresdeep cervical soft-tissue structures

AGAG
Demonstrating the feeding arteryDemonstrating the feeding artery Jugulare tumors involve higher external carotid brancJugulare tumors involve higher external carotid branc
h vessels; the ascending pharyngeal, tympanic, and oh vessels; the ascending pharyngeal, tympanic, and occipital arteries dominate the arterial blood supply. ccipital arteries dominate the arterial blood supply.
Arteriovenous fistulae may be present. Arteriovenous fistulae may be present. Rarely, the internal carotid and vertebral arteries may Rarely, the internal carotid and vertebral arteries may
contribute feeders to the neoplasms. contribute feeders to the neoplasms. Typically, these tumors are evaluated, with attention pTypically, these tumors are evaluated, with attention p
aid to all potential feeding arteries. aid to all potential feeding arteries.

Contraindication Contraindication
Biopsy is prohibitive for patient with gloBiopsy is prohibitive for patient with glomus jugular tumormus jugular tumor Due potential hemorrhage Due potential hemorrhage

Surgical Intervention Surgical Intervention
Surgery is the preferred method of treatment for Surgery is the preferred method of treatment for glomus tumors. glomus tumors. Most paragangliomas are slow-growing and benign, rMost paragangliomas are slow-growing and benign, r
adiotherapy alone or no treatment at all is preferred in adiotherapy alone or no treatment at all is preferred in elderly patients in whom the risks of surgery are relatielderly patients in whom the risks of surgery are relatively high and the tumor is unlikely to cause serious mvely high and the tumor is unlikely to cause serious morbidity or mortality. orbidity or mortality.
If the patient is young, surgery is the best option that If the patient is young, surgery is the best option that allows total cure.allows total cure.

Surgical InterventionSurgical Intervention
Current techniques are highly successful Current techniques are highly successful with relatively low morbidity rates: Blood with relatively low morbidity rates: Blood loss and CN neuropathies are the major loss and CN neuropathies are the major complications. complications.
Depending on the specific type and Depending on the specific type and location of the tumor, different surgical location of the tumor, different surgical approaches are required. approaches are required.

Surgical InterventionSurgical Intervention
Extensive facial recess approachExtensive facial recess approach

Surgical InterventionSurgical Intervention Mastoid –neck approach: Mastoid –neck approach:
tumors are confined to jugular foramen and tumors are confined to jugular foramen and may extend to the middle ear and mastoid. Tmay extend to the middle ear and mastoid. They do not involve the carotid artery or the inhey do not involve the carotid artery or the intracranial compartment.tracranial compartment.
Infratemporal fossa approach: Infratemporal fossa approach: tumors involve in carotid artery and transdurtumors involve in carotid artery and transdur
al tumor are far more extensive. al tumor are far more extensive.


Radiotherapy Radiotherapy
Gamma-knife irradiation is used in patients who Gamma-knife irradiation is used in patients who are poor candidates for surgical excision or embare poor candidates for surgical excision or embolization due to their age or disease state or becolization due to their age or disease state or because of unacceptable morbidity. ause of unacceptable morbidity.
This procedure is expensive, and clear remissioThis procedure is expensive, and clear remission is not reported. n is not reported.
It can control the tumor and prevent it from growiIt can control the tumor and prevent it from growing larger. ng larger.

Embolization Embolization
Embolization is a common technique used as thEmbolization is a common technique used as the lone treatment option or as a precursor to surgie lone treatment option or as a precursor to surgical excision. cal excision. Starving the lesion of its blood supply and inducing neStarving the lesion of its blood supply and inducing ne
crosis..crosis.. embolization is often used to reduce blood loss, and it embolization is often used to reduce blood loss, and it
has been proven to be highly effective.has been proven to be highly effective. Care must be taken to avoid inadvertent extracranial-iCare must be taken to avoid inadvertent extracranial-i
ntracranial embolization and the subsequent the risk ontracranial embolization and the subsequent the risk of strokef stroke