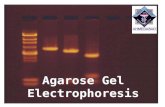
Gel Electrophoresis
-
Upload
marcia-mcfarland -
Category
Documents
-
view
17 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Gel Electrophoresis

Gel ElectrophoresisBy: Brian Barnes, Gary Pope, Eliza Morgan

What is GE?
• Pronounced Gel ee-LEK-tro-fo-REE-sis• Technique for separating DNA or Protein
Molecules into strands according to length

What’s The Point?
• Used to separate DNA and identify strands of interest
• Strands of interest are further analyzed once identified

The Process• Test tube contains DNA• Samples put in different “wells”• Each well contains unique enzyme

The Process• Gel Matrix, usually agarose• Blue tracking dye added for identification
purposes• Electric current applied to move negatively
charged DNA through agarose

• Agarose like a spongy barrier• Shorter strands of DNA move more freely
through the gel• Longer strands have more difficulty moving
The Process

The Process
• Blue Dye is visible moving through gel• As dye touches the end, current is turned off

The Process• Fluorescent dye is added to identify molecules• Size Standards Well contains known DNA
fragments to compare sizes• Measured by Base Pairs (bp)

The Process
• Each band is comprised of millions of fragments of the same size

Analysis
• Now to isolate fragments of interest…• The Blot- a copy of the results which enables
the researcher to identify fragments of interest

Analysis
• Gel is placed in basic solution• DNA denatures into single strands rather than
double helix

Analysis• Transferred to salt solution• Nylon Filter placed on top• Absorbent paper towels placed on filter

Analysis• Salt solution drawn upward by paper towels• DNA adheres to nylon filter• Filter is treated, DNA adheres permanently

Analysis• Radioactive DNA “probe” added• DNA probe complimentary to band of interest• Probe hybridizes with bands of interest

Analysis• Filter washed to remove un-hybridized DNA• X-Ray film placed over filter• Radioactive probe exposed under X-Ray

Using the Analysis• Now the strands of interest are identified• Identical gel is made• DNA of interest is cut out for further analysis