GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. Classification based on Mobile Phase Gas Chromatography Gas - solid Gas - liquid...
Transcript of GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. Classification based on Mobile Phase Gas Chromatography Gas - solid Gas - liquid...

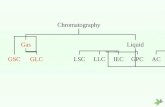
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHYGAS CHROMATOGRAPHY

Classification based on Mobile Classification based on Mobile PhasePhase
Gas ChromatographyGas Chromatography
Gas - solidGas - solid Gas - liquidGas - liquid
Stationary Phase
Sample MUST be volatile at temperatures BELOW 3500C
Pyrolysis GC -heat solid materials
to 500 - 10000Cso they decompose
into gaseous products

Gas chromatography (GC)Gas chromatography (GC), is a common , is a common type of type of chromatography used in used in analytic chemistry for for separating and and analyzing compounds that can be analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. vaporized without decomposition.

In GC, the moving phase (mobile phase) is a In GC, the moving phase (mobile phase) is a carrier gas, usually an inert gas such as helium or carrier gas, usually an inert gas such as helium or nitrogen. nitrogen.
The stationary phase is a microscopic layer of The stationary phase is a microscopic layer of liquid or polymer on an inert solid support, inside liquid or polymer on an inert solid support, inside a piece of glass or metal tubing called a column. a piece of glass or metal tubing called a column.
The instrument used to perform GC is called a gas The instrument used to perform GC is called a gas chromatograph.chromatograph.

– Similar to column chromatography, but differs in 3 ways:Similar to column chromatography, but differs in 3 ways:
Partitioning process carried out between Partitioning process carried out between Moving Gas PhaseMoving Gas Phase and and Stationary Liquid PhaseStationary Liquid Phase
Temperature of gas can be controlledTemperature of gas can be controlled
Concentration of compound in gas phase is a function of the Concentration of compound in gas phase is a function of the vapor pressure vapor pressure only.only.
– GC also known as GC also known as Vapor-Phase ChromatographyVapor-Phase Chromatography (VPC) and (VPC) and Gas-Gas-Liquid Partition ChromatographyLiquid Partition Chromatography (GLPC) (GLPC)

Gas ChromatographyGas ChromatographyLowLow boiling point compounds have boiling point compounds have higher vapor higher vapor pressurespressures..
HighHigh boiling point compounds have boiling point compounds have lower vapor lower vapor pressurespressures requiring more energy to reach equilibrium requiring more energy to reach equilibrium vapor pressure, i.e., atmospheric pressure.vapor pressure, i.e., atmospheric pressure.
Boiling point increases as molecular weight increases.Boiling point increases as molecular weight increases.
04/11/2304/11/2366

Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Gas ChromatographyGas Chromatography– UsesUses
Separation and analysis of organic compoundsSeparation and analysis of organic compoundsTesting purity of compoundsTesting purity of compoundsDetermine relative amounts of components in mixtureDetermine relative amounts of components in mixtureCompound identificationCompound identificationIsolation of pure compounds (microscale work)Isolation of pure compounds (microscale work)
04/11/2304/11/2377

GLC ADVANTAGES
1. Very good separation
2. Time (analysis is short)
3. Small sample is needed - l
4. Good detection system
5. Quantitatively analyzed

Types Of Samples For GC
•Volatilized Comp• Samples that can be converted to volatile compounds• The sample may be organic or inorganic, but not ionic•the molecular weight ranges from 2 to 1000• ( polymers with high molecular weight cannot be separated.

Limited to volatile samples –T of column limited to ~ 380 °C
–Need Pvap of analyte ~ 60 torr at that T –Analytes should have b.p. below 500 °C •Not suitable for thermally labile samples
•Some samples may require intensive preparation –Samples must be soluble and not react with the
column •Requires spectroscopy (usually MS) to confirm
the peak identity
GLC DISADVANTAGES

– Choice of Liquid PhaseChoice of Liquid PhaseMolecular weights, functional groups, and polarities of Molecular weights, functional groups, and polarities of component molecules are factors in selecting liquid phase.component molecules are factors in selecting liquid phase.
– Length of ColumnLength of ColumnSimilar compounds require longer columns than dissimilar Similar compounds require longer columns than dissimilar compounds. Isomeric mixtures often require quite long compounds. Isomeric mixtures often require quite long columnscolumns

InstrumentationInstrumentation

Schematic Diagram of Gas Chromatography

The gaseous compounds being analyzed The gaseous compounds being analyzed interact with the walls of the column, which is interact with the walls of the column, which is coated with different stationary phases.coated with different stationary phases.
This causes each compound to elute at a This causes each compound to elute at a different time, known as the retention time of different time, known as the retention time of the compound. the compound.
The comparison of retention times is what The comparison of retention times is what gives GC its analytical usefulness.gives GC its analytical usefulness.

The time the different compounds in the sample The time the different compounds in the sample spend in the Vapor Phase is a function of their spend in the Vapor Phase is a function of their Vapor Pressure.Vapor Pressure.
The more volatile (Low Boiling Point / Higher Vapor The more volatile (Low Boiling Point / Higher Vapor Pressure) compounds arrive at the end of the Pressure) compounds arrive at the end of the column first and pass into the detectorcolumn first and pass into the detector
The detecting cell responses are recorded on a The detecting cell responses are recorded on a chart, from which the components can be chart, from which the components can be identified both qualitatively and quantitativelyidentified both qualitatively and quantitatively

Instrumentation for GCInstrumentation for GC
Carrier gasCarrier gas– NN22, He, H, He, H22
InjectorInjectorColumnColumnDetectorDetectorComputerComputer
oven

Carrier gas:Carrier gas:The carrier gas must be chemically inert. The carrier gas must be chemically inert. Commonly used gases include nitrogen, Commonly used gases include nitrogen, helium, argon, and carbon dioxide. helium, argon, and carbon dioxide. The choice of carrier gas is often dependant The choice of carrier gas is often dependant upon the type of detector which is used. upon the type of detector which is used. The carrier gas system also associated with The carrier gas system also associated with pressure regulators and flow meters.pressure regulators and flow meters.In addition, it contains a molecular sieve to In addition, it contains a molecular sieve to remove water and other impurities. remove water and other impurities.


Flow Rate of Carrier GasFlow Rate of Carrier Gas
Flow rates must be precisely controlledFlow rates must be precisely controlled– – Reproducible retention times, minimize Reproducible retention times, minimize detector driftdetector driftFlow rates of carrier gas:Flow rates of carrier gas:– – Linear flow rate (cm/s): Linear flow rate (cm/s): u = L/tru = L/tr– – Volumetric flow rate (mL/min): Volumetric flow rate (mL/min): u (π r2)u (π r2)L is length of column, tr is retention time, r is L is length of column, tr is retention time, r is the internal radius of columnthe internal radius of column

Flow control:Flow control:Flow rates are controlled by a 2 stage pressure Flow rates are controlled by a 2 stage pressure regulator:regulator:– At the gas cylinder.At the gas cylinder.– Mounted in the chromatograph.Mounted in the chromatograph.
Inlet pressure 10-50 psi → Inlet pressure 10-50 psi → F = 25-150 ml/min with packed columnF = 25-150 ml/min with packed columnF = 1-25 ml/min with capillary columnF = 1-25 ml/min with capillary column
The flow rate will be constant if the inlet pressure The flow rate will be constant if the inlet pressure remains constant.remains constant.


Flow rate depends on type of columnFlow rate depends on type of column– – Packed column: 25-100 mL/minPacked column: 25-100 mL/min– – Capillary column: μL/min to 1 mL/minCapillary column: μL/min to 1 mL/min• • Flow rate will Flow rate will decrease as column T decrease as column T increasesincreases– – Viscosity of carrier gas increases with TViscosity of carrier gas increases with T

Necessary propertiesNecessary properties
– – INERTINERT• • Does not chemically interact with sampleDoes not chemically interact with sample– – COMPATIBLE with detectorCOMPATIBLE with detector• • No noise or explosionsNo noise or explosions– – HIGHLY PURIFIEDHIGHLY PURIFIED• • Impurities will degrade column and cause noise in Impurities will degrade column and cause noise in detectordetector• “• “Research grade” is very expensive, so purify a Research grade” is very expensive, so purify a cheaper gradecheaper grade

Sample injection port:Sample injection port:The injector is a piece of hardware attached to The injector is a piece of hardware attached to the column head.the column head.It provides the means to introduce a sample into It provides the means to introduce a sample into a continuous flow of carrier gas.a continuous flow of carrier gas.For optimum column efficiency, the sample For optimum column efficiency, the sample should not be too large, and should be should not be too large, and should be introduced onto the column as vapor.introduced onto the column as vapor.Slow injection of large samples causes band Slow injection of large samples causes band broadening and loss of resolution.broadening and loss of resolution.

Common injector types are:Common injector types are:
Microflash vaporizer direct injector:Microflash vaporizer direct injector:– It involves the use of a microsyringe to inject the It involves the use of a microsyringe to inject the
sample through a rubber septum into a flash sample through a rubber septum into a flash vaporizer port located at the head of the column. vaporizer port located at the head of the column.
– The temperature of the sample port is usually The temperature of the sample port is usually about 50°C higher than the boiling point of the about 50°C higher than the boiling point of the least volatile component of the sample. least volatile component of the sample.
– Used for packed columns, where the sample size Used for packed columns, where the sample size vary from a few tenth of microliter to 20 ul.vary from a few tenth of microliter to 20 ul.


Capillary columns require much smaller samples Capillary columns require much smaller samples ( 10( 10-3-3 ul), so a sample splitter system is ul), so a sample splitter system is used to deliver only a small fraction of the used to deliver only a small fraction of the injected sample to the column head, with injected sample to the column head, with the rest going to wastethe rest going to waste..

Sample splitter (Split/Splitless) injector:Sample splitter (Split/Splitless) injector:– The injector can be used in one of two modes; split or The injector can be used in one of two modes; split or
splitless.splitless.– a sample is introduced into a heated small chamber a sample is introduced into a heated small chamber
via a syringe through a septum (the heat facilitates via a syringe through a septum (the heat facilitates volatilization of the sample). volatilization of the sample).
– The vaporized sample/carrier gas mixture then either The vaporized sample/carrier gas mixture then either sweeps entirely (sweeps entirely (splitlesssplitless mode) or as portion ( mode) or as portion (splitsplit mode) into the column. mode) into the column.
– In split mode, a part of the sample/carrier gas mixture In split mode, a part of the sample/carrier gas mixture in the injection chamber is exhausted through the in the injection chamber is exhausted through the split vent. split vent.
– Split injection is preferred when working with samples Split injection is preferred when working with samples with high analyte concentrations (>0.1%).with high analyte concentrations (>0.1%).
– Splitless injection is best suited for trace analysis with Splitless injection is best suited for trace analysis with low amount of analyte (<0.01%). low amount of analyte (<0.01%).


For quantitative work, more reproducible For quantitative work, more reproducible sample size are required and this can be sample size are required and this can be obtained by a rotary sample valve.obtained by a rotary sample valve.

Rotary sample valve:Rotary sample valve: – gaseous samples in collection bottles are gaseous samples in collection bottles are
connected to what is most commonly a six-port connected to what is most commonly a six-port switching valveswitching valve. .
– The carrier gas flow is not interrupted while a The carrier gas flow is not interrupted while a sample can be expanded into a previously sample can be expanded into a previously evacuated sample loop. evacuated sample loop.
– Upon switching, the contents of the sample loop Upon switching, the contents of the sample loop are inserted into the carrier gas stream. are inserted into the carrier gas stream.



Column:Column:There are two general types of column:There are two general types of column:– Packed column Packed column – Capillary column (open tubular). Capillary column (open tubular).
All the GC studies in the early 1950s were carried All the GC studies in the early 1950s were carried out on packed column.out on packed column.
In the late 1950s capillary column were In the late 1950s capillary column were constructed that much superior in speed and constructed that much superior in speed and column efficiency (≈ 300000 plates).column efficiency (≈ 300000 plates).


Packed column:Packed column:Packed columns contain a Packed columns contain a finely divided, inert, solid finely divided, inert, solid support material coated with support material coated with a thin layer of liquid stationary a thin layer of liquid stationary phase. phase. Most packed columns are 1.5 - Most packed columns are 1.5 - 10m in length and have an 10m in length and have an internal diameter of 2 - 4mm.internal diameter of 2 - 4mm.They are made from glass, They are made from glass, metals, or Teflon.metals, or Teflon.

Capillary columns did not gain widespread Capillary columns did not gain widespread until the late 1970s due to several reasons:until the late 1970s due to several reasons:– Small sample capacity.Small sample capacity.– Difficulties in coating the column.Difficulties in coating the column.– Tendencies of columns to clog.Tendencies of columns to clog.– Short lifetimes of poorly prepared columns.Short lifetimes of poorly prepared columns.– Fragileness of columns.Fragileness of columns.– Mechanical problems in sample introduction and Mechanical problems in sample introduction and
connection to the detector.connection to the detector.

Capillary column:Capillary column:Capillary columns have an internal diameter of a few tenths Capillary columns have an internal diameter of a few tenths of a millimeter. of a millimeter. They were constructed of stain-less steel, aluminum, They were constructed of stain-less steel, aluminum, copper, plastic, or glass.copper, plastic, or glass.They can be one of two types; They can be one of two types; wall-coated open tubularwall-coated open tubular (WCOT) or (WCOT) or support-coated open tubularsupport-coated open tubular (SCOT). (SCOT). Wall-coated columns consist of a capillary tube whose Wall-coated columns consist of a capillary tube whose walls are coated with liquid stationary phase. walls are coated with liquid stationary phase. In support-coated columns, the inner wall of the capillary is In support-coated columns, the inner wall of the capillary is lined with a thin layer of support material, onto which the lined with a thin layer of support material, onto which the stationary phase has been adsorbed. stationary phase has been adsorbed. SCOT columns are generally less efficient than WCOT SCOT columns are generally less efficient than WCOT columns, but both types are more efficient than packed columns, but both types are more efficient than packed columns.columns.


In 1979, a new type of WCOT column appeared, In 1979, a new type of WCOT column appeared, the Fused Silica Open Tubular (FSOT) column.the Fused Silica Open Tubular (FSOT) column.It was drawn from specially purified silica that It was drawn from specially purified silica that contains metal oxides.contains metal oxides.These have much thinner walls than the glass These have much thinner walls than the glass capillary columns, and are given strength by an capillary columns, and are given strength by an outside protective polyimide coating.outside protective polyimide coating. These columns are flexible and can be bent into These columns are flexible and can be bent into coils.coils. They have the advantages of physical strength, They have the advantages of physical strength, flexibility and low reactivity.flexibility and low reactivity.


Properties and characteristics of GC columnsProperties and characteristics of GC columnsFSOTWCOTSCOTPacked
Length, m10-10010-10010-1001-6
Inside diameter, mm
0.1-0.530.25-0.750.52-4
Efficiency, plates/m
2000-40001000-4000600-1200500-1000
Sample size, ng10-7510-100010-100010-106
Relative back pressure
LowLow Lowhigh
Relative speedFastFastFastslow
Chemical inertnessBest→→Poorest
FlexibleYesNoNoNo

GC DetectorsGC Detectors

After the components of a mixture are After the components of a mixture are separated using gas chromatography, they separated using gas chromatography, they must be detected as they exit the GC column. must be detected as they exit the GC column.

A A non-selectivenon-selective detector responds to all detector responds to all compounds except the carrier gas,compounds except the carrier gas, a a selectiveselective detector responds to a range of detector responds to a range of compounds with a common physical or compounds with a common physical or chemical property and chemical property and a a specific specific detectordetector responds to a single chemical compound.responds to a single chemical compound.

Detectors can also be grouped into Detectors can also be grouped into concentration dependant concentration dependant detectors and detectors and mass mass flow dependantflow dependant detectors. detectors. The signal from a concentration dependant The signal from a concentration dependant detector is related to detector is related to – the concentration of solute in the detector, the concentration of solute in the detector, – does not usually destroy the sample. does not usually destroy the sample.
Mass flow dependant detectors Mass flow dependant detectors --usually destroy the sample usually destroy the sample -the signal is related to the rate at which solute -the signal is related to the rate at which solute molecules enter the detectormolecules enter the detector. .

The requirements of a GC detector depends The requirements of a GC detector depends on the separation application. on the separation application.
For example, one analysis might require a For example, one analysis might require a detector that is selective for chlorine-detector that is selective for chlorine-containing molecules, another analysis might containing molecules, another analysis might require a detector that is non-destructive so require a detector that is non-destructive so that the analyte can be recovered for further that the analyte can be recovered for further spectroscopic analysis.spectroscopic analysis.

Characteristics of ideal detector:Characteristics of ideal detector:
Adequate sensitivity.Adequate sensitivity.Good stability and reproducibility.Good stability and reproducibility.A linear response to solute.A linear response to solute.A temperature range from room temp. to A temperature range from room temp. to 400400ooC .C .A short response time.A short response time.High reliability and ease of use.High reliability and ease of use.Nondestructive to samples. Nondestructive to samples.

Detectors for GCDetectors for GC
Electron capture (ECD)Electron capture (ECD)Thermal conductivity (TCD)Thermal conductivity (TCD)Flame ionization (FID)Flame ionization (FID)Fourier transform infrared (FTIR)Fourier transform infrared (FTIR)Mass spectrometry (MS)Mass spectrometry (MS)

Method development:Method development:
The The methodmethod is the collection of conditions in is the collection of conditions in which the GC operates for a given analysis. which the GC operates for a given analysis.
Method developmentMethod development is the process of is the process of determining what conditions are adequate determining what conditions are adequate and/or ideal for the analysis required.and/or ideal for the analysis required.

Conditions which can be varied to accommodate a Conditions which can be varied to accommodate a required analysis include:required analysis include:– Column temperature and temperature program.Column temperature and temperature program.– Carrier gas and carrier gas flow rates. Carrier gas and carrier gas flow rates. – Column's stationary phase, diameter and length. Column's stationary phase, diameter and length. – Inlet type and flow rates.Inlet type and flow rates.– Sample size and injection technique.Sample size and injection technique.– Depending on the detector installed on the GC, Depending on the detector installed on the GC,
there may be a number of detector conditions there may be a number of detector conditions that can also be varied. that can also be varied.

Column temperature and temperature Column temperature and temperature program:program:

The column(s) in a GC are contained in an The column(s) in a GC are contained in an oven, the temperature of which is precisely oven, the temperature of which is precisely controlled electronically. controlled electronically.
The optimum column temperature is The optimum column temperature is dependant upon the boiling point of the dependant upon the boiling point of the sample. As a rule of thumb, a temperature sample. As a rule of thumb, a temperature slightly above the average boiling point of the slightly above the average boiling point of the sample results in an elution time of 2 - 30 sample results in an elution time of 2 - 30 minutes.minutes.

The rate at which a sample passes through the The rate at which a sample passes through the column is directly proportional to the column is directly proportional to the temperature of the column. The higher the temperature of the column. The higher the column temperature, the faster the sample column temperature, the faster the sample moves through the column. However, the moves through the column. However, the faster a sample moves through the column, faster a sample moves through the column, the less it interacts with the stationary phase, the less it interacts with the stationary phase, and the less the analytes are separated.and the less the analytes are separated.

If a sample has a wide boiling range, If a sample has a wide boiling range, temperature is ramped either continuously or temperature is ramped either continuously or in steps to provide the desired separation. This in steps to provide the desired separation. This is referred to as a is referred to as a temperature programtemperature program..


Electronic pressure control can also be used to Electronic pressure control can also be used to modify flow rate during the analysis, aiding in modify flow rate during the analysis, aiding in faster run times while keeping acceptable faster run times while keeping acceptable levels of separation.levels of separation.

Carrier gas selection and flow rates:Carrier gas selection and flow rates:The choice of carrier gas is important, with The choice of carrier gas is important, with hydrogen being the most efficient and hydrogen being the most efficient and providing the best separation.providing the best separation. However, helium has a larger range of flow However, helium has a larger range of flow rates that are comparable to hydrogen in rates that are comparable to hydrogen in efficiency, with the added advantage that efficiency, with the added advantage that helium is non-flammable, and works with a helium is non-flammable, and works with a greater number of detectors. greater number of detectors. Therefore, helium is the most common carrier Therefore, helium is the most common carrier gas used.gas used.

The carrier gas flow rate affects the analysis in The carrier gas flow rate affects the analysis in the same way that temperature does.the same way that temperature does.
The higher the flow rate the faster the analysis, The higher the flow rate the faster the analysis, but the lower the separation between analytes. but the lower the separation between analytes.
Selecting the flow rate is therefore the same Selecting the flow rate is therefore the same compromise between the level of separation and compromise between the level of separation and length of analysis as selecting the column length of analysis as selecting the column temperature.temperature.

With GCs made before the 1990s, carrier flow With GCs made before the 1990s, carrier flow rate was controlled indirectly by controlling rate was controlled indirectly by controlling the carrier inlet pressure.the carrier inlet pressure.
Many modern GCs, however, electronically Many modern GCs, however, electronically measure the flow rate, and electronically measure the flow rate, and electronically control the carrier gas pressure to set the flow control the carrier gas pressure to set the flow rate. Consequently, carrier pressures and flow rate. Consequently, carrier pressures and flow rates can be adjusted during the run, creating rates can be adjusted during the run, creating pressure/flow programs similar to pressure/flow programs similar to temperature programs.temperature programs.

Detectors for GCDetectors for GCElectron capture (ECD)Electron capture (ECD)– radioactiveradioactive– good for Xgood for X--, NO, NO22
-- and conjugated and conjugated
Thermal conductivity (TCD)Thermal conductivity (TCD)– change in resistance of heated wirechange in resistance of heated wire
Flame ionization (FID)Flame ionization (FID)– destruction of combustible sample in flame produces destruction of combustible sample in flame produces
measurable currentmeasurable current
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR)Fourier transform infrared (FTIR)Mass spectrometry (MS)Mass spectrometry (MS)