FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA H Ali Djumhana.
-
Upload
alaina-lynch -
Category
Documents
-
view
233 -
download
1
description
Transcript of FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA H Ali Djumhana.

FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIAFUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA
H Ali DjumhanaH Ali Djumhana

DEFINITION
Dyspepsia refers to pain or discomfort centered in the upper abdomen

Centered implies that the pain or discomfort is mainly in or around the midline.
Pain in the right or left hypochondrium is not considered to be representative of dyspepsia

DyspepsiaDyspepsia
Discomfort may be characterized by or associated with upper abdominal fullness, early satiety, bloating , or nausea
These symptoms typically are accompanied by a component of upper abdominal distress

Spectrum of DyspepsiaSpectrum of Dyspepsia

DyspepsiaDyspepsia
The painful or uncomfortable symptoms may be intermittent or continuous , and may or may not be related to meals

Causes of dyspepsiaCauses of dyspepsiaThose with an identified cause for the Those with an identified cause for the symptomssymptomsThose with an identifiable of Those with an identifiable of pathophysiological or microbiological pathophysiological or microbiological abnormalities, however the clinical abnormalities, however the clinical relevance is uncertainrelevance is uncertainThose with no identifiable explanation Those with no identifiable explanation for the symptomsfor the symptoms

FUNCTIONAL FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIADYSPEPSIA
FD is a clinical syndrome which is FD is a clinical syndrome which is defined by chronic or recurrent upper defined by chronic or recurrent upper abdominal symptoms without a cause abdominal symptoms without a cause that is identifiable by conventional that is identifiable by conventional diagnostic means such as endoscopy, diagnostic means such as endoscopy, radiology or histology.radiology or histology.

Diagnostic approachDiagnostic approachSymptom alone are unable to discriminate Symptom alone are unable to discriminate organic dyspepsia from non organic organic dyspepsia from non organic dyspepsiadyspepsiaPatients need to have further examination Patients need to have further examination to rule out relevant organic diseaseto rule out relevant organic diseaseFunctional dyspepsia is a diagnosis of Functional dyspepsia is a diagnosis of exclusion exclusion

Definition of Functional DyspepsiaDefinition of Functional Dyspepsia

CLASSIFICATION (Based 0n Clinical symptoms)
• Ulcer like dyspepsiaPain is the predominant symptom
• Dysmotility like dyspepsiaDiscomfort is the predominant symptom and accompanied with abdominal fullness , early satiety, bloating, or nausea
• Unspecified ( non specific) dyspepsiaThe symptom is not fulfill the criteria for ulcer-like or dysmotility-like3 dyspepsia

FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA Dyspepsia is a very common complaintDyspepsia is a very common complaint..
In western country:In western country:The prevalence rateThe prevalence rate of FD :10-40%. of FD :10-40%. The remission rate The remission rate :10-20% annually:10-20% annually
The recurrence rate The recurrence rate :20-55% :20-55%

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIAFUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA
Pathophysiology of FD is poorly Pathophysiology of FD is poorly understoodunderstood
The symptoms can be associated withThe symptoms can be associated with
Motility abnormality of the stomachMotility abnormality of the stomach
Visceral hyperalgesia/hypersensitivityVisceral hyperalgesia/hypersensitivityHp gastritisHp gastritisPsychosocial factorPsychosocial factor

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIAFUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA
In such a group of patient the symptoms In such a group of patient the symptoms are associated with abnormal motor are associated with abnormal motor function of the stomach:function of the stomach:Impairment of gastric accommodationImpairment of gastric accommodationDelayed gastric emptyingDelayed gastric emptyingAntral hypomotilityAntral hypomotilityBradygastria / TachygastriaBradygastria / TachygastriaIntragastric maldistribution of solid and liquid foodIntragastric maldistribution of solid and liquid foodsmall bowel dysmotilitysmall bowel dysmotility(Malagelada etal.1985;Camilleri etal.1986;Waldron etal.1991;Hveem etal.1996;Stanghellini (Malagelada etal.1985;Camilleri etal.1986;Waldron etal.1991;Hveem etal.1996;Stanghellini etal.1996)etal.1996)

Disorders of gastric neuromuscular function:Disorders of gastric neuromuscular function:myoelectrical and contractile abnormalitiesmyoelectrical and contractile abnormalities
Impaired fundic relaxationImpaired fundic relaxationAbnormal fundic emptyingAbnormal fundic emptying
Weak 3 cpm rhythmWeak 3 cpm rhythm
Dilated gastric antrumDilated gastric antrumAntral hypomotilityAntral hypomotility
GastroparesisGastroparesis
Gastric dysrhythmiasGastric dysrhythmias
Small bowelSmall boweldysmotilitydysmotility

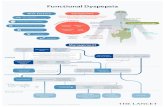
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACHDIAGNOSTIC APPROACH Careful history taking and Physical examinationCareful history taking and Physical examination– Alcohol, smoking, drugs (NSAID), weight loss, abdml Alcohol, smoking, drugs (NSAID), weight loss, abdml
surgery , intractable pain,dysphagia, recurrent vomiting surgery , intractable pain,dysphagia, recurrent vomiting GI bleeding, pallor, jaundice abdominal mass, abdominal GI bleeding, pallor, jaundice abdominal mass, abdominal scar.scar.
Laboratory examinationLaboratory examination– CBC, Liver function test, Renal function test, ECG, Test CBC, Liver function test, Renal function test, ECG, Test
for Hpfor Hp X ray examination and USG upper abdomenX ray examination and USG upper abdomen Endoscopy examination and biopsyEndoscopy examination and biopsy EGG, Gastric emptying study, Manometry, 24 hEGG, Gastric emptying study, Manometry, 24 h pH monitoringpH monitoring

TreatmentTreatmentEmpirical treatment could be started to the patient Empirical treatment could be started to the patient
with uninvestigated dyspepsia without alarm with uninvestigated dyspepsia without alarm symptoms. The treatment should be individualizesymptoms. The treatment should be individualize
First line treatment is prokinetic agent or anti First line treatment is prokinetic agent or anti secretory drug. However the placebo response is secretory drug. However the placebo response is high (20-60%)high (20-60%)
Some patients should be avoid precipitating food or Some patients should be avoid precipitating food or drinkdrink
Other patients may be need anti anxiety or anti Other patients may be need anti anxiety or anti depressant drugsdepressant drugs

Uninvestigated vs InvestigatedUninvestigated vs InvestigatedDyspepsiaDyspepsia
It is important to distinguish the patient who presents dyspepsia that has not been investigated (uninvestigated dyspepsia ) from patients with diagnostic label after investigation, with either a structural diagnosis ( such as Peptic ulcer or GERD) or Functional dyspepsia


Alarm symtomsAlarm symtomsWeight lossWeight lossAnaemiaAnaemiaDysphagiaDysphagiaRecurrent vomitingRecurrent vomitingHaematemesis and or maelenaHaematemesis and or maelenaAbdominal massAbdominal mass

Pharmacologic Treatment for FDPharmacologic Treatment for FDProkinetic agentProkinetic agent– Dopaminergic ( Metoclopramid , Domperidone)Dopaminergic ( Metoclopramid , Domperidone)– Serotonergic ( Cisapride, Ondansetron, Granisetron)Serotonergic ( Cisapride, Ondansetron, Granisetron)
Anti secretionAnti secretion– H2 blockers(Cimetidin,Ranitidin,Nizatidin,Famotidin,Roxatidin)H2 blockers(Cimetidin,Ranitidin,Nizatidin,Famotidin,Roxatidin)– PPI ( Omeprazole,Mesomeprazole,Lansoprazole,Rabeprazole, PPI ( Omeprazole,Mesomeprazole,Lansoprazole,Rabeprazole,
Pantopprazole)Pantopprazole)
AntacidAntacidCytoprotector agentCytoprotector agent– SucralfateSucralfate– RebamipideRebamipide– TrepenonTrepenon
Anti anxiety or Anti depressionAnti anxiety or Anti depression