Foundations of Civilization First Civilizations Egypt Mesopotamia.
-
Upload
candice-mcbride -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Foundations of Civilization First Civilizations Egypt Mesopotamia.

Foundations of Civilization
First CivilizationsEgypt
Mesopotamia

Guiding Questions
What was the relationship between people and their
environment?
What were the push/pull factors for migration?
How does migration affect other civilizations/cultures
What is trade?
How does an economy function?

What I Know about First Civilizations
What I Learned about First Civilizations
What I Want to Learn about First Civilizations
K-W-L Early Civilizations

Foundations of Civilization
Scientist believe that humans
first appeared over two million
years ago.
It is also suggested that the first
humans were wandering Hunters
and Gatherers.
TTYN: What were Hunters and Gatherers?.

Foundations of Civilization
Hunters and Gatherers –
During the Stone Age, Hunters and
Gatherers, also known as Nomads, were
people who moved from place to place, hunting
and gathering their food.
They made simple tools and weapons from
stone, bone, and wood. They developed their
own language, which allowed them to
communicate during a hunt.

Foundations of Civilization Spiritual Beliefs –
Towards the end of the
Old Stone Age,
Nomads began to bury
their dead, which
suggests that they
believed in an afterlife.
Where it all began –
Evidence suggests that the
earliest people lived in E. Africa.
Eventually, their descendants
spread to all parts of the world.
There some evidence that
suggests Nomads migrated over a
land bridge into N. America.

Foundations of Civilization
TTYN: Describe Migration
Migration led to Cultural Diffusion, or the exchange of
ideas, customs, and goods among cultures.
TTYN: From your prior knowledge, describe -
How Cultural Diffusion has had an impact on
American Culture.
How Cultural Diffusion has had an impact on your life

Foundations of Civilization
TTYN: Describe the term Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution(In with the New and out with the Old)
Due to environmental changes and changes to weather
patterns, the Old Stone Age came to a close.
Warmer weather promoted vegetation where,
previously, sheets of ice had dominated the landscape.
Around 10,000 B.C., civilizations made several
important discoveries – they learned how to plant seeds
and domesticate animals.

Foundations of Civilization
TTYN: Describe the term Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution(In with the New and out with the Old)
Too tired to wander - The need to wander was over
People could live in permanent settlements
The end of the Old Stone Age and the beginning of the
New Stone Age, or Neolithic Period.
FYI – Many historians refer to the Neolithic Revolution as
the Agricultural Revolution because farming and
domestic animals changed the way people lived.

Foundations of Civilization
TTYN: Try to Identify at least three different ways that
life may have changed during the Neolithic Revolution -
1. Permanent Settlements
2. New Social Classes – Not everything was “peaches
and cream.” When resources were scarce, groups
went to war and Chiefs or headsmen emerged. As a
result, men gained prestige and obtained great
power and influence.

Foundations of Civilization
TTYN: Try to Identify at least three different ways that life may have changed during the Neolithic Revolution -
3. New Technology –
• The wheel
• Metal weapons
• Metal tools
• Plows
• Calendar
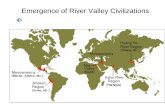
There’s no place like homeWhere did most
civilizations develop?
First civilizations began to develop along river valleys. The rich fertile lands helped new civilizations thrive.

Pa l e o l i t h i c v s . N e o l i t h i cCompare and Contrast

Foundations of Civilization
Pa l e o l i t h i c v s . N e o l i t h i c
lasted 2.5 million years to
8000 BC
Otherwise known as the
Old Stone age”
Cave paintings
Hunters and gatherers
nomadic ( never stayed in
one place (followed herd)
Science and Technology
Stone tools, use of rocks,
teeth
“Neo” means new
New Stone Age
People learn to farm
No longer have to follow
herd
Can stay in one place
and live
establishment of
villages
permanent homes
Domestication of
Animals
people learn to raise
animals and
keep them as a food
source
pigs, chickens, cows

New tools make
farming easier and life
Use of Bronze
Plates
Bowls
Ox drawn
Development of
agriculture
Food surpluses
This period is also
sometimes called the
Agricultural Revolution
So, What does it all
MEAN?
People stopped
chasing food and
started
living in permanent
settlements growth
of villages, towns,
cities
Leisure time will lead
to advancements in
record keeping and
technology
Foundations of Civilization

Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Early Civilizations
TTYN - Can you name one of the earliest civilizations? Hint!! This country recently experienced a revolution
EGYPT

3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 5003500
2625 B.C.Old KingdomBegins
1539 B.C.New KingdomBegins
730 B.C.Nubian DynastyRules Egypt
270 B.C.Meroitic PeriodIn Kush
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Timeline

Along with the Great Pyramid
of Giza, the Sphinx is one of
the greatest enigmas and the
most studied ancient
monument of mankind’s
history. The whole complex
of Giza, composed of the
Sphinx, the Great Pyramid,
other pyramids, and distinct
structures, definitely holds
the key to understanding
advanced past civilizations.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Two schools of thoughts concerning
the origin, age, and the builder of the
Sphinx in Egypt.
First, that Pharaoh Khafre built the
Sphinx around 2500 B.C., which suggests that the
Sphinx is about 5,000 years old.
Second, that the Sphinx was built by an advanced
civilization 8,000 to 10,000 B.C. This school of thought
has been around for hundreds of years, but new
findings give it more credibility.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

The second finding would suggest that
mankind’s history is older than the
6,000 years of Christian tradition
and an advanced ancient civilization
built the Sphinx. This would mean that
history would have to be rewritten or a better
understanding of Moses account of creation.
TTYN: Why is knowing when the Sphinx was built
important?
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Geography

Ancient Middle East and Egypt Geography

Ancient Middle East and Egypt Geography

Ancient Middle East and Egypt Geography

Geography
Most of Egypt is a desert
Early civilizations settled along
the Nile River.
The Nile River provided water for
drinking and irrigation.
The river also served as a
transportation highway.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Major River: Nile River
“Gift of the Nile”
Each year the Nile
floods leaving behind
rich resources (silt)
which aid in farming
Unlike the Tigris and
Euphrates- Nile floods
like clockwork (yearly)

People were not able to survive in the harsh desert
and began to move into the Nile River Valley.
The Nile River Valley has
fertile land along each side of
the river.
It is the world’s longest river.
The river flows northward for more
than 4,000 miles from its main source at
Lake Victoria in central Africa.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Vocabulary
Savanna
A grassy plain with many trees and animals.
Delta
Low land formed at the mouth of some rivers by the silt the river drops there.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt


Fertile soil
Deserts provided protection and shelter from outside
influences
Access to Mediterranean increased and expanded
trade and culture….Cultural Diffusion!!!
Culture was one of stability and not rapid change
Deserts were an important source of minerals and
building supplies (copper, tin, gold and natron, the
drying agent used in mummification
The Geographical Effects
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

What I Know about First Civilizations
What I Learned about First Civilizations
What I Want to Learn about First Civilizations
K-W-L Early Civilizations

Religion in Ancient Egypt

Government in Ancient Egypt

Religion
Source of Egyptian Religion
The Ancient Egyptians believed in many gods
TTYN: The belief in many gods is known as what?
and used stories about them to explain events in
nature.
They believed the sun was a god that was born each
day and died each night.
They believed religion was important to their survival
in the Nile River Valley.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Religion
Egyptians were polytheistic.
In other words, they believed in
more than one god.
For example, the sun god,
Amon-Ra or Amon-Re was the
chief god, Osiris was the god of
the Nile, and a host of other gods
who had specific functions.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
TTYN: If
polytheistic is the
belief in more than
one god, what is
monotheistic ?

Thoth – the god of wisdom
Hathor – the goddess of love
Orisis - ruled over the dead
Hapi – the god of the river
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Egyptian gods

The Egyptians prayed to their gods and
believed in life after death – the Afterlife
A book of prayers called The Book of the Dead was
placed in their tombs , which is to be used as a guide in
the afterlife.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
The Afterlife

Amon Ra
The cornerstone of the
religious faith for Egyptians
was a belief in life after death.
Egyptians prepared their dead
for the afterlife through the
preservation process called
mummification
More on Religion….
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Government, Society, and Contributions
Government
The Egyptian ruler was called a
pharaoh and Egyptians believed he was
both a god and a king.
After the death of a pharaoh, power
usually
passed to another member of the family.
Thus, these ruling families were called
dynasties.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Government style known as a Theocracy

Government, Society, and Contributions
Society
Egyptian society was divided into classes.
The pharaoh was at the top
Next were the priests, who served the gods and
goddesses, and third were the nobles, who fought the
pharaoh’s wars.
Next were the craftspeople and merchants
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Government, Society, and Contributions
Society
The biggest group, the peasant farmers.
The lowest group were the slaves.
Women had a higher status in Egyptian society than
in any other ancient civilization…a woman could own
property, conduct business transactions, and obtain a
divorce.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Government, Society, and ContributionsContributions
Egyptians made many advancements in science and art.
Mummifications helped them understand the human
body, which helped them diagnose illnesses and
perform surgery. They developed a calendar, which is
very similar to what we use today. They also created
picture writing called hieroglyphics. Egyptian temples,
monuments, and pyramids have survived thousands of
years.
Ancient Middle East and Egypt

http://www.nationalgeographic.com/pyramids/pyramids.htmlEgyptian Hieroglyphics
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
The Rosetta Stone: Key to understanding hieroglyphics
Found in 1799 by the French
Took 23 years to crack code

Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Science and Technology:
Pyramids

Ancient Middle East and Egypt
The first form of paper Something they could write on other than stone
or clay
Papyrus

Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Calendars• 365 day calendar (to keep track of
flooding of Nile) …learned this by watching stars


Achievements

VI. Ramses II (1279-1213)

VI. Tutankhamen 1335-1325 BCE
(King Tut)
child ruler
ruled nine years, died at 18
young death meant burial
in the tomb of a lesser
person (noble) resulting in
preservation

Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Ancient Middle East and Egypt

Ancient Middle East and Egypt

In summary format, discuss the development
of locally dominant towns along the Nile in the
Egyptian Neolithic. How might their
development set the stage for the development
of a unified Egypt?
Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Short-Answer Response

What I Know about First Civilizations
What I Learned about First Civilizations
What I Want to Learn about First Civilizations
K-W-L Early Civilizations

MesopotamiaAncient Middle East and Egypt
The Land Between Two Rivers


TimelineMesopotamia was ruled by four
different empires
Sumerian 3,500 BC – 2,300 BC
Akkadian 2,300 BC – 1,900 BC
Babylonian 1,900 BC – 1,300 BC
Assyrian 1,300 BC – 612 BC

Mesopotamia Location - Located along the Tigris and
Euphrates Rivers, the first civilization in Mesopotamia
was Sumer (Su Mer).
Growth - Villages grew into busy cities and these
city-states, political units made up a city and the
surrounding land, made up the civilizations of Sumer.
Growing Pains - As the cities grew, various city-
states fought each other for land and water.

Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a Greek word meaning between
the rivers
Ancient Mesopotamia was located between the Tigris
and Euphrates Rivers
Most of Mesopotamia was located in present day
Iraq
The hot dry climate was mixed with seasonal
flooding from the rivers
TTYN – Identify and describe one negative and one
positive that would result from the flooding of the
rivers.



Geography
To the Northeast of Egypt, the
Fertile Crescent, a region of good
Farmland created by the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers,
stretches from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean.
In this area great civilizations developed, giving the
Fertile Crescent the name “the cradle of
civilization.”
Mesopotamia

Agriculture - (The Fertile Crescent)
Farmers turned the land into a rich
food growing area by using irrigation
and the plow
Farmers grew wheat, barley, dates, and other
vegetables and fruit
They raised goat, pig, sheep and cattle
Irrigation created a surplus of food which led to the
growth of cities…remember the flooding issue???
Surplus led to a flourishing system of trade
Mesopotamia

Sumerian Civilization
Making do with what they had
Had few raw materials such as stone and lumber
Built with earth and water
Bricks of clay
The First Cities
The Ziggurats
Mesopotamia


Economy
The Mesopotamian plain was lacking in resources such as metals,
timber, stone, and grapevines, so the Sumerians had to trade
abroad to get them
At first, the Sumerians traded surplus barley for these goods
Later, the Sumerians began to manufacture trading goods that
they could transport more easily, such as cloth and bronze
ornaments
The Mesopotamians made written contracts, loans and created a
credit system
They used a barter system
Mesopotamia

Trade Routes

Government Sumer – included many independent city-states
TTYN: Can you think of a possible downside to having
so many independent city-states in such close
proximity to each other?
Protection – people would turn to courageous and
resourceful war leaders, which would turn into
hereditary ruler
Mesopotamia

Government Role of the Ruler
Maintaining city walls and irrigation systems
Led armies into war and enforced laws
Employed scribes
Collected taxes and kept records
Chief servant to the gods
Mesopotamia

Social Classes
Mesopotamia

Social Classes
Mesopotamia
Ruling Family, Leading
Officials, High Priests
Middle Class – Merchants, Artisans,
and lesser Priests
The majority of people and peasant farmers

Mesopotamia - (Land of Firsts)
First to invent the wheel
First to use sails on boats
One of first to make up a
story (Gilgamesh)
First to use cuneiform
(writing)
Mesopotamia is known as, “The Cradle of Civilization,”
because it was first in many things: First to use the
calendar
First to use the seeder
plow
First to give a number
place value and
recognize the concept
of zeroPair and Share – Select at least five “First’s” and describe why they may be important to civilization of Mesopotamia

Language
Mesopotamians were the first to
use writing (around 3,000 BC)
Cuneiform - The system of
writing was called cuneiform
Cuneiform was wedge shaped
symbols pressed into clay
tablets
The Mesopotamians wrote many
myths
The most famous was the epic
poem called Gilgamesh
Why Writing was
important then…and
still is
Writing allowed
people to keep
records of their
transactions
People could send
messages with
couriers to far away
lands without
traveling..exchange
ideas and information
Writing allowed
people to pass on
their accumulated
knowledge to future
generations…
HISTORY!!
Mesopotamia

Cuneiform Tablets
Mesopotamia

Religion
The people of Mesopotamia believed in many gods
TTYN – The belief in many gods is known as?
Each town was protected by its own, unique deity or
god
The temple, the center of worship, was also the
center of every city
Around the year 2000 B.C., temple towers called
ziggurats were built to link heaven and earth
Mesopotamia


The Mesopotamians had written laws that everyone
in the empire had to follow
There were 282 laws created by King Hammurabi
Known as Hammurabi's Code, the laws were written
in stone and placed in a public location
The Mesopotamians believed the gods called the king
to establish justice and order; whoever disobeyed the
king disobeyed the gods
Hammurabi
Mesopotamia

Concept Ladder
Topic: Hammurabi Code Hammurabi Code

city-state
Definition: A self-governing state consisting of a city and
surrounding territory
Context: Nippur was the most important city-state in Sumer.
cuneiform
Definition: The system of writing used by the ancient Sumerians
Context: Cuneiform writing looks more like symbols than pictures.
demon
Definition: An evil spirit
Context: According to Sumerian legend, Gilgamesh killed the
demon Huwawa with the help of the sun god.
Vocab

scribe
Definition: A person paid to write, especially in ancient times
Context: Mesopotamian scribes worked closely with the priests and
kings.
stylus
Definition: A hard, pointed writing tool cut from a reed
Context: Sumerian scribe wrote with styluses they made from reeds.
Sumerians
Definition: Residents of Sumer, a region of the ancient land of
Mesopotamia
Context: The Sumerians developed many inventions, such as the wheel
and the plow.
tablet
Definition: A flat slab – often of clay or stone – suitable for an inscription
Context: The Sumerians etched symbols into wet clay tablets to create a
permanent document of their activities.

epic
Definition: A long poem telling the deeds of a hero and often centering
on the ideals of a nation or culture
Context: The Epic of Gilgamesh teaches us to enjoy the time we have on
Earth.
immortality
Definition: The quality or state of having an endless life
Context: Gilgamesh was unable to achieve immortality, but he was able
to leave behind a legacy through the work he had done during his
lifetime.
Mesopotamia
Definition: An ancient land located where we find the modern country of
Iraq
Context: Mesopotamia means, “land between the rivers” and got its
name because it was located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Nippur
Definition: A major city-state in the ancient Sumerian region of
Mesopotamia
Context: Nippur was a busy trading center in Sumer and its most
important religious city.

What I Know about First Civilizations
What I Learned about First Civilizations
What I Want to Learn about First Civilizations
K-W-L Early Civilizations

Mesopotamia DBQ









Additional Resources












Daily Lesson Planner






Student Notes Packet

Notes Packet Instructions and Suggestions:
How extensive your Notes Packet really depends on whether or
not if you ask your students to maintain a notebook.
My notes packets include space for notes PLUS a copy of each
literacy activity I ask the students to complete
I require my students to re-write each ‘Do Now’ and/or TTYN
question PLUS to record their response in their Notes Packet
Grading the Notes Packet – I grade based on accuracy and depth.
Particular attention is given to literacy activities and ‘Do
Now’s/TTYN”

Next….Warfare and the emergence of the Persian Empire