Formal case ( 5 problems duodenal ulcer , hypertension , anemia , smoking , headache )
-
Upload
aya-ali -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.241 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Formal case ( 5 problems duodenal ulcer , hypertension , anemia , smoking , headache )

King Saud University
College of Pharmacy
Clinical Pharmacy
Dept PHCl 429
Facilitator: T.A. Ghadah Assiri, MSc
Presenting students:
Aya Kamel
Malak Algamdi
Najwa AlOtaibi
Salma Alsalman
Formal Case Presentation Code: 04
Dec-18-2013

› Name: A.S
› Age: 55 years
› Gender: male
› Race: African American
› Height: 172 cm
› Weight: 73 Kg
› BMI:
Patient Information

› A.S present to clinic complaining of “epigastric abdominal pain, vague abdominal discomfort and dizziness”
Chief Complaint (CC)

› Epigasteric abdominal pain, vague abdominal discomfort and
dizziness. His pain started 1 year ago he took OTC antacid with
no improvement the pain come between 1-3 am and relived
by food He describes it of being moderately to severe.
› He complains of postprandial bloating and darkening of stool
one week ago.
History of Present illness (HPI)

› Also he suffers from moderate throbbing head pain unilateral
and temporal , the pain stay for 2 hours in the morning.
› The patient had hypertension 5 years ago which is
uncontrolled due to issue of non-compliance.
History of Present illness (HPI)

› Hypertension (Stage 1) diagnosed 5 years ago.
Past Medical History (PMH)

› Current prescribed medication :-
1. Furosemide 40 mg orally twice daily started × 5 years
› Current non-prescribed medications:-
1. Ibuprofen 200 to 400 mg orally qid , prn
2. Maalox 30 ml orally after meal and at bed time
3. Bismuth subsailcylate occasional use (1-2 times a week )
Medication History

Medication History
Drug Dose Route Frequency Indication
Furosemide 40 mg orally BID HTN
a- Current prescribed medications:
b- Current Non-prescribed medications:
Drug Dose Route Frequency Indication
Ibuprofen 200 to 400 mg
Orally QID PRN Headache
Maalox 30 ml Orally BID**after meal and at bed
time
Duodenal Ulcer
Bismuth subsailcylate Not known Orally 1-2 times/week Duodenal Ulcer
c- Supplements: None

› NKA
Allergies

› His father died at age of 59 of shock due to severe GI bleeding 2ry to untreated PUD.
› The Mother died in a motor vehicle accident 4 years ago.
Family History (FH)

› He is a manger in a stress job, married with two grown children.
› He smokes 1ppd of cigarettes for 10 years .
Social History (SH)

Slightly pale , thin male in moderate distress GEN
BP average 185 \ 96 , HR 90 , RR 20 , T 37 C , Wt 73 Kg , Ht 172 cm VS
WNLHEENT
WNLChest
Mild tenderness , no masses Abd
Non-tender, melenic stool found in rectal valut , stool heme +veRect
WNLExt
Memory intact ; no nystagmus ; no tremor ; or ataxia ; (-) Romberg : CN II-XII INTACT ; SENSORY INTAVT ; DTRs : 2+ throughout : babinski (-) bilaterallly .
Neuro
NormalECG
Physical Examination (PE)

WBC 9 Th/mm3Na 137 mg/dL
RBC 4.23 Mil/mm3K 4.0 mEq/dL
Hgb 11.0 mg/dLCl 106 mEq/dL
Hct 33HCO3 26.8 mEq/dL
MCV 79Cr 1.4 mg/dL
MCH 26BUN 32 mg/dL
Glu 100 mg/dL
Laboratory Data:

The patient has 5 main problems , almost all of them are untreated .
General overview about the case

Problem list:1. Untreated Peptic Ulcer.
2. Untreated Anemia.
3. Untreated Headache.
4. Uncontrolled Hypertension.
5. Untreated Smoking.
General overview about the case

NSAID Induced Duodenal Ulcer

› Subjective :-
• He complains clinic of epigasteric abdominal pain, vagueabdominal discomfort and dizziness.
• He noticed darkening of stool one week ago.
• The pain come between 1-3 am and relived by food, hedescribes it of being moderately to severe.
• Manager of stressful job.
• His father died at age of 59 of shock due to severe GIbleeding 2ry to untreated PUD.
SOAP Assessment

› Objectives :-
• Hgb 11.0 mg/dL
• Hct 33
• Abd: Mild tenderness, no masses.
• Rect: Non-tender ; melenic stool found in rectal valut ; stool heme +ve.
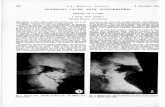
• Endoscopy shows multiple gastric ulcer.
SOAP Assessment

A.S 55 year-old African-American male appears slightly pale suffer from epigastric abdominal pain which is releived by food he has many risk factor for peptic ulcer his endoscopy shows multiple gastric ulcer , he tried to releive pain by otcantacid but its not effective in contrast bismuth subsalycilateworsen his case and cause bleeding , his fecal blood test gives positive heme and his hemoglobin level is low
He has NSAID induced duodenal ulcer with secondary gastericulcer and ulcerative bleeding , he also needs further tests for H.Pylori
Patient needs initial treatment by high dose PPI to prevent complication and treat the symptoms .
Assesment

› Assessment :-
• Drug related problem (DRP):Category/Subcategory: Indication / Need Additional Drug Therapy
(Untreated condition).
• Statement :
A.S 55 year-old African-American male who suffers fromepigastric abdominal pain 1 year ago which not relieved by usingOTC antacid (Maalox & Bismuth subsalicylate ) needs additionaldrug therapy.
SOAP Assessment

› Assessment :-
• Drug related problem (DRP):Category/Subcategory: Safety (Adverse drug reaction) / Undesirable
effect.
• Statement :
A.S 55 year-old African-American male who takes OTC bisthmussubsalicylate for epigasteric abdominal pain , but his condition becomeworse and develops bleeding as a side effect which increase risk ofrecuurance. He needs to stop using it.
SOAP Assessment

• Drug related problem (DRP):Category/Subcategory: Safety (Adverse drug reaction) / Undesirable
effect.
A.S 55 year-old African-American male who takes Ibuprofen ( Nsaid ) OTC to treat headache which causing undesirable effect a duodenal ulcer and may cause further complication , the drug must be stooped and choose appropriate alternatives.
SOAP Assessment

Fig.1.1

› Short term goals :
1. Prevent complication (perforation, penetration, obstruction, malignancy
2. Promote ulcer healing Stop the ulcer bleeding.
3. Symptoms relive.
› Long term goals :
1. Preventing recurrence and avoiding potential complications.
2. Reduce financial cost of treatment .
Therapeutic goal

According to blatchford score, patient has high risk of bleeding.
Fig.1.2

› Ranitidine double dose 300 mg q.i.d
› Endoscopy treatment
› Injection treatment .
Therapeutic Alternatives

› Stop using ibuprofen to prevent further complication.
› Stop using bismuth subsalicylate to minimize the risk of bleeding.
› Continue using Maalox to relieve symptoms
Pharmacological Intervention
Cost Trade name
Duration Dosage form
Rout Frequency Dose Drug
Maalox4-6 weeks Suspension Orally After meals and
at bed time
30 ml Aluminummagnesium
hydroxide

› Start
Pharmacological Intervention
CostTradename
Duration Dosage form
RoutFrequency Dose Drug
27 S.RGasec4-6 weeksCapsule Orally B.i.d1 hour before meals
20 mg Omeprazole

› Omega -3 fatty acids has anti-inflamatory effect help to protect the stomach from ulcers.
› Acupuncture treatments.
› Endoscopy treatment.
› Injection therapy.
› Yoga practice to manage stress.
Non-pharmacological Intervention

› Efficacy
• Symptomatic improvement.
› Safety
• The appearance of adverse events like: muscle cramps, muscle weakness or limp feeling; seizures
Monitoring

Testing for H.pylori
Patients taking the test should stop taking PPIs for at least 2 weeks (they interfere with the test) and starve for 4 hours before.
Fecal Occult Blood Test
CBC & Hemoglobin
Blood urea
Mg level
Monitoring

› Assess the adherence.
› Assess the signs and symptoms of progression of ulcer
› Follow up session should be scheduled 2-4 weeks after initiating the therapy.
› If patient is H.pylori positive start eradicating regimen .
› Repeat endoscopy to confirm healing at 6 to 8 weeks.
› If ulcer healed decrease omeprazole dose gradually to maintenance dose to prevent recurrence.
Follow-up

› Take omeprazole 1 hour before meals .
› Take vitamins and iron supplement 1-2 hours after taking Omeprazole and Antacid .
› Avoid spicy food and xanthin containing beverage and, drinks containing caffeine.
› Avoid heavy meals before bed time.
› Smoking increases the amount of acid produced by the stomach . need smoking cessation plan .
› Encourage small frequent low caloric meals.
› Avoid ulcerating drug e.g NSAIDs,Corticosteroid.
› Eat Magnesium containing food like banana, Avocado and fish.
Patient Education

Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Lanza FL, Chan FKL, Quigley EMM, Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009
›Management of patients with ulcer bleeding.Laine L, Jensen DM. Management of patients with ulcer bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;107(3):345-60.
Reffrence :

› Fig.1.1
› Management and Prevention of upper GI Bleeding Guidelines 2009 by ACCPhttp://www.eguidelines.co.uk/eguidelinesmain/guidelines/summaries/gastrointestinal/nice_dyspepsia.php?page=3
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1399777/
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/545617_3
› Fig.1.2Management of Dyspepsia 2005 BY ACG Nicholas J. Talley, M.D., Ph.D., Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, 200 First Street S.W., PL6–56, Rochester, MN 55905.
Reffrences


› Subjective :-
• He has noticed slight darkening of his stool and dizziness.
› Objectives :-
• Stool heme (+).
• Hgb 11.0 mg/dL Low.
• Hct 33 Low.
• MVC 79 Low.
• MCH 26 Normal.
• Its Microcytic Anemia ( MVC is below 80 Fl ).
SOAP Assessment

› Assessment :-
• DRP category and sub- category:
Indication/Need Additional Drug Therapy
(untreated condition)
• Medical problems:
Untreated Anemia
• Statement:
A.S is a 55 years old African male suffering from anemia which need a medical intervention , that due to GI bleeding secondary to untreated PUD.
SOAP Assessment

› Short term goals :-
• Normalized lab value that related to anemia ( Hgb, Hct, MVC).
• Alleviate signs and symptoms.
› Long term goal :-
• Prevent recurrence of anemia.
Therapeutic Goals

1. Ferrous Sulfate 325 mg.
2. Ferrous Gluconate 325 mg.
3. Polysaccharide iron complex 150 mg.
Therapeutic Alternatives

› Start :
› The hemoglobin concentration should rise by 2 to 4 g/dl after 3 weeks.
Pharmacological Intervention
CostDurationDosage Form
RoutFrequencyDoseDrug
5 SR3 monthsTabletOrallyEvery 12 hours
325 mgFerrous Sulphate

› Advise the patient to eat more
foods that are rich in iron.
› Avoid Phosphate, Calcium, Tea
(tannic acid), Coffee, Colas,
Soy protein and Bran/fiber
which are inhibit Iron absorption.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Figure.2.1 “Iron-Rich Foods”
MedScape : http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/452692_8

› Iron therapy should cause :
• Reticulocytosis in 5 to 7 days.
• Raise Hb by 2 to 4 g/dL every 3 weeks.
› Once normal, the Hb concentration and red cell indices should be monitored at intervals.
• Every 3 month for 1 year, then after a further year, and again if symptoms of anemia develop after that.
Monitoring and Follow-up

› Advise patient to expect iron to darken stools.
› The drug may cause constipation or nausea, to overcome this
problem advice the patient to drink water and eat fibers.
› Instruct patient to avoid eating eggs, milk, cheese, yogurt, tea
coffee within 1 h before or 2h after taking iron supplement.
› For maximum absorption take on empty stomach, but may take
with or after meals to minimize GI irritation.
› Vitamin C may enhance absorption.
Patient Education

› (1) Barbara g. , joseph t. , terry l. , cecily v.. Hematologic disorder. In: cecily v. (eds.)pharmacotherapy handbook . 7th ed. new York : McGraw-hill companies ; 2009. p(363-370)
› (2) THAD WILKINS, MD; NAIMAN KHAN, MD; AKASH NABH, MD; and ROBERT R. SCHADE, MD, Georgia. Diagnosis and Management of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. http://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0301/p469.html (accessed 3-april-2013).
› (3) Irene Alton, MS, RD. IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA. In: Jamie Stang, PhD, MPH, RD (eds.)GUIDELINES FOR ADOLESCENT NUTRITION SERVICES. 1st ed. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota;; 2005. p(101-108)
› (4)http://www.oocities.org/hotsprings/falls/4809/meds/ferroussulfate.htm
› (5) http://nassersite.com/drugdb/view.php?id=2207
References

Migraine headache

SOAP Assessment
Subjective “Throbbing head pain, unilateral, temporal, occurring in the morning, which lasts for 2 hours, with photophobia and phonophobia”
Objective None
Assessment A.S is a 55 years old African male. He developed migraine headache without aura, he is receiving Ibuprofen around 3-4 times/week this caused adverse effects on him, he needs different drug therapy since his previous drug therapy is unsafe.Medical ProblemMigraine headache without auraDrug Related ProblemCategory/SubcategorySafety / Adverse drug reaction (undesirable effect)

›Goals for acute migraine treatment:
• Treat migraine attacks rapidly and consistently without recurrence.
• Restore the patient’s ability to function.
• Minimize the use of backup and rescue medications.
• Be cost-effective in overall management.
• Cause minimal or no adverse effects.
Therapeutic Goals

› Long term goals :
• Reduce migraine frequency, severity, and disability. (Aim for fewer than 5 headache days per month.)
• Reduce reliance on poorly tolerated, ineffective, or unwanted acute pharmacotherapies.
• Improve quality of life.
• Avoid escalation of headache medication use.
• Educate and enable patients to manage their disease.
• Reduce headache-related distress and psychological symptoms.
Therapeutic Goals

Other alternative
› Sumatriptan
› Naratriptan
Therapeutic alternativeDrug Dosage Rout of
administration
Comment Cost (month)
Isometheptene65mg/dichloral-
phenazone 100 mg/
acetaminophen 325 mg (Midrin)
2 capsules at onset; repeat 1 capsule
every hour as needed
orally Maximum of 6 capsules/day and
20capsules/month
70 SR

› Application of ice to the head and periods of rest or sleep, usually in a dark, quiet environment, may be beneficial.
› Preventive management should begin with identification and avoidance of factors that provoke migraine attacks.
Non-pharmacological treatment

› A headache diary that records the frequency, severity, and duration of attacks can facilitate identification of migraine triggers.
› Patient also can benefit from adherence to a wellness program that includes regular sleep, exercise, and good eating habits, smoking cessation, and limited caffeine intake. Behavioral intervention such as Relaxation Training, Biofeedback, and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Non-pharmacological treatment

Non-pharmacological treatment
Patient triggers How to manage them
Environmental triggers
Tobacco smoking Smoking cessation
Loud noises Rest or sleep in a quiet environment
Glare or flikering lights Rest or sleep in a dark environment
Behavioral-physiologic triggers
Stress Relaxation Training, Biofeedback, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy

Pharmacological Intervention
Drug Dosage Rout of administration
Comment Cost (month)
FIORICET (butalbital,
acetaminophen, and caffeine)
1-2 tablet every 4-6 hours
orally Limit dose to 4 tablets/day and
usage to 2 days/week
26.5 SR

› Patients should be specifically assessed at follow-up visits to determine if their acute migraine medications need to be changed.
› Evaluate the effectiveness of therapy through the use of patient diaries that record headache frequency, drug use, and disability levels
Monitoring and follow up

› Educate the patient about Keeping a headache diary that can help identify frequency, severity, triggers, and response to treatment.
› Patients should be advised to adjust their lifestyle to avoid exacerbating their migraine (e.g., avoid missing meals; avoid dehydration; maintain adequate, regular sleep).
› A general exercise program should be considered part of comprehensive migraine management.
› Patient should Learn and use stress management skills (relaxation training, biofeedback and cognitive behavioral therapy).
› Patient should know that It may not be possible to eliminate the primary headache completely.
Patient Education

› About Medication:
› Advise patients to take their medication early in their migraine attack, where possible, to improve effectiveness.
› Educate the patient of the risk of chronic daily headaches is increased if headache treatment medication are used more than nine days a month.
› Fioricet may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Such tasks should be avoided while taking this product.
Patient Education

› Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression when taken with Fioricet, and should be avoided.
› Butalbital may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
Patient Education

DiPiro, Joseph T. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach.Neurologic Disorder “Headache“. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill
Medical, 2011. 106-131.Pages(1066-1075)
-primary-for-http://www.topalbertadoctors.org/file/guidelineadults.pdf-in-headache-of-management-care
Headache.pdfhttps://www.icsi.org/_asset/qwrznq/
pdf.60854/60854/13901://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/http
pdf.60853/60853/13901http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/
https://www.icsi.org/_asset/qwrznq/Headache.pdf
Reference

Uncontrolled Hypertension

Subjective
55-year-old-African-American male. HTN (uncontrolled) x5 years. The patient non-compliance with his medication.

Objective
AGE= 55 years old BP= 158/96 mmHg HR= 90 bpm Na= 137 mg/dL K= 4.0 mEq/dL Cr= 1.4 mg/dL BUN= 32 mg/dL WEIGHT= 73 kg HIGHT= 172 cm BMI= 24.67 Furosemide 40 mg orally twice daily, started x5 years

CV Risk factor Smoking
Age ( 55 years)
High stress job
Increase of Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) > 20 mmHg
Increase of Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) > 10 mmHg

AssessmentThe patient is African American in stage I primary hypertension without comorbid disease or drug is responsible for elevating BP.
His blood pressure barely controlled due to issues of compliance and effectiveness.
So its current therapy Not the best choice even if he compliant with his medication.
The Thiazide–type diuretics is first line therapy for this condition and particularly chlorthalidone.
The SBP is more than 15 mmHg above the goal and the DBP is more than 10 mmHg above the goal,(the goal is 140/90 mmHg) so the patient need for combination therapy to attain and maintain BP goals, also he needs modification of his lifestyle regarding to diet style, physical activity and restriction regimen.

Drug Related Problems (DRP):
Effectiveness (Needs Different Drug
Product)
More effective drug available
A.S 55-year-old-African-American male taking Furosemide 40 mg orally twice daily, started x5 years for hypertension management but his BP out of theestablished range for his specific condition, so he needs more effective drug to reach the desired range <140/90 mmHg.

Drug Related Problems (DRP):
Compliance (Non-Compliance) Patient forgets to take
A.S 55-year-old-African-American male with uncontrolled hypertension due to issues of non-compliance.
He is a manager in high stress job and may forget to take within his busy life.He need to improve adherence.
In order to this status, he needs fixed-dose combination product

Short term goals:
Increase the adherence and compliance of patient
Implementation of life style changes
Involve pharmacotherapy and patient education programe

Intermediate term goals:
Achieve desired target BP value (140/90 mmHg).
Long term goals: Prevent CV risk and complications (Cerebrovascular events , heart
failure , kidney disease)
Reduce hypertension associated morbidity and mortality
Improve patient’s quality life

Therapeutic Alternative Therapeutic Life Changes (TLC)
Thiazide-Type-Diuretics (Hydrochlorothiazide Esidrix 25mg PO Once daily in the morning)
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme(ACE) Inhibitors (Captopril Capoten25mg PO Twice daily)
Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB) (Diltiazm Cardizem 120mg PO Twice daily)

Non pharmacotherapy
Life style modification:
Maintain normal body weight( body mass index “BMI” = 18.5-24.9kg/m2)
Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension(DASH) is a style of diet including consume a diet rich in fruits , vegetables, and low fat dairy products with a reduced content of saturated and total fat.
Reduce daily dietary sodium intake as much as possible, ideally to =65 mmol/day (1.5g/day sodium, or 3.8g/day sodium chloride)
Regular aerobic physical activity at least 30 minutes/day

Pharmacotherapy Intervention Initiate following drug instead of Furosemide.
Drug Dose Frequency Rout Dosage form
Duration Cost
chlorthalidone/reserpine
Regroton®
50 mg / 0.25 mg
Once a daily PO Tablet

Monitoring the pharmacotherapy plan
Monitor for signs and symptoms of progressive hypertension –associated target –organ disease (palpitation, Dizziness, dyspnea, sudden changes in vision) periodically.
Routine goal BP values should be attained but the actual BP lowering can occur at a very gradual pace over a period of several months to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
Monitoring BP response should be evaluated 2 to 7 weeks after initiating or making a change in a therapy then every 6 to 12 months in stable patient.
For thiazide diuretic the response needs to be monitored 4 to 6 weeks later because it will show better represent steady state BP values.

Monitoring the pharmacotherapy plan
Self-measurement of BP or automated BP monitoring can be useful clinically to establish effective 24-hour control; BP at home needs to be measured during the early morning hours.
Monitor the BUN/serum creatinine because of Diuretics use, to prevent any kidney diseases may occur.
Monitor blood magnesium level periodically, because patient is Using omeprazole together with chlorthalidone, this may cause hypomagnesemia.

Follow up Evaluation Check periodically to make sure that the blood pressure is in the
recommended range. If it is not, the treatment should be adjusted. Patients with high blood pressure should see their providers at least once per year and more frequently during medication adjustment phases.
Periodically, at the follow-up visits, the patient should be screened for any complications may occur like damage to the heart, eyes, brain, kidney, and peripheral arteries that may be related to high blood pressure
Follow-up visits are a good time to let know about any side effects may the patient is having from his medication. That may needs suggestions for coping with side effects or may change the treatment.

Patient Education Encourage the patient on the home BP monitoring to achieve
more adherences, see the prognosis of his disease and how the therapy is effective.
Lifestyle modification should always be recommended to provide additional BP lowering.
- Eat less salt.
- Exercise.
- Follow the DASH eating plan (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)

Patient Education Educate the patient on importance of compliance.
- Use reminder calls, text or emails as needed
- Preparing a dosing card containing only the most essential elements of the patient’s medications including the name of the pill, image, indication and time for drug taken.
- Give the patient clear instructions about medications
- Ask someone in the family or friends to be medication buddy to help reminder him about daily dosing and getting prescription refills.

References DiPiro, Joseph T. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach. Cardiovascular
Disorder "Hypertension“. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2011. 106-131.Pages(106-131)
European Society of Hypertension and of the European Society of Cardiology,
ESH-ESC-GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION,2013.Print
Brotman, D. J. "The JNC 7 Hypertension Guidelines." JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association 290.10 (2003): 1313-b-314. Print.
Micromedx phone application

Untreated Cigarette smoking

A.S smokes 1 ppd of cigarettes.
Subjective

As smokes 1 ppd, this is equal to 20 cigarettes per day, so the patient is nicotine depended because he smokes more than 10 cigarettes per day.
Objective

A.S is a 55 years old African-American male, nicotine dependent smoker who smokes 1 ppd of cigarettes x10 years.
The patient has Duodenal ulcer , HTN, Anemia and migraine headache
He should be started on smoke cessation therapy.
Assessment

Indication (Needs Additional Drug Therapy) Untreated Condition
AS is a70 year old African-American male, nicotine dependent smoker who smoke 20 cigarettes per day.Currently, He don’t use medication for this condition and need to start on smoking cessation drug.
Drug Related Problem (DRP)

Quit smoking
Short term goals

Reducing the risks for developing smoke induced diseases (lung cancer, COPD, CHD, stroke, esophageal cancer, and others).
Improving the patient health in general.
Improve the patient life quality.
Increase in life expectancy and reduce smoking induced mortality and morbidity.
Long term goals

a) Start the patient in a single medication:
1-Nicotine replacement therapy(patch, gum, inhaler, lozenge ,sublingual tablet)
Ex: (patch)dose: 21 mg/24 hr or15 mg/16 hr ,for more t2-Varenicline:
Dose: 1 mg twice per day following a 1 week titration (risk of cardiovascular events).
han 8weeks.
Pharmacotherapy Alternatives

a) Start the patient in a single medication cont:3-Bupropion:
The dose of bupropion is 150 mg once per day for the first 3 days and then increased to 150 mg twice per day. The patient should stop smoking in the second week of treatment.
4-Nortriptyline:
75 mg/day for 12 weeks.
( risk of arrhythmia in patients with cardiovascular disease.)
B) Advice patient for Smoking reduction rather than smoking cessation
Pharmacotherapy Alternatives

Apply the smoke cessation treatment algorithm( 5A’s):
oAsk – patients about smoking status
oAdvise – patients about the health risks of tobacco use and to quit
oAssess – patients’ readiness to quit
oAssist – patients that are ready to quit Arrange – follow up
Non-pharmacological

Counseling
Cognitive and behavioral coping strategies: delay, deep breathe, drink water, do something else.
Offer written information (eg. Quit Pack)
Offer Quit line referral or other assistance
Arrange follow up visit, if appropriate.
Non-pharmacological

Start the patient on nicotine replacement therapy as patches
Dose:
21 mg/24 hour.
2- Treatment duration should be more than 8 weeks.
Pharmacological intervention

Ask AS to return to clinic soon after the quit date, preferably during the first week to assess and monitor:
oQuitting cigarette smoking
oThe patient compliance to his medication .
oThe development of any drug adverse effects:
Skin erythema, skin irritation and sleep disturbance (abnormal dreams).
Monitoring & Follow up

If withdrawal not controlled, consider combination nicotine replacement therapy (oral NTR could be added).
If patient needs extra support, Consider a further follow-up visit.
Monitoring & Follow up

Educate the patient how to use nicotine patches. (Applied directly to the skin once a day, usually at the same time each day. A apply it to clean hairless aria, With the sticky side touching the skin, press the patch in place with the palm of your hand for about 10 seconds. Wash your hands with water alone after applying the patch. If the patch falls off or loosens, replace it with a new one … etc.).
Educate the patient about the possible adverse effects of nicotine patches(skin irritation, sleep disturbance)
Educate the patient about the importance of compliance to his medication and encourage him to complete his therapy for at least 10 weeks.
Encourage the use of support services.
Educate the patient about the importance of the follow-up visits.
Patient Education

Supporting smoking cessation: a guide for health professionals. 2011. [e-book] South Melbourne: The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners College House. pp. 1-53. Available through: RACP http://www.racgp.org.au/download/documents/Guidelines/smoking-cessation.pdf [Accessed: 27 Oct 2013].
"Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: A Quick Reference Guide for Clinicians." Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: A Quick Reference Guide for Clinicians. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Nov. 2013.
http://www.ahrq.gov/legacy/clinic/tobacco/tobaqrg2.htm
References:

Thank you..