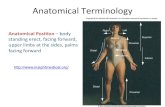
Final Review Honors Biology. Matching A.Chloroplasts B. Mitochondria C. Nucleus D. Central vacuole...
-
Upload
blaise-clark -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Final Review Honors Biology. Matching A.Chloroplasts B. Mitochondria C. Nucleus D. Central vacuole...

Final Review
Honors Biology

MatchingA.ChloroplastsB. Mitochondria C. NucleusD. Central vacuoleE. Rough ERF. RibosomeG. Cell MembraneH. LysosomeI. Golgi apparatusJ. Nucleolus K. Centrioles
1. Small structure that makes protein2. Contains chromatin 3. Controls what enters or leaves the cell4. “Powerhouse” of the cell5. Cell control center6. Numerous ribosomes attached to it7. Help to pull chromosome pairs apart to opposite
ends of the cell8. May store water, needed chemicals, wastes in plant cells9. Converts energy from the sun into chemical energy(photosynthesis)10. Proteins and molecules modified, sorted, and shipped from here11. Digests food, waste, and foreign substances12. Transports Proteins13. Produces ribosomes14. Make cellular energy (ATP)

A.ChloroplastsB. Mitochondria C. NucleusD. Central vacuoleE. Rough ERF. RibosomeG. Cell MembraneH. LysosomeI. Golgi apparatusJ. Nucleolus K. Centrioles
1. Small structure that makes protein F2. Contains chromatin C3. Controls what enters or leaves the cell G4. “Powerhouse” of the cell B5. Cell control center C6. Numerous ribosomes attached to it E7. Help to pull chromosome pairs apart to opposite
ends of the cell K8. May store water, needed chemicals, wastes in plant Cells D9. Converts energy from the sun into chemical energy(photosynthesis) A10. Proteins and molecules modified, sorted, and shipped from here I11. Digests food, waste, and foreign substances H12. Transports Proteins E13. Produces ribosomes J14. Make cellular energy (ATP) B

ProteinDescribe the pathway of how protein is made and
what organelles does it go through? THINK OF THE FUNCTION OF THE ORGANELLES!

• NucleolusribosomesRERGogli apparatusETC

Fill out table


Macromolecules
1) What are 4 macromolecules are we made up of?
2) Function of the 4 macromolecules

• Carbohydrates-Short Term Energy Storage!!• Lipids-Main Function = Energy Storage• Proteins-Your body uses protein to build and
repair tissues. You also use protein to make enzymes, hormone, and other body chemicals. Protein is an important building block of bones, muscles, cartilage, skin, and blood.
• Nucleic Acids-Stores genetic information Gene – specific piece of DNA that codes for a specific protein.

Monomers and Polymers
Name the monomers and polymers for each Macromolecule:
• Carbohydrates:• Proteins:• Lipids:• Nucleic Acids:

Carbohydrates: • Monomer = Monosaccharides• Polymer = Polysaccharides – many monosaccharides
Proteins:– Monomer = Amino Acids– AA’s connected by peptide bond – Polymer = Many AA’s = Polypeptide = PROTEIN!
Lipids:• No polymers + No True monomer– Instead glycerol + fatty acid chains
Nucleic Acids:• Monomer = Nucleotides• Polymer = DNA or RNA

Water and Enzymes1) 5 properties of water2) What does an enzyme do?3) Endothermic reaction?4) Exothermic reaction?

WATER PROPERTIES:1. Cohesion2. Adhesion3. High Specific Heat4. Less Dense as a Solid5. Water is a terrific solvent
ENZYME:• Special type of protein (a catalyst) that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering
activation energy• Involved in most chemical reactions
REACTIONS:• Endothermic (Endergonic) Reactions – absorbs energy
– Energy absorbed from surroundings and stored in bonds– Ex: Photosynthesis– Products have more ENERGY than reactants
• Exothermic (Exergonic) Reactions – releases energy– Releases ENERGY to environment– Ex: Cellular Respiration– Reactants have more ENERGY than products


1. At what pH, do the two enzymes have the same amount of activity?2. At what pH, is the optimal pH for both each enzyme?3. Which enzyme active over a wider range of pH level?


Homeostasis and body systems
1) How does each body system to help maintain homeostasis?
1) Digestive system2) Nervous system3) Circulatory system4) Respiratory system

Feedback
1) What is the difference between positive and negative feedback? Provide an example of each
2) How does our body regulate body temperature (thermoregulation)?






![Towards multidimensional genome annotation · Towards multidimensional genome annotation ... golgi aparatus [x]: peroxisome [p]: periplasm [v]: vacuole [h]: chloroplast [l]: lysosome](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5b8685b17f8b9a8f318cac35/towards-multidimensional-genome-annotation-towards-multidimensional-genome-annotation.jpg)