FDI DETAILS AND ASPECTS
-
Upload
avhinandan-khajuria -
Category
Education
-
view
101 -
download
0
Transcript of FDI DETAILS AND ASPECTS
Foreign Direct Investment was introduced in 1991 under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), driven by then Finance Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a direct investment into production or business in a country by an individual or company in another country, either by buying a company in the target country or by expanding operations of an existing business in that country.In its classic form, Foreign direct investment (FDI) is defined as a company from one country making a physical investment into business in another country.
WHY INVEST IN INDIA ?India is the 7th largest and 2nd most populous country in the world and is world’s largest liberal democracy with sufficient natural resources.
4th largest economy in the world in terms of PPP(Purchasing Power Parity)
Skilled managerial and technical manpower that matches the best available in the world.
Transparent environment that guarantees the security of their long term investments.
Availability of highly competitive private sector that provides considerable scope for foreign direct investment, joint ventures and collaborations.
India has been growing with 8% gross domestic product.
India has been ranked at the second place in global foreign direct investments in 2013 and will continue to remain among the top five attractive destinations for international investors during 2012-15 period, according to United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) in a report on world investment prospects titled, 'World Investment Prospects Survey 2010-2013‘.
FDI may take place in following forms :• Greenfield investment: direct investment in new facilities or the
expansion of existing facilities.•Mergers, Acquisitions and Joint Ventures• Resource Seeking: Investments which seek to acquire factors of
production that are more efficient than those obtainable in the home economy of the firm.•Market Seeking: Investments which aim at either penetrating new
markets or maintaining existing ones.• Efficiency Seeking: Investments which firms hope will increase their
efficiency by exploiting the benefits of economies of scale and scope
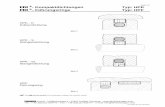
Entry Routes for fdi in IndiaInvesting in India
Automatic Route Prior Permission(FIPB)*
General ruleNo prior permission required.Only information to the Reserve Bank of India within 15 days of inflow/Issue of shares
By exceptionPrior Government Approval needed
Decision generally Within 4-6 weeks
* Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB)
FDI limits in main sectors of India :Insurance – …………………………………………… 49%Telecommunications – ………………………………………. 74%
Petroleum Refining (Private Sector) – …………………..100% Housing and Real Estate – ………………………………….100%
Power sector– ………………………………………………100%Private Sector Banking - …………………………………… 74 %
Advertising - ……………………………………………..100%Electricity- ……………………………………………..100%Trading- ……………………………………… 51%Single Brand Retail- …………………………………........100%Multi Brand Retail- ………………….51%Defense manufacturing- ………………………………… 49%Railway Infrastructure- ………………………… 100%
Cotd……….
Drugs & Pharmaceuticals- ………………………………….100%Hotel & Tourism - …………………………………………100%Civil Aviation- …………………………………………..49%Tourism- …………………………………100%Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC)- ……….……….100%Print Media- ……………………………………………26%Public Sec. Banking - ……………………...20%
Cotd……….
i)Atomic Energyii) Lottery Businessiii) Gambling and Bettingiv) Business of Chit Fundv) Agricultural (excluding Floriculture, Horticulture, Development of seeds, Animal Husbandry, Pisciculture and cultivation of vegetables, mushrooms, etc. under controlled conditions and services related to agro and allied sectors) and Plantations activities (other than Tea Plantations)
FDI is not permitted in following sectors:
vi) Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDRs).vii) Manufacture of cigars, cheroots, cigarillos and cigarettes, of tobacco or of tobacco substitutes.viii)Mining of : iron, manganese, chrome, gypsum, sulphur, gold, diamonds, copper, zinc and other precious stones, metals & mineralsix)Coal and Lignitex)Arms And Ammunition
1991 - Indian economy opened & Actual trading in wholesale & retail started.1997 - FDI up to 100% allowed under automatic route in cash & carry wholesale only after Govt. approval.2006 - 51% FDI in Single Brand Retail.2011 - 100% FDI in Single Brand Retail.2012 - 51% FDI in Multi Brand Retail.India 5th Largest retail market globally & -third largest in Asia.Contributes 14-15% in total GDP.Fastest growing retail market in world.
Retail Sector In India - analysis
Lifestyle products that are widely accepted by the urban Indian consumer.(Apparels, Cosmetics, Shoes, Watches, Beverages, Food and even Jewellery)Currently Indian Retail sector have sales of around $500 billion.The retail sector of India handles about $250 billion every year, and is expected by veteran economists to reach to $990 billion by the year 2015. The business in the organized retail sector of India is expected to grow at the rate of 15-20% every year, and can reach the level of $200 billion by the year 2015.
Types of Retail market in IndiaOrganized - trading activities undertaken by licensed retailers, that is, those who are registered for sales tax, income tax, etc. E.g.: Corporate backed hypermarkets, supermarkets, retail chains etc.Unorganized - traditional formats of low-cost retailing, for example, the local kirana shops, owner manned general stores, paan/beedi shops, convenience stores, hand cart and pavement vendors, etc.
Improves FOR-EX position of the country.Employment generation and increase in production.Help in capital formation by bringing fresh capital.Helps in transfer of new technologies, management skills, intellectual property.Increases competition within the local market and this brings higher efficiencies.Helps in increasing exports.Benefits to farmers.
Advantages of FDI in Retail
Disadvantages of FDI in RetailForeign Players would displace
the unorganized retailers because of their superior financial strengths.Limited Employment Generation as it cannot provide employment opportunities to semi-illiterate people. The entry of large global retailers such as Wal-Mart would kill local shops and millions of jobs.FDI in retail will drain out the country’s share of revenue to foreign countries.Increase in real estate prices and marginalize domestic entrepreneurs.
MY VIEWSOn the one hand because of penetrating pricing definitely creates monopolistic market and because it has potential to cause loss millions of families which will occur to unorganized sector; FDIs shall not be allowed in Retail sector.Whereas on the other hand the concept of globalization is the theme of LPG. By closing door of your home, world outside will not stop from up gradation and developing.
Our foreign dependency will affect our overall development in technology, agriculture, production etc. Accepting changes and challenges is the truth of life. As far as organized sector in India is concerned there should be regulatory framework. As a countrymen I hope for the best but at last its all about natures law:“Survival of the Fittest!”
After considering all the aspects related to FDI, we can conclude that, though there are slight disadvantages of it, but it is very important or we can say life blood for a developing country for there economic growth and stability and for developed country, to continue their stability. Considering foreign direct investment as an important measure of a country’s economic growth and development through introduction of foreign advance technology which is beneficial for both consumer and seller ,it must be promoted .
CONCLUSION