Farmaci antiulcera gastrica. A peptic ulcer, also known as ulcus pepticum, or peptic ulcer disease...
-
Upload
carlita-casini -
Category
Documents
-
view
254 -
download
3
Transcript of Farmaci antiulcera gastrica. A peptic ulcer, also known as ulcus pepticum, or peptic ulcer disease...

Farmaci antiulcera gastrica

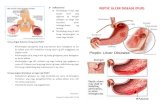
A peptic ulcer, also known as ulcus pepticum, or peptic ulcer disease (PUD), is an ulcer (defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm) of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful. It is a sore in the lining of the stomach or duodenum. If peptic ulcers are found in the stomach, they are called gastric ulcers. If they are found in the duodenum, they are called duodenal ulcers.
Definizione di ulcera
J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2011 Apr-Jun; 3(2): 236–241.

Definizione di ulcera: Ferita che non evolve a guarigione spontanea. L’ulcera gastrica è una lesione profonda della mucosa gastrica di almeno 3 mm o più di diametro.


Inibitori di Pompa protonica

Omeprazole, the first drug in this class, was introduced in 1989. Since then, 4 other proton pump inhibitors have been introduced: lansoprazole (1995), rabeprazole (1999), pantoprazole (2000), and esomeprazole (2001). In 2003 omeprazole became available over-the-counter in the United States.

Chimicamente tutti gli inibitori di pompa protonica sono costituiti da un anello benzimidazolico e un anello piridinico e variano tra di loro in base alle sostituzioni presenti in queste due strutture. Sono piridine facilmente protonabili. Una volta che hanno raggiunto la mucosa gastrica dopo assorbimento sistemico si accumulano selettivamente nei canalicoli secretori gli spazi altamente acidi della cellula parietale. All’interno di questo spazio gli inibitori di pompa protonica subiscono una conversione catalitica verso specie altamente reattive le sulfenamidi tiofiliche che sono dei cationi permanenti. Queste specie reattive interagiscono in superficie con una H+, K+/ATPase sul lume dello spazio secretorio della cellula parietale formando un legame disulfidico attraverso due cisteine localizzate nell’unità alfa dell’enzima. Questo è il residuo che è coinvolto nel trasporto dello ione idrogeno. Questo legame covalente con l’enzima da parte della sulfenamide tiofilica risulta in un impedimento della secrezione gastrica specifica e di lunga durata.
Meccanismo di azione dei PPI

La comparsa di malformazioni gravi nel gruppo trattato con omeprazolo non era significativamente diverso da quelle presenti nel gruppo di controllo e il controllo con GERD. Anche gli altri PPI non hanno mostrato gravi malformazioni durante la somministrazione in donne gravide. In ogni caso l’omeprazolo rimane il farmaco di elezione nel trattamento della GERD in donne in gravidanza.
Vol 52: july 2006• Canadian Family Physician

Crescita batterica da PPI
Sebbene i PPI causano un cambiamento della flora intestinale nell’intestino tenue fino ad ora non c’è evidenza che questo fenomeno interferisca con i processi digestivi o di assorbimento.


Farmacocinetica dei PPI
Il lansoprazolo è il farmaco più biodisponibile (80-90%) mentre l’omeprazolo è il meno biodisponibile (205-40%). L’omeprazolo e il pantoprazolo hanno una clearance inalterata indipendentemente dalla funzionalità renale.
Eur J Clin Pharmacol (2008) 64:935–951

Metabolismo dei PPI
Dalla figura si può notare che i PPI vengono metabolizzati nel fegato tramite il CYP2C19 inizialmente e poi dal CYP3A4 in maggior misurca rispetto al contrario.


Gli inibitori di pompa protonica vengono usati nelle condizioni in cui si richiede la riduzione della secrezione acida gastrica quali il reflusso gastro-esofageo, il reflusso non-erosivo, ulcere gastro-duodenali e nella sindrome di Zollinger-Ellison . Sono usati nella terapia dell’eradicazione dell’ Helicobacter pylori un microrganismo patogeno implicato nellosviluppo di ulcere gastro-duodenali.Il rabeprazolo ha il vantaggio di non interagire con altri farmaci in quanto non segue una via metabolica enzimatica coinvolgente i vari CYP.
Uso terapeutico

Terapia di eradicazione dell’ H. pilori Eur J Clin Pharmacol (2008) 64:935–951
La terapia di prima scelta nell’eradicazione è l’uso di un PPI, amoxicillina e claritromicina o metronidazolo.Il trattamento di seconda scelta è basata sull’uso di bismuto in aggiunta alla terapia di prima scelta.Il trattamento di terza scelta è basato sui test di suscettibilità del microorganismo per l’uso dell’antibiotico.

Uso di altri antibiotici in caso di precedenti fallimenti nell’eradicazione dell’H.pilori

Anti-istaminici antiulcera
Lancet 2009; 374: 119–25
I farmaci antistaminici antiulcera sono diretti nei confronti dei recettori H2. Questi sono cimetidina, ranitidina e famotidina.

Protonic pump inhibitors in kidney transplant patients: efficacy and safety.Cianciolo G, Feliciangeli G, Comai G, Stefoni S.U.O. Nefrologia, Dialisi e Trapianto Renale Policlinico S. Orsola-Malpighi, Bologna.
Kidney transplant patients show a significantly elevated incidence of gastrointestinal disorders. Protonic pump inhibitors (PPI) are considered to be the correct therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcers, as they have proven to be safe and efficient. The metabolization of the PPIs mainly occurs on a hepatic level; therefore, there is no need to change the therapy accordingly, as there is with the inhibitors of the histamine receptors (anti-H2). The PPIs currently available are omeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, rabeprazole which present different pharmacokinetic characteristics and different metabolic routes which are responsible both for differences in terms of efficacy between the different molecules, and for the possible side-effects they may have. All the PPIs, apart from rabeprazole, are metabolized through an oxidization and sulphurization processes which involves the enzymatic system of the P450 cytochrome. The rabeprazole metabolism is different from the other molecules of the same category in that it only moderately involves the CYP450 (CYP3A4 and CYP2C19) from the moment its metabolization begins through nonenzymatic routes and 80% is involved in a thioether non enzymatic reduction mechanism. Consequently, rabeprazole represents: a) a potentially low pharmacological interaction with immunosuppressive drugs; b) a pharmacokinetic aspect much less subject to interindividual differences between one patient and another, due to genetically determined polymorphisms of the CYP2C19 and of the CYP3A4. Moreover, rabeprazole may be administered safely in standard doses with no need to change the dosage of the other pharmaceutical drugs taken simultaneously in nephropathic patients, patients undergoing dialysis and transplanted patients.

Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011 Oct;20(10):1043-9. doi: 10.1002/pds.2202. Epub 2011 Aug 8.Relationship between cardiovascular outcomes and proton pump inhibitor use in patients receiving dual antiplatelet therapy after acute coronary syndrome.Hsiao FY, Mullins CD, Wen YW, Huang WF, Chen PF, Tsai YW.Graduate Institute of Clinical Pharmacy, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan. [email protected]:There is conflicting evidence regarding the potential interaction between clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), with observational studies suggesting an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular (CV) outcomes and clinical trials suggesting there is no such risk.METHODS:We conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess CV outcomes of 9753 patients taking dual antiplatelet therapy of aspirin plus clopidogrel with or without a PPI after hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess our primary endpoint of re-hospitalization for ACS in overall sample and a propensity score matching subsample.RESULTS:Among patients taking clopidogrel plus aspirin, concomitant use of PPI was not associated with the risk of re-hospitalization for ACS (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.12 [95%CI 0.72-1.73]). The findings were consistent in the propensity score matching cohort (adjusted HR 0.82 [95%CI 0.43-1.54]). Compared with PPI nonusers, there is no significant association between each specific PPI users and the risk of re-hospitalization for ACS (adjusted HR; omeprazole 0.96 [95%CI 0.35-2.66], pantoprazole 1.05 [95%CI 0.38-2.92], rabeprazole 0.60 [95%CI 0.17-2.17], esomeprazole 0.31 [95%CI 0.10-0.99], and lansoprazole 0.82 [95%CI 0.32-2.07]).CONCLUSION:In conclusion, this population-based cohort study found that concomitant use of clopidogrel and PPI in patients who received dual antiplatelet therapy after ACS was not associated with risk of ACS re-hospitalization. Together, our study and findings of recently published clinical trials suggest that there was no apparent CV interaction between clopidogrel and PPI in patients who received dual antiplatelet therapy.


Proton pump inhibitor-induced hypocalcemic seizure in a patient with hypoparathyroidism.Milman S, Epstein EJ.Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, New York 10467, USA.
AbstractOBJECTIVE:To report a case of proton pump inhibitor-induced hypocalcemic seizure in a patient with hypoparathyroidism.METHODS:We describe the clinical history, physical examination findings, and laboratory values of the patient and briefly review the relevant literature.RESULTS:A 48-year-old woman with a history of postsurgical hypoparathyroidism who was taking calcium carbonate, 1500 mg 3 times daily, and cholecalciferol, 1200 IU daily, presented with a generalized seizure in the setting of hypocalcemia 12 days after initiating therapy with the proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole. Physical examination revealed a positive Chvostek sign. Electrocardiogram was notable for a prolonged QT(c) interval of 576 milliseconds. Laboratory data were notable for the following values: total serum calcium, 5.3 mg/dL; ionized calcium, 2.51 mg/dL; and intact parathyroid hormone, 5.8 pg/mL. The patient's condition responded to therapy with intravenous calcium gluconate, oral calcium carbonate, and calcitriol. As an outpatient she remained asymptomatic off lansoprazole, treated with calcium carbonate and calcitriol.CONCLUSIONS:Caution should be exercised in prescribing proton pump inhibitors to patients with a history of hypoparathyroidism treated with calcium carbonate supplementation because severe hypocalcemia is a potential adverse effect.