Experiment 1
description
Transcript of Experiment 1

Electronic InstrumentationExperiment 1
* Part A: Circuit Basics, Equipment, Sound Waves
* Part B: Resistors, Circuit Analysis, Voltage Dividers
* Part C: Capture/PSpice

Part A
Circuit Basics Equipment Sound Waves

Automobile Electronics
Previously all mechanical systems have become increasingly electronic
Over the past few years, for example, the automobile has begun to use more computers (microcontrollers)
How many microcontrollers are typically found in a modern automobile?

Automobile Electronics

Physical Model for a DC circuit

Physical Model for Resistance

Physics vs. Electronics

Ohm’s Law

Alternating Current Generators
http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/electromag/java/generator/ac.html

AC Circuits

Review of Sinusoids

General form of the Sinusoid

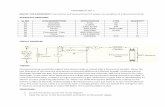
DC Source E3631A
TOGGLE OUTPUT ON/OFF
ADJUST VOLTAGE LEVEL
0 to 6 VOLTS GROUND GROUND
0 to 25 VOLTS
-25 to 0 VOLTS
Do Not Use

Function Generator 33120A

Digital Multimeter 34401A

Oscilloscope 54600B

Impedance
Definition: a general measure of how a circuit affects the current through it.
Impedance = resistance + reactance Impedance is used to refer to the behavior
of circuits with resistors, capacitors and other components.
In a resistive circuit, impedance=resistance.

Equipment Impedances Each measuring device changes the circuit
when you use it. The impedance of the device helps you
understand how much. Device Impedances
• Function Generator: 50 ohms• ‘Scope: 1Meg ohms• DMM (DC voltage): 10Meg ohms• DMM (AC voltage): 1Meg ohms• DMM (DC current): 5 ohms (negligible)

Effect of Impedance on Circuit

What to do

How Ears Work
http://members.aol.com/tonyjeffs/text/dia.htm

Part B
Resistors Circuit Analysis Voltage Dividers

Combining Resistors in Series

Combining Resistors in Parallel

Reading Resistors
http://www.dannyg.com/javascript/res/resload.htm

Measuring Voltage

Voltage Dividers

More on Voltage Dividers

Kirchoff’s Laws

Circuit Analysis (Kirchoff Method)

Circuit Analysis (Combination Method)

Protoboards

Part C
Capture/PSpice• Circuit Analysis Software

Capture

Simulations

PSpice

Cursors

Adding Traces