Experiment 1
description
Transcript of Experiment 1

Ateneo de Naga UniversityCollege of Engineering
ECE and CpE DepartmentS/Y 2014-2015
Group Members:Joa Allen See
Timothy Paul PronJohn Kristoffer Villareal
GE41
Date Performed: June 19, 2014Date Submitted: June 26, 2014
EXPERIMENT NO. FAMILIARISATION

OBJECTIVES:
To be able to understand the theories and concepts of a transformer and its operation. To be able to understand how a transformer works without a load. To be able to understand how a transformer works with a load.
PRACTICAL 1.1 – FAMILIARISATION TEST
Procedures:
1) Take the Dissectible Transformer apart as described in Chapter 1.
2) Remove the large coil and reassemble the transformer with just two smaller coils in
position.
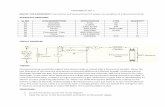
3) Assemble the equipment into the frame as shown in fig 4.1.3 Make all connections
shown, including connections d to g of the transformer.
4) Ensure that the dial on the Variable ac/dc Supply 60-121 is set to the zero position and
that the output switch is in the ac position.
5) Switch on the Earth Leakage Breaker 60-142, if connected.
6) Switch on the 60-121 by pressing the green power on/off button and raise the set voltage
to 5V using the ‘output voltage’ dial. This is the voltage applied to the primary and is
read on the left hand voltmeter.
7) Now read the voltage induced in the secondary coil displayed on the right hand
voltmeter. This should also read approximately 5V.
8) Switch off the 60-121 by pressing the green power on/off button.
9) Remove the coils from the core but keep them together.
10) Switch on the 60-121, and reset the primary voltage (left hand voltmeter) to read 5V.
Read the secondary voltage value (right hand voltmeter). The voltage will have fallen to a
very low level, hardly readable.
11) Place the “I” lamination through the center of the two coils and observe a small increase
in secondary voltage.
12) Separate the two coils and observe that the secondary voltage becomes negligibly small.
13) Switch off the 60-121 by pressing the green power on/off button when there tests are
completed.

Results:
Primary Voltage Secondary Voltage
At transformer core 5.11V 4.52V
No core 5.15V 264mV
With I core 5.15V 1.135V
Separated coils 5.15V 6mV
PRACTICAL 1.2-VOLTAGE RATIOS ON NO LOAD
Procedures:
1) Make the connections on the mimic panel as shown in fig 4.1.4. Assemble the
transformer according to the instructions in Chapter 1. Connect the Dissectible
Transformer leads into the sockets a to g on the front panel ensuring that the identifying
letters on the leads and sockets correspond.
2) Switch on the 60-121, set the primary voltage to 20V (read on the left hand voltmeter).
3) Record the voltage read on the secondary voltmeter (right hand side) in Table 4.1.1
(secondary connection de).
4) Switch off the 60-121.
5) Repeat the experiment for the other connections listed in Table 4.1.1 and record the
results.
6) Switch off the 60-121.
Results:
Voltmeter 1 Voltmeter 2 Voltmeter Ratioon no load
Primary Connection
Reading Secondary Connection
Reading
AC 20 DE 5.85V 0.2925
AC 20 FG 7.75V 0.3875
AC 20 dg (ef linked) 6.37V 0.3185
BC 20 dg (ef linked) 7.82V 0.391

PRACTICAL 1.3-VOLTAGE AND CURRENT RATIOS ON LOAD
Procedures:
1) Make the connections to the mimic panel as shown in fig. 4.1.6. Connect the Dissectible
Transformer leads into the sockets labelled a to g on the front panel ensuring that the
identifying letters on the leads and sockets correspond.
2) Ensure all switches on the load unit are switched on and that the load switch on the
Transformer Mimic Panel is switched on.
3) Switch on the 60-121, set the primary voltage to 100V (read on the left hand voltmeter).
4) Measure the primary and secondary voltages and currents and records the results in Table
4.1.2
Results :
Primary Voltage V1 (V)
Primary Current I1 (A)
Secondary Voltage V2
(V)
Secondary Current I2
(A)
Load Resistance
(Ω)100.98 0.46 100 0.18 60

Figure 4.1.3 Figure 4.1.4
Figure 4.1.6