EXCRETORY SYSTEM
-
Upload
eligardi-enterprises-inc -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
4.809 -
download
0
Transcript of EXCRETORY SYSTEM

EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Celeste R. Desingaño

Excretory System
Consists of 2 kidneys, 2 ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
Essential in the removal of wastes from the body

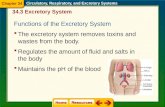
Parts of the Excretory System
1. Kidneys The bean-shaped organs found just above the waistline
Renal Fascia This is the thin fibrous layer, which anchors the kidney to the
surrounding structures to maintain the normal position of the organ.

The Work of the Kidneys The work of the kidney
is to separate urine from the blood which flows through it.
Kidney plays a role in regulating the composition of the plasma by extracting excess wastes and other substances into the urine.
Each kidney receives the renal artery directly from the dorsal aorta and are drained by the renal veins which pass to the postcaval vein.

The Work of the Kidney
Three Processes:1. Filtration The blood plasma is
filtered through the walls of the glomerulus and collects in the Bowman’s capsule
This process forms a fluid, the nephric filtrate, which contains all the ions and small molecules present in the blood plasma.

The Work of the Kidney
Three Processes:2. Tubular reabsorption The nephric filtrate
passes through the tubular parts of the nephron where very large quantities of water and smaller quantities of glucose and other useful compounds are saved and reabsorbed.
This process of selective reabsorption demands that the gland cells in the tubule wall transfer the reabsorbed compounds back into the blood through the capillaries surrounding the tubule.

The Work of the KidneyThree Processes:3. Tubular secretion The nephric tubules secrete
additional quantities of metabolic wastes into the nephric filtrate
Waste are extracted from the capillaries around the tubule and passed into the lumen of the nephron.
Reabsorption and secretion
greatly change the composition of the nephric filtrate as this fluid drains through the nephron toward the collecting tubules.
The fluid as it reaches the
collecting tubule contain a number of amber colored liquid with metabolic waste called urine

Excretory System
2. Ureters These are two tubes which
function to convey urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Passes from the pelvis to the posterior aspect of the urinary bladder
Peristalsis begins at the renal pelvis and ending at the bladder.

Parts of the Excretory System
3. Urinary Bladder This sac lies posterior to the
pubis. Separated from the rectum by
the seminal vesicles in the male and by the vagina and uterus in the female.
Serves as reservoir for urine, gradually fills and becomes distended
Peritoneum Covering of the superior surface
of the bladder.

Parts of Excretory System
4. Urethra This is where urine
is expelled.

1. Skin Excretes wastes,
secretes fluid and make possible growth and repair of hair cells.
Through sweating, the skin excretes excess salt, water and other metabolic wastes in the form of perspiration through pores
2. Large intestine 12-24 hours are
required for the waste products of digestion to pass through the colon and rectum.
Other Excretory Organ

3. Lungs Excreting CO2
4. Liver Produces bile
which is concentrated by the removal of water and salts.
Other Excretory Organ