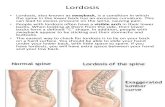
Exaggerated thoracic kyphosis and compensatory lumbar lordosis
-
Upload
miriam-clavel -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
45 -
download
4
Transcript of Exaggerated thoracic kyphosis and compensatory lumbar lordosis

2015
Thoracic hyper-kyphosis and compensatory
lumbar lordosis


PATIENT: Age: 21 years old. Profession: Student.
VISUAL INSPECTION Findings Observations
• Head: Forward. • Cervical Spine: Hyperextended. • Scapulae: Abducted. • Thoracic Spine: Increased flexion
(kyphosis). • Lumbar Spine: Hyperextended (lordosis). • Pelvis: Anterior tilt. • Hip Joints: Flexed. • Knee Joints: Slightly hyperextended. • Ankle Joints: Slight plantar flexion
because of backward inclination of the leg.
• Elongated and Weak: Neck flexors,
upper back erector spinae, external oblique, middle and lower trapezius fibers. Hamstrings are slightly elongated but may or may not be weak.
• Short and Strong: Neck extensors, hip
flexors, lumbar spine extensors, pectoralis minor and shoulder adductors
FUNCTION TEST OF THE SPINE Range of ACTIVE movement
ACTIVE movement Findings: • Normal(N) • Hypermobility (Hpe) • Hipomobility (Hpo)
Observations
Flexion - Lumbar - Dorsal
D12-D8, D3-D1 (Hpo) • Schober Test: 10 cm from S1 to cranial. Does it increase 4-6cm? 1cm of increment, which shows us a hipomobility in the low dorsal area.
• Ott Test (cm). 30 cm from C7 to caudal. Does it increase 8 cm? Hypomobility in the upper dorsal area. It has only increased 4 cm.
Extension - Lumbar - Dorsal
Distance from chin to bench (cm) 40 cm. Reference data for monitoring treatment.

Right Rotation - Lumbar - Dorsal
(N) 55 grades
Left rotation - Lumbar - Dorsal
(N) 40 grades
Right lateral flexion (S1-C7) - Lumbar - Dorsal
D7-D4 (Hpo) 40 grades
Left lateral flexion (S1-C7) - Lumbar - Dorsal
D12-D8 (Hpo) 49 grades
Coupled flexion/extension movements
Painful? NO
Non coupled flexion/extension movements
Painful? NO

TRANSLATORY MOVEMENTS
Translatory movements Findings: • Normal(N) • Hypermobility (Hpe) • Hipomobility (Hpo)
Which segment is Painful?
Elastic Rebound Test (from caudal to cranial) (lumbar and dorsal area)
D8-D12 (Hpo)
Palpation by Spinous Process Impulse (from caudal to cranial ) (lumbar and dorsal area)
L1-L2 D8-D12
Mild discomfort in the lower back
Rebound test transverse process (from caudal to cranial) (lumbar and dorsal area)
D8-D12 (Hpo)
Lateral compression on spinous process (lumbar area)
(N)
Segmental Instability: Test with pressure in the abdomen area from ventral to dorsal (lumbar and dorsal area)
D8-D12 (Hpo)
Traslatory joint play in lateral lying position (lumbar area)
(N)
Global Vertebral compression and Traction
(N)
Lumbar traction (global and specific segments)
(N)
Rib Mobility in sitting position Rib Mobility Test in lateral lying position (dorsal area)
D8-D12 (Hpo)
Measure the circumference of the chest at maximum inspiration and expiration (3’6-6 cm)
Cm? 4 cm of difference between max inhalation and exhalation.(N) Maximal inhalation 84 cm Exhalation 80 cm
FUNCTIONAL MUSCLE TESTING Spine stability and intramuscular coordination/weakness ( with sphygmomanometer)
Mm Hg variability from 40 mm Hg? Yes
Prone position and quadruped position
Does the Pt maintain lumbar stability? No

ADDITIONAL TEST
Positive- Negative Right Positive-Negative Left
Rolling pincer Which segment? Pain or mobility restriction. L1-L2
Which segment? Pain or mobility restriction. (N)
Connective tissues friction test
Which segment? Pain or mobility restriction. (N)
NEURAL TEST Neurodynamic Right (positive or negative) Left (positive or negative) Lassegue Test (-) (-) Bragard Test (-) (-) Slump Test (-) (-) Femoral Test (-) (-) Bowstring Test (-) (-)
Is it possible to perform these actions? Yes or no
Squat Test
With difficulty
Heel support Test
With difficulty
Tip Toe
Yes
Lateral Side Support
Yes

Procedure Goal Global lumbar spine traction grade I-II Pain Relief
Prone trunk lift with fit ball, keeping the arms aligned with her shoulders and cervical and lumbar spine in neutral. For the progression of the exercise the patient can handheld dumbbells.
• Strengthen spinal extensors of the upper back, middle and lower trapezius
• Scapula and trunk stabilization • Reduce anterior tightness.
Prone trunk lift to neutral Strengthen spinal extensors Base muscle contraction (BMC) Education: Sphygmomanometer feedback maintaining contraction of abdominal and pelvic floor muscles, during the extension of the hip and knee. (40 mm of Hg)
Strengthen and improve motor control of spine stabilizer muscles
Chest stretching and diaphragmatic breathing on foam roller applying cross open technique
Lengthen pectoralis muscles, expand ribcage
Prone hip extension/knee flexion using theraband help
Lengthen iliopsoas and rectus femoris
Sidelying stretching posterolateral spine muscle
Lengthen quadratus lumborum and paravertebral muscles
Techniques to decrease adhesions within the fascial sheaths:
• Cupping technique+ diapason • Skin rolling
Myofascial Release
Postural correction: • Sit to stand • Proper lifting techniques.
• Improve spinal proprioception and postural alignment.
• Integrate neutral spine alignment into activities.
• Gentle oscillations. • Educate the patient in joint
mobilization technique with wedge.
Increase joint play in restricted areas. (D8-D12)
Weighted spinal kyphosis orthosis
Provides proprioceptive input to facilitate upright postural alignment

Procedure Goal Spinomed
Provides proprioceptive input to facilitate upright postural alignment and facilitates spinal extensor muscle activity
Apply therapeutic tape from the acromioclavicular joint diagonally across trapezius to T6 bilaterally
Passive support from the tape
(Additional info obtained of PubMed article: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2907357/#R19)