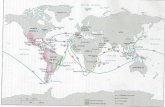
European Age of Discovery
description
Transcript of European Age of Discovery

European Age of Discovery
Why Europeans were interested in discovering new lands and some of
the important explorers

Factors contributing to the European discovery of lands in the Western
Hemisphere• Demand for gold, spices, and natural resources
in Europe• Support for the diffusion of Christianity• Political and economic competition between
European empires• Innovations in navigational arts (European and
Islamic origins) – printing press, astrolabe, and Mercator projection
• Pioneering role of Prince Henry the Navigator

Establishment of overseas empires and decimation of indigenous populations
•Portugal—Vasco da Gama• Spain—Christopher Columbus, Hernando
Cortez, Francisco Pizarro, Ferdinand Magellan• England—Francis Drake• France—Jacques Cartier

Means of diffusion of Christianity
• Migration of colonists to new lands• Influence of Catholics and Protestants, who
carried their faith, language, and cultures to new lands
• Conversion of indigenous peoples

Americas
• Expansion of overseas territorial claims and European emigration to North and South America
• Demise of Aztec, Maya, and Inca Empires• Legacy of a rigid class system and dictatorial
rule in Latin America• Forced migration of some Africans into slavery• Colonies’ imitation of the culture and social
patterns of their parent country

Africa & Asia
• European trading posts along the coast • Trade in slaves, gold, and other products
• Colonization by small groups of merchants (India, the Indies, China)
• Influence of trading companies (Portuguese, Dutch, British)

Columbian Exchange
• Western Hemisphere agricultural products such as corn, potatoes, and tobacco changed European lifestyles.
• European horses and cattle changed the lifestyles of American Indians (First Americans).
• European diseases like smallpox killed many American Indians (First Americans).

Impact of the Columbian Exchange
• Shortage of labor to grow cash crops led to the use of African slaves.
• Slavery was based on race.• European plantation system in the Caribbean
and the Americas destroyed indigenous economics and damaged the environment.
• The triangular trade linked Europe, Africa, and the Americas. Slaves, sugar, and rum were traded.

Export of precious metals
• Gold and silver (exported to Europe and Asia)• Impact on indigenous empires of the
Americas• Impact on Spain and international trade

Maya, Aztec, and Inca civilizations
• developed advanced and complex societies before the arrival of the Europeans-(math-calendar)
• established extensive trade with Pacific Rim nations
• were strongly influenced by their contact with Asian and African civilizations
• were relatively large, but not well organized

Which was an immediate result of the European Age of Exploration?
A. Islamic culture spread across Africa and AsiaB. European influence spread to the Western
hemisphereC. Independence movements developed in Asia
and AfricaD. Military dictatorships were established
throughout Europe Answer is B.

A major result of the Age of Exploration was
A. A long period of peace and prosperity for the nations of Western Europe
B. Extensive migration of the peoples from the Western hemisphere to Europe and Asia
C. The fall of European national monarchies and the end of the power of the Catholic Church
D. The end of regional isolation and the beginning of a period of European global domination
Answer is D.

Which of these events during the Age of Exploration was a cause of the other three?
A. Europeans brought food, animals and ideas from one continent to the another
B. European diseases had an adverse (bad) effect on the native populations of new territories
C. Warfare increased as European nations competed for land and power
D. Advances in learning and technology made long ocean voyages possible
Answer is D.

The Native American population in 1492 was est. to be 25 million and by 1608 it was est. to be 1.7
million. This decrease was mainly a result of
A. Crop failures brought on by poor weather conditions
B. Emigration of Native Americans to Europe and Africa
C. Wars between various native groupsD. Diseases introduced by the Spanish Answer is D.

In Latin America during the early period of Spanish colonialism, the deaths of large numbers
of the native people led to
A. A decline in Spanish immigration to the Americas
B. The removal of most Spanish troops from the Americas
C. The importation of slaves from AfricaD. Improved health care in the colonies
Answer C.

The influence of African culture on some areas of Latin America was largely a result of the
A. American RevolutionB. Building of the Panama CanalC. Success of Communist RevolutionsD. Atlantic slave trade
Answer is D.

One result of the European conquest of Latin America was that in Latin America
A. Spanish became the major spoken languageB. Native American cultures flourishedC. The Aztec religion spreadD. Many parliamentary democracies were
established
Answer is A.

In Latin America, the Maya and the Aztec civilizations were similar in that they
A. Showed little evidence of urbanization (cities)B. Lacked a strong central governmentC. Developed complex mathematical and
calendar systemsD. Used military weapons superior to those of
EuropeansAnswer is C.

The printing press, the astrolabe and the Mercator projection were technological advances
that contributed to the
A. Exploration and overseas expansion of the colonial empires
B. Unification of Germany and Italy in the late 1800’s
C. Growth of industry in Latin America in the late 1900’s
D. Spread of Islam in the 700’s and 800’sAnswer is A.

Commercial Revolution
• Mercantilism: An economic practice adopted by European colonial powers in an effort to become self-sufficient; based on the theory that colonies existed for the benefit of the mother country.

Commercial Revolution
• European maritime nations competed for overseas markets, colonies, and resources.
• A new economic system emerged.• New money and banking systems were created.• Economic practices such as mercantilism
evolved.• Colonial economies were limited by the
economic needs of the mother country.