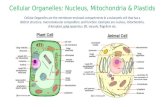
Eukaryotic Membranes: Plastids and Vacuoles Vacuoles are single membrane sacs that separate some...
-
Upload
cynthia-ray -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Eukaryotic Membranes: Plastids and Vacuoles Vacuoles are single membrane sacs that separate some...

Eukaryotic Membranes: Plastids and Vacuoles
• Vacuoles are single membrane sacs that separate some substance from the cytosol.

Eukaryotic Membranes: Plastids and Vacuoles
• Vacuoles have varied functions– Central vacuole in plants is for support and
storage of metabolic wastes– there are food storage vacuoles– there are waste storage vacuoles

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
• Organelles do not drift about the cytoplasm haphazardly, rather they are attached to a network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
• Parts of complex metabolic pathways may be fastened in sequence to the cytoskeleton so that molecules pass from one enzyme to the next.

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
• The cytoskeleton is constructed of:1. Microfilaments (thin)2. Intermediate filaments (medium)3. Microtubules (thick)

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
• The cytoskeleton performs the following important functions:
1. Cell shape – without cell walls, the cytoskeleton, especially networks of intermediate filaments, determines the shape of the cell

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
2. Cell movement – the assembly, disassembly, and sliding of microfilaments and microtubules causes cell movement. Cell movement includes both the familiar “crawling” of amoebae and white blood cells and the migration and shape changes that occur during the development of multicellular organisms.

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
3. Organelle Movement – Microtubules and microfilaments move organelles from place to place within a cell. For example, microfilaments attach to vesicles formed during endocytosis, when large particles are engulfed by the plasma membrane and pull the vesicles into the cell. Vesicles budded off the ER and Golgi complex are probably guided by the cytoskeleton as well.

Eukaryotic Membranes: Cytoskeleton
4. Cell division – microtubules and microfilaments are essential to cell division in eukaryotic cells. First, when eukaryotic nuclei divide, microtubules move the chormosomes into the daughter nuclei. Second, in animal cells, division of the cytoplasm of a single parent cell into two daughter cells results from the contraction of a ring of microfilaments that pinch the “waist” of the parent c ell around the middle.

Eukaryotic Membranes: Flagella and Cillia
• Cilia and flagella are slender extensions of the plasma membrane.– Each contains a ring of nine fused pairs of
microtublules in the center of a ring arrangement.
– The main difference in these two is the number, length, and direction of force.

Eukaryotic Membranes: Flagella and Cillia
• Cilia – are short and numerous. They provide force in a direction parallel to the plasma membrane. “oars”

Eukaryotic Membranes: Flagella and Cillia
• Flagella are long, not numerous, and provide forse perpendicular to the plasma membrane. “motorboat”

Eukaryotic Membranes: Centrioles
• Centrioles are short, barrel-shaped rings of microtubules.
• Their function will be discussed later