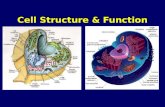
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
description
Transcript of Eukaryotic Cell Structure

Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Mader-Chapter 4

Essential knowledge 2.B.3: Eukaryotic cells maintain internalmembranes that partition the cell into specialized regions.a. Internal membranes facilitate cellular processes by minimizingcompeting interactions and by increasing surface area wherereactions can occur.b. Membranes and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cellslocalize (compartmentalize) intracellular metabolic processes andspecific enzymatic reactions. [See also 4.A.2]To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors canchoose an illustrative example, such as:• Endoplasmic reticulum• Mitochondria• Chloroplasts• Golgi• Nuclear envelopec. Archaea and Bacteria generally lack internal membranes andorganelles and have a cell wall.

Essential knowledge 4.A.2: The structure and function of subcellularcomponents, and their interactions, provide essential cellular processes.
a. Ribosomes are small, universal structures comprised of twointeracting parts: ribosomal RNA and protein. In a sequentialmanner, these cellular components interact to become the site ofprotein synthesis where the translation of the genetic instructionsyields specific polypeptides. [See also 2.B.3]
b. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) occurs in two forms: smooth andrough. [See also 2.B.3]
1. Rough endoplasmic reticulum functions to compartmentalizethe cell, serves as mechanical support, provides site-specificprotein synthesis with membrane-bound ribosomes and plays arole in intracellular transport.
2. In most cases, smooth ER synthesizes lipids.c. The Golgi complex is a membrane-bound structure that consists ofa series of flattened membrane sacs (cisternae). [See also 2.B.3]
1. Functions of the Golgi include synthesis and packaging ofmaterials (small molecules) for transport (in vesicles), andproduction of lysosomes.
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed sacs that contain hydrolyticenzymes, which are important in intracellular digestion, therecycling of a cell’s organic materials and programmed cell death(apoptosis). Lysosomes carry out intracellular digestion in a varietyof ways. [See also 2.B.3]
A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that plays roles in intracellulardigestion and the release of cellular waste products. In plants, alarge vacuole serves many functions, from storage of pigments orpoisonous substances to a role in cell growth. In addition, a largecentral vacuole allows for a large surface area to volume ratio. [Seealso 2.A.3, 2.B.3]

Do not try to memorize the parts… Instead, try to learn how all the parts cooperate to keep it
living and reproducing

Evolution of the eukaryotic cell
1. Monomers2. Polymers• Protein first• RNA first
3. Protocell4. Prokaryote5. Autotrophic prokaryote6. Endosymbiosis7. Eukaryotic cell8. Multicellularity

To understand cells, you need to understand the four major macromolecules and their role in the cell
Who can name the four biological macromolecules?• Proteins-building blocks and enzymes• Carbohydrates-energy and some structure• Lipids-membranes and energy storage• Nucleic acids-information storage
Who can associate certain organelles with macromolecules?

Lets focus on the production of protein
This is known as the “Endomembrane” system

Making ATP… from the breakdown of carbohydrates
CO2 +H2O
+ Light
Glucose + O2
ATPI can do both!
Not impressed

A cells gotta detox!
1. Lysosomes-specialized vesicles produced by the endomembrane system that carry enzymes for breaking down cell parts
2. Peroxisomes-specialized vesicles synthesized by free ribosomes that break down byproducts of cellular respiration and excess lipids
3. Vacuoles-can store toxins, water, sugar, and salts

Never call a cell “just a blob!”Cytoskeleton
1. Actin filament-globular actin
2. Intermediate filaments-fibrous protein
3. Microtubules-globular alph and beta tubulin-Kinesin and dynein move
vesicles through the cell

Cell division and movement