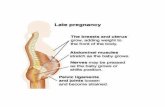
Epigastric pain in pregnancy
-
Upload
drmcbansal -
Category
Documents
-
view
5.799 -
download
0
Transcript of Epigastric pain in pregnancy

Epigastric Pain In Pregnancy Prof. M.C.BANSAL
MBBS. MS. FICOG. MICOG .Ex Principal & Controller .,
Jhalawar Medical College and Hospital.&
MGMC & H. Sitapura,. Jaipur.

• History Taking• A detailed history of presenting symptoms is extremely important . The
complaints should be co related and interpreted with reference to period of gestation , Etiology & changes through out pregnancy.
Following questions may be enquired to reach an appropriate diagnosis : 1. Is the onset of pain gradual or sudden ? 2. Is it dull, aching and constant or is it sharp and stabbing ? 3. Is it associated with meals ? 4. Is it localizing or radiating / shifting / piercing to back ? 5. is there any associated nausea / vomiting ? 6. Is there any exacerbating / relieving factor ?
Symptoms And Signs

Physical Examination
• Clinical features may be less obvious and more difficult to elicit in pregnancy as compared to non pregnant woman .
• Peritoneal signs are absent in pregnancy as a result of stretching of abdomen and peritoneal cavity, as inflamed organ is not in direct contact of parietal peritoneum hence guarding is reduced.
• Try to distinguish between extra uterine and intra uterine tenderness. Examination of patient in lateral decubitus position may be useful . This maneuver displaces the pregnant uterus to one side .

Conditions with increased Frequency in Pregnancy
• 1.Gastro-oesophagial reflux /oesophagitis .• Biliary Colic.• Acute Chole-cystitis.• Diaphragmatic Hernia.


Conditions Due To Pregnancy.
• Rupture of the rectus abdominis muscle.• Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy.• HELLP ( Haemolysis ,Elevated liver enzymes
and Low Platelet counts. )• Spontaneous rupture of Liver due to HELLP .• Prodromal symptom of impending Eclampsia .

Conditions Incidental to Pregnancy.
• Non ulcer Dyspepsia.• Gastric / duodenal ulcer –Oral Iron therapy.
( usually become silent during pregnancy but incidence of aggravated symptoms or even perforation increase during post partum period.)
• Acute and chronic Pancreatitis.

Investigations• Routine CBP, Urine analysis and Serological investigations for
sugar , creatinin , electrolytes ,Urea ,Liver Enzymes, Bleeding / clotting Profile.
• USG --- Liver, Gall Bladder , Kidneys , Pancreas can be evaluated easily .
• Ionizing radiation that produces exposure < 0.05Gy =50 rad have not been found associated with foetal anomalies., however prenatal X ray exposure has been co related with increased possibility of childhood cancers.
• Ionizing radiations should be used when absolutely indicated and other imaging options have been considered and rejected.
• MRI and MRI contrast media are contra indicated in early gestational period .
“ It must be remembered that the duty of any doctor is primarily to the mother as the fetus has no legal standing while in utero.”

Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease.
• It is almost universal to some degree in pregnancy.• It is due to an increased intra abdominal pressure
from a gravid uterus , dysfunction of lower oesophageal sphincter , delayed gastric empting due to smooth muscle relaxant effect of progesterone.
• There is also delayed clearance of the reflux leading to increased acid exposure time, esophageal mucosa is not acid resistant –leading to esophagitis.

Clinical Features of GORD.
• Heart burn , retrosternal pain related to meals , posture and exercise.
• Water wash ( excess salivation especially during an episode of pain ).
• Regurgitation of acid and bile can cause rarely nocturnal sore throat or indeed asthma.
Treatment Elevation of head end of bed by 30 degree , small frequent meals, keep seated in erect posture after meals, avoid any thing that obviously exacerbate the symptoms.
Alginates are effective for relief of symptoms. There is no conclusive evidence regarding safety of H2 blocker and proton pump inhibitors in pregnancy.

Biliary Colic and Acute cholecystitis• Asymptomatic gall bladder disease occurs in 3-4 % of pregnant women .• Acute cholecystitis occurs in 1:1130 -12890 pregnancy.
Clinical Features: 1. Pain is usually moderately severe and constant in both acute chloecystitis
and biliary colic. In these cases It is commonly felt in the right upper quadrant and can be epigastric radiating to the back and right shoulder.
2. Vomiting occurs in 50% of cases , fever is present in cholecystitis. 3 . USG is diagnostic and safe . 4 .Leucocytosis and raised Alkaline phosphatase levels may be present in
healthy pregnancy hence inconclusive . 5 .Transient increase in Amylase can occur in 30 % those with biliary colic
but markedly raised suggests Pancreatitis.

Biliary Colic And Acute Cholecystitis
• Treatment 1. Conservative treatment with intravenous
fluids , analgesics , broad spectrum antibiotics are started.
2. Surgery should be undertaken preferably in mid 2nd trimester or post partum period , laparoscopy is safe in this period of gestation.

Acute Pancreatitis
• This occurs most often secondary to gall stones and associated with a fetal loss of 10-20 %.
• In these cases , endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticogram and sphincterectomy can be performed safely in pregnancy . Uterus should be lead shielded.

Gastric Ulcer /Duodenal Ulcer
• Pre existing gastric ,duodenal ulcer become silent during pregnancy and de novo ulceration is rare.
• It presents with epigastric pain after / before meals and often associated with anorexia and weight loss.
• It is commonly caused by Helicobacter pylori and unprotracted use of NSAIDs ,diagnosed endoscopically.
• Treatment for H. pylori can be given during pregnancy.

Thank you