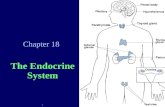
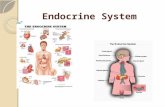
Endocrine System Ch. 51. Endocrine System Series of glands and organs that secrete hormones....
-
Upload
frank-pope -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
Transcript of Endocrine System Ch. 51. Endocrine System Series of glands and organs that secrete hormones....
Endocrine System
• Series of glands and organs that secrete hormones.
• Hormones function as chemical messengers in the blood stream affecting cells throughout the body.
Your body contains two types of glands:1. Exocrine (sweat, mucous, salivary)
2. Endocrine (ductless, secrete directly into blood stream)
Your body has two general types of hormones:
1. Amino-Acid Based (epinephrine including proteins, peptides, amino acids, and other forms from amino acids)
2. Steroid (lipid based including estrogen and testosterone, come from cholesterol)
Prostaglandins: group of hormone-like lipids that also regulate cell activities. Examples- relax smooth muscles, regulate blood pressure, contraction of the intestines and uterus, immune response)
Hypothalamus
• Links the Nervous System to the Endocrine System.
• Neurosecretory cells produce hormones that are either stored in the Pituitary Gland or control it.
• The Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland are the primary regulators of the Endocrine System
Pituitary gland
• Secretes hormones that affect other glands and organs.
• Regulated by the hypothalamus.
Pituitary Gland: Major Hormones
1. ACTH: stimulates secretion of cortisol and aldosterone by the adrenal cortex.
2. ADH: stimulates reabsorption of water by the kidneys.
3. FSH: stimulates egg & sperm production.
4. GH: regulates muscle and bone growth.
5. LH: ovulation; stimulates estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone production.
6. Oxytocin: uterine contractions; flow of milk during lactation.
7. PRL: stimulates milk production for lactation.
8. TSH: stimulates secretion of thyroid hormones.
Thyroid Gland• TSH: regulates the
thyroid gland.
Hormones released: 1. Thyroxin- growth and
metabolism.
2. Triiodothyronine- growth, body temp. and heart rate.
3. Calcitonin causes the bones to store calcium. Important for proper bone growth.
Illnesses Associated with the Thyroid Gland:Hypothyroidism: deficiency causing growth
retardation, weight gain, lethargy, low heart rate and low body temp.
Hyperthyroidism- overproduction causing overactivity, weight loss, high blood pressure, heart rate and body temp.
Cretinism: mental retardation during fetal and childhood development.
Goiter- iodine deficiency, swelling of the thyroid gland.
Adrenal Gland
1. Epinephrine (adrenaline) and Norepinephrine – nervous system fight or flight response.
2. ACTH- from the pituitary gland, stimulates production of cortisol and aldosterone.
cortisol: metabolism of carbs and proteins.
aldosterone: affects kidneys and salt/water balance.
Sex Hormones regulate body changes that begin at puberty.
1. LH & FSH: stimulate secretion of estrogen and progesterone.
2. Estrogen and Progesterone: egg release, buildup of uterine lining; female sex characteristics.
3. LH causes males to produce Androgens (testosterone): male sex characteristics and sperm production.
Pancreas
Function: secretes two key hormones, insulin and glucagon.
Islets of Langerhans- specialized cells
Diseases: Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (excessive insulin)
Thymus Gland
Located beneath the sternum, between the lungs.
Function: proper development of the immune system
Secretes thymosin: stimulates production of T-cells.
Parathyroid Gland
Four of them located on the thyroid.
Secretes Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): controls the balance of calcium in the blood.