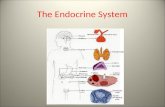
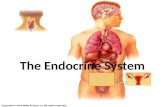
Endocrine System
-
Upload
victoria-brown -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Endocrine System

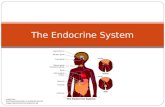
Endocrine
System
By:
Sheravia Bryant
Victoria Brown

PURPOSE
• Produces and releases different types of hormones to maintain
and control a number of functions throughout the body such as:
• Growth and development
• Metabolism
• tissue function
• The main purpose is extracellular communication

HORMONES
• Vasopressin – helps to maintain blood pressure and monitor
electrolyte balance
• Growth Hormone (GH) – stimulates growth during childhood and
also cell reproduction which helps adults maintain muscle and
bone mass
• Calcitonin – aides in bone construction
• Insulin – regulates glucose by bringing blood into cells
• Adrenaline – Also called the “Fight or flight instinct”;
• Noradrenaline – works with Adrenaline to help the endocrine
system produce the fight or flight response

HORMONES CONT.
• Androgen – stimulates or controls the development and
maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates; main male
sex hormone
• Estrogen – crucial for woman’s health; main female sex
hormone
Fact:
Everybody, male and female, have both androgens and estrogen,
only the amount varies by sex.

CUSHING’S SYNDROME
• A condition when the pituitary gland releases too much
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
• Usually caused by a tumor, excess growth (hyperplasia) of the
pituitary gland or ACTH hormone medications
• Tumors are usually located at the base of the brain

CUSHING’S SYNDROME
• Signs –
• Seizures
• Anxiety
• Short term memory loss
• High Cortisol levels
• Symptoms –
• Upper body obesity
• Purple marks (1/2 inch or more wide), called strae, on the skin of the abdomen, thighs, and chest
• Thin skin with easy bruising
• Severe fatigue

CUSHING’S SYNDROME
• Prognosis –
• It greatly depends on the cause of the disease
• Most cases can be cured
• Who’s at risk?
• Affects women five times more frequently than men and most commonly occurs between 25-40 years of age
• Facts –
• It is relatively rare, affecting only about 2 people per million per year

CUSHING’S SYNDROME
• Diagnosis –
• based on a review of the patient's medical history, physical
examination and laboratory tests
• X-rays of adrenal or pituitary gland to look for tumors
• 24 hour Urinary Free Cortisol Level (in adults levels higher
than 50-100 micrograms suggest Cushing’s)

CUSHING’S SYNDROME
• Treatment –
• depends on the specific reason for Cortisol excess
• May include radiation, chemotherapy, the use of Cortisol-
inhibiting drugs, or the most common, surgical removal of
any tumor(s)

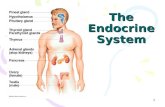
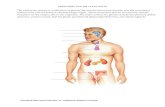
ORGANS
• Testis – male gonads; the organ that produces sperm, the male
reproductive cell, and androgens, the male hormones;
• Ovaries – gonad and endocrine gland found in women; ovum
producing reproductive organs
• Liver – vital organ; detoxification, protein synthesis, and
production of biochemicals needed for digestion
• Pancreas – located deep in the abdomen; produces important
hormones such as insulin and secretes pancreatic juice that
help in the break down of carbohydrates, protein, and fat

GLANDS
• Pituitary Gland – “master gland” under the control of the
hypothalamus; secrete hormones important to female functions
• Hypothalamus Gland – in control of pituitary gland and together
they manage other endocrine functions
• Pineal Gland – stimulated by nerves from the eyes; directly
stimulated by light; affects thyroid and adrenal cortex functions

GLANDS
• Thyroid Gland – regulate metabolism (body temperature and
weight); contain iodine which is needed to manufacture
hormones
• Parathyroid Gland – produce parathyroid hormone control
amount of calcium in the blood and within bones
• Adrenal Gland – two parts, outer cortex secretes cortisone (anti-
inflammatory) and inner medulla responds to stressors (fight,
anger, caffeine, low blood sugar)
• Thymus Gland – produces and helps adapt T cells which are
critical of the adaptive immune system

WORKING WITH OTHER SYSTEMS
• Works with and helps control:
• Nervous system
• Reproductive system
• Consequently, because it produces hormones, it has an effect
on all of the body systems

EFFECTS OF AGING
• As you age hormone levels and target organs are altered in the
endocrine system
• Hormones usually increase or decrease depending on the
person, this can lead to a number of different problems

LEARNED MEDICAL WORDS
• Acromegaly – abnormal enlargement of the extremeties that is
caused by excessive secretion of growth hormone after puberty
• Adrenalitis – inflammation of the adrenal glands
• Aldosteronism – abnormality of elelctrolyte balance caused by
the excessive secretion of aldosterone

REFFERENCES
• http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cushings-syndrome/DS00470\
• http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001388/
• http://www.medicinenet.com/cushings_syndrome/article.htm
• http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/cushings/cushings.htm
• ww.nadf.us/diseases/cushings.htmw