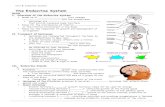
Endocrine System Marie Černá. Regulatory systems Nervous system Endocrine system.
Endocrine System
-
Upload
whitchur -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
2.736 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Endocrine System

Endocrine SystemFlorida State College of Jacksonville – FSCJ
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS
HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

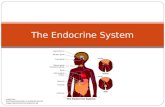
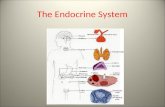
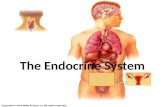
The endocrine system consists of glands that perform very different functions. They are related to each other because they all secrete hormones into the blood.
Organs and glands of the endocrine system secrete hormones to regulate various body functions
(EN-doh-kin-AWL-oh-jee)

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System at a Glance
Endocrine glands secrete hormones Hormones regulate body activities
Metabolic rate Water and mineral balance Immune system reactions Sexual functioning

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System at a Glance
Organs of the Endocrine System Adrenal glands Ovaries Pancreas (islets of Langerhans) Thyroid & Parathyroid glands Pineal gland Pituitary gland Testes Thymus gland Thyroid gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth EditionBonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht
Copyright ©2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
endocrine system

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System Suffixes
–crine to secrete
–dipsia thirst
–prandial relating to a meal
–tropin stimulate

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Anatomy and Physiology
Collection of glands Secrete hormones directly into bloodstream
Chemicals that act on target organs Increase or decrease target’s activity level
Instrumental in maintaining homeostasis Maintain stable internal environment

End
ocrin
e S
yste
m
home/o = same-stasis = condition of standing still; staying in one place

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Types of Glands
Two types of glands in bodyExocrine glands and Endocrine glands
Exocrine glands Release secretions into duct that carries them to
outside of body Example: sweat glands
Endocrine glands Release hormones directly into bloodstream Have no ducts, referred to as ductless glands Example: thyroid gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Glands of the Endocrine System
Adrenal glands – two Parathyroid glands – four Pancreas Pineal gland Pituitary gland Ovaries – two in females Testes – two in males Thymus gland Thyroid gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Adrenal Glands
Two glands, one located above each kidney Each gland is composed of two sections:
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The adrenal glands

adrenal gland cortex and medulla

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Adrenal Cortex
Mineralocorticoid Example: aldosterone Regulates sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) levels
Glucocorticoid Example: cortisol Regulates carbohydrates
Steroid sex hormones Androgens, estrogen, and progesterone Regulate secondary sexual characteristics

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Adrenal Medulla
Inner portion Secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
Epinephrine is also called adrenaline Critical during emergency situations
Increases blood pressure Increases heart rate Increases respiration rate

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Ovaries
Two ovaries located in pelvic cavity of females
Secrete female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone
Estrogen is responsible for: Female sexual characteristics Regulation of menstrual cycle
Progesterone Maintains suitable uterine environment for
pregnancy

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The ovaries

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Testes
Two oval glands located in scrotum
Secrete male sex hormone, testosterone
Testosterone Produces male secondary
sexual characteristics Regulates sperm
production

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The testes. The testes.
Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pancreas
Located along lower curvature of stomach
Only organ that has
both endocrine and exocrine functions
Pancreas

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pancreas
Exocrine portion Releases digestive enzymes
through duct into duodenum
Endocrine sections of the pancreas Islets of Langerhans Produce insulin and glucagon

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pancreas
Insulin Produced by beta cells Stimulates cells of body to take in glucose from
bloodstream Lowers blood sugar level Occurs after eating a meal and absorbing
carbohydrates

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pancreas
Glucagon Produced by alpha cells Stimulates liver to release stored glucose into
bloodstream Raises blood sugar levels Occurs when body needs more glucose

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The pancreas

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Diabetes Video

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thyroid Gland
Located on either side of trachea
Resembles a butterfly in shape
Divided into right and left lobes

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid hormonesThyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Needs iodine to make hormones These hormones:
Regulate energy productionAdjust metabolic rate

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thyroid Gland
Also secretes calcitonin Regulates level of calcium in bloodstream
If calcium levels in blood rise too high: Calcitonin levels in blood increase Increases deposition of calcium into bone Lowers levels of calcium in bloodstream
Its action is opposite of parathyroid hormone
homeostasis

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The thyroid gland is divided into a left and right lobeThe thyroid gland is divided into a left and right lobe
HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Parathyroid Glands
Four tiny glands Located on dorsal surface
of thyroid gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Parathyroid Glands
Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) Regulates level of calcium in bloodstream
If calcium levels in blood fall too low:Parathyroid hormone levels in the blood
increase Stimulate bone breakdown Releasing more calcium into bloodstream

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The parathyroid glands.

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine Glands of the Brain
Pineal gland
Pituita
ry gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pineal Gland
Small pine cone-shaped gland Part of thalamus region of brain

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pineal Gland
Secretes melatonin Not well understood, but
plays a role in regulating body’s circadian rhythm 24-hour clock that governs
periods of wakefulness and sleepiness

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The pineal gland is a part of the thalamus region of the brain.

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pituitary Gland
Small marble-shaped gland
Located underneath brain
Divided into anterior and posterior lobes
Regulated by hypothalamus

Pituitary gland
The anterior pituitary gland produces and secretes seven different hormones.
The posterior pituitary gland stores and secretes two hormones that are actually produced by the hypothalamus.
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pituitary gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Anterior Pituitary
Referred to as “master gland” Secretes hormones that regulate other
endocrine glands
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Regulates function of thyroid gland
Adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH) Regulates function of adrenal cortex

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Anterior Pituitary
GonadotropinsFollicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)Luteinizing hormone (LH)
FSH Responsible for development of ova and sperm Also stimulates ovary to secrete estrogen
LH Stimulates secretion of sex hormones Plays a role in releasing ova in females

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Anterior Pituitary
Growth hormone (GH) Also called somatotropin Stimulates cells to grow and divide
Prolactin (PRL) Stimulates milk production in breast
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The different hormones and target tissues for the anterior pituitary. The different hormones and target tissues for the anterior pituitary.
Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Posterior Pituitary
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Also called vasopressin Promotes water re-absorption by the kidney tubules
Oxytocin (OXT) Stimulates uterine contractions during labor and
delivery After birth stimulates release of milk from breast

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thymus Gland
Located in mediastinum Part of immune system Also endocrine gland
Secretes thymosin
Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thymus Gland
Thymosin Essential for growth and development of thymic
lymphocytes or T cells Critical part of body’s immune system
Present at birth and grows to largest size during puberty
At puberty begins to shrink and eventually is replaced with connective and adipose tissue
Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
The thymus gland. The thymus gland.

Effects of Hormones
Hormones from the various endocrine glands affect body metabolism, blood glucose, blood calcium, and blood sodium in complementary or opposite ways.
Homeostasis
home/o = same-stasis = condition of standing still; staying in one place Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Word Building with adren/o & adrenal/o
–ectomy adrenalectomy removal of adrenal gland
–itis adrenalitisinflammation of adrenal gland
–al adrenalpertaining to adrenal gland
–megaly adrenomegaly enlarged adrenal gland
–pathy adrenopathy adrenal gland disease

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Word Building with calc/o & crin/o
endo– –ologist endocrinologistspecialist in endocrine system
endo– –pathy endocrinopathyendocrine system disease
hyper– –emia hypercalcemiaexcessive calcium in blood
hypo– –emia hypocalcemia low calcium in blood

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Word Building with glyc/o, kal/i, & natr/o
hyper– –emia hyperkalemiaexcessive potassium in blood
hyper– –emia hyperglycemiaexcessive sugar in blood
hypo– –emia hypoglycemia low sugar in blood
hypo– –emia hyponatremia low sodium in blood

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Word Building with parathyroid/o & pancreat/o
–ic pancreatic pertaining to pancreas
–al parathyroidalpertaining to parathyroid
–ectomy parathyroidectomy removal of parathyroid
hyper– –ism
hyperparathyroidismstate of excessive parathyroid
hypo–
–ismhypoparathyroidism
state of insufficient parathyroid

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Word Building with pituitar/o & thym/o
–ic thymic pertaining to thymus
–ectomy thymectomy removal of thymus
–itis thymitis inflammation of thymus
–oma thymoma thymus tumor
–ary pituitary pertaining to pituitary
hypo– –ism hypopituitarism state of low pituitary
hyper– –ism hyperpituitarismstate of excessive pituitary

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Word Building with thyr/o & thyroid/o
–al thyroidal pertaining to thyroid
–ectomy thyroidectomy removal of thyroid
hyper– –ism hyperthyroidismstate of excessive thyroid
hypo– –ism hypothyroidism state of low thyroid
–megaly thyromegaly enlarged thyroid

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System Vocabulary
acidosis excessive acidity of body fluids
edema excessive fluid in body tissues
endocrinologydiagnosis and treatment of conditions of endocrine glands
exophthalmos protruding eyeballs
gynecomastia development of breast tissue in males
hirsutism excessive amount of hair

exophthalmos
Exophthalmos is a well-known sign of hyperthyroidism. Edema behind the eyeballs causes them to bulge and protrude forward, and the large amount of white sclerae makes the eyes appear to be staring.
Custom Medical Stock Photo, Inc.
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System Vocabulary
hypersecretionexcessive hormone production by endocrine gland
hyposecretioninsufficient hormone production by endocrine gland
obesity having abnormal amount of fat
syndromegroup of symptoms and signs that combine to present a clinical picture of disease or condition

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Adrenal Gland Pathology
Two glands, one located above each kidney Each gland is composed of two sections:
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Adrenal Gland Pathology
Addison’s disease
hyposecretion of adrenal cortex; symptoms include generalized weakness and weight loss
adrenal feminization
hypersecretion of estrogen by adrenal cortex in males; develops female secondary sexual characteristics like gynecomastia
adrenal virilism
hypersecretion of testosterone by adrenal cortex in females; develops male secondary sexual characteristics

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Adrenal Gland Pathology
Cushing’s syndrome
hypersecretion of adrenal cortex; symptoms include weakness, edema, excess hair growth, and osteoporosis
pheochromocytoma
hypersecretion of epinephrine by adrenal medulla tumor; usually benign; symptoms include anxiety, heart palpitations, dyspnea, and headache

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Cushing’s syndrome
(Biophoto Associates/ Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.)
Cushing’s syndrome
(Biophoto Associates/ Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.)

Cushing’s syndrome
(a) This patient shows the characteristic signs of Cushing’s syndrome. Deposits of fat in the cheeks give a moon face appearance. Breakdown of protein in the connective tissues of the skin makes the skin thin, allowing blood vessels to show through and give the cheeks a reddened appearance.
Biophoto Associates/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

Cushing’s syndrome
(b) The abdomen is obese, while the extremities are thin and there is muscle wasting and weakness. Dark facial hair and amenorrhea occur only with Cushing’s disease.
Biophoto Associates/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pancreas Pathology
diabetes mellitus (DM)
Chronic disorder of carbohydrate metabolism
Results in hyperglycemia and glycosuria
Two very distinct types:
- insulin-dependent
- non-insulin-dependent

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Diabetes Mellitus
Insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
Also called Type 1 Develops early in life Destruction of islet cells Person makes too little
insulin Must take insulin injections
Non-insulin-dependent diabetes
mellitus (NIDDM)
Also called Type 2 Develops later in life Person makes enough
insulin, but it has lost ability to regulate cells
Do not take insulin Treated by diet, exercise, and
oral medications

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Diabetes Video

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pancreas Pathology
diabetic retinopathy
accumulation of damage to retina; complication of diabetes mellitus
ketoacidosisacidosis due to excess of acidic ketone bodies; serious complication of diabetes mellitus
peripheral neuropathy
damage to nerves in lower legs and hands as a result of diabetes mellitus
insulinomaislet of Langerhans tumor; secretes excessive amount of insulin

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Parathyroid Gland Pathology
tetany
nerve irritability and painful muscle cramps due to hypocalcemia; may be caused by hypoparathyroidism
Recklinghausen disease
hypersecretion of parathyroid hormone; causes degeneration of bones

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pituitary Gland Pathology
acromegalychronic hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults; causes enlargement of bones of head and extremities
diabetes insipidus (DI)
hyposecretion of antidiuretic hormone; symptoms include polyuria and polydipsia
dwarfismhyposecretion of growth hormone in children; causes short stature

acromegaly
Increased levels of growth hormone (GH) in adulthood cause the face and extremities to widen rather than grow longer. The foot on the left is normal. The foot on the right shows acromegaly with enlargement and widening.
NMSB/Custom Medical Stock Photo, Inc.
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Acromegaly. The hand on the right is from a normal person, the hand on the left is a person with acromegaly.
(Bart's Medical Library/Phototake NYC)
Acromegaly. The hand on the right is from a normal person, the hand on the left is a person with acromegaly.
(Bart's Medical Library/Phototake NYC)

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Pituitary Gland Pathology
gigantismhypersecretion of growth hormone in child; results in very tall adult
panhypopituitarism
hyposecretion of all pituitary hormones; results in problems with the glands controlled by pituitary gland

gigantism
The tallest man who ever lived suffered from gigantism. His name was Robert Wadlow. He was born in 1918 in Illinois and was of average weight and length at birth. By the time he was 18 years old, he was 8’11” and weighed 491 pounds. He wore size 37AA shoes that were over 18” in length. He died in 1940, at the age of 22. The tallest living man now is Bao Xishun, a herdsman in Mongolia, China. He was born in 1951 and is 7’9”.
CORBIS-NY
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
panhypopituitarismpanhypopituitarism

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thyroid Gland Pathology
cretinismcongenital hyposecretion of thyroid; results in poor physical and mental development
goiter enlarged thyroid gland
Graves’ diseasehypersecretion of thyroid; symptoms include exophthalmos and goiter

goiter
A goiter can be a mild, subtle swelling in the neck, or it can enlarge enough to cause difficulty swallowing and breathing.
Marka/Custom Medical Stock Photo, Inc.
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

Palpation of thyroid gland
The anterior location of the thyroid gland means that even mild enlargement can be detected. This physician is palpating the edges of the patient’s thyroid gland to determine its size.
Pearson Education/PH College
Endocrine System | Medical Terminology for Health Professionals

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth EditionBonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht
Copyright ©2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
Goiter

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Thyroid Gland Pathology
Hashimoto’s disease
autoimmune destruction of thyroid; results in hyposecretion disorder
myxedemahyposecretion disorder in adult; symptoms include anemia, edema, and mental lethargy
thyrotoxicosismarked hypersecretion; symptoms include rapid heart rate, tremors, thyromegaly, and weight loss

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine Gland Pathology
adenocarcinoma
cancerous tumor in gland that produces hormones secreted by that gland; results in hypersecretion pathologies

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Clinical Laboratory Tests
blood serum testmeasures level of substances, such as calcium, glucose, or hormones, in blood
total calciummeasures calcium in blood; used to diagnose parathyroid or bone disorders
radioimmunoassay (RIA)
measures levels of hormones in blood

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Clinical Laboratory Tests
fasting blood sugar (FSB)
measures glucose in bloodstream after 12-hour fast
glucose tolerance test (GTT)
measures blood sugar level over several hours after person drinks large dose of glucose
two-hour postprandial glucose tolerance test
measures blood glucose level two hours after a meal

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Clinical Laboratory Tests
protein bound iodine test (PBI)
measures T4 blood level; iodine in the hormone becomes bound to blood proteins
thyroid function test (TFT)
measures levels of T3, T4, and TSH in blood

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Diagnostic Imaging
thyroid echogram
ultrasound image of thyroid gland
thyroid scannuclear medicine image based on accumulation of radioactive iodine in thyroid gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Medical Treatments
chemical thyroidectomy
large dose of radioactive iodine is given to kill a portion of the thyroid gland; avoids surgery
hormone replacement therapy
administering replacement hormones; treats hyposecretion disorders

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Surgical Treatments
laparoscopic adrenalectomy
removal of adrenal gland through small abdominal laparoscopic incision
lobectomy removal of a lobe of thyroid gland

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System Pharmacology
antithyroid agents
blocks production of thyroid hormones
Tapazole
corticosteroidsreplaces adrenal cortex hormones
Deltasone
human growth hormone therapy
replaces growth hormone
Genotropin, Protropin

HSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare ProfessionalsFlorida State College Jacksonville
Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS, OT/L
Endocrine System Pharmacology
insulintreats type 1 diabetes mellitus
Humulin L
oral hypoglycemic agents
decreases blood sugar in type 2 diabetics
Glucophage, Glucotrol
thyroid replacement hormone
replaces thyroid hormones
Levo-T, Cytomel
vasopressin treats diabetes insipidusDesmopressin, Vaprisol