ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
-
Upload
shari-blake -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 1/38
UNIT 1 –
REGULATION ANDCONTROL I –
HOMEOSTASIS AND THE ENDOCRINESYSTEM

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 2/38
Homeostasis – Role of regulatory
systems1. Define and cite examples of Homeostasis.
2. Discuss the need for homeostasis in livingorganisms

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 3/38
HomeostasisHomeostasis refers to the appropriate, balanced internal
environment.
Metabolic processes occur continuously in every organism,
and they must be carefully regulated to maintainhomeostasis.
When enough of a cell product has been made, itsmanufacture must be decreased or turned off .
When a particular substance is required, cell processes thatproduce it must be turned on.
These homeostatic mechanisms are self-regulating controlsystems that are remarkably sensitive and efficient.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 4/38
Stressors (changes in the internal or external environment) that
affect normal conditions within the body, continuously challengehomeostasis.
An internal condition that moves out of its homeostatic range(either too high or too low) causes stress.
An organism functions effectively because homeostaticmechanisms continuously operate to manage stress
Many animals are conformers for certain environmentalconditions.
Some of their internal states vary with changes in their surroundings.
Mammals are superb regulators.
They have complex homeostatic mechanisms that maintainrelatively constant internal conditions despite changes in theoutside environment.
How do homeostatic mechanisms work?

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 5/38
Example
Your cells require a constant supply of glucose molecules,which they break down to obtain energy.
The circulatory system delivers glucose and other nutrients
to all the cells.When the concentration of glucose in the blood rises above
normal limits, glucose is stored in the liver and in musclecells.
When you have not eaten for a few hours, the glucoseconcentration begins to fall.
Your body converts stored nutrients to glucose, bringing theglucose concentration in the blood back to normal levels.
When the glucose concentration decreases, you also feel

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 6/38
Feedback Regulation:
Negative feedback systems restorehomeostasis
3. Describe and provide examples from mammalian biology of
negative and positive feedback reactions.
4. Discuss the role of positive and negative feedback in thefunction of an organism

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 7/38
In a negative feedback system, a change in some
steady state triggers a response that counteracts, orreverses, the change.
A sensor detects a change,( a deviation from the normalcondition), or set point.
The sensor signals a control centre.
Based on the input of the sensor, the control centreactivates homeostatic mechanisms that restore thesteady state
The response counteracts the inappropriate change,thereby restoring the steady state.
Note that in a negative feedback system, the response of
the

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 8/38
Example
v Most homeostatic mechanisms in the body arenegative feedback systems.
1. When the glucose concentration in the blooddecreases below its homeostatic level, negativefeedback systems increase its concentration.
If the glucose concentration in the blood is too low,
alpha cells in the pancreas secrete a hormone thatincreases glucose concentration.
3. When body temperature decreases below normallimits, s ecialized nerve cells (sensors) si nal the

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 9/38

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 10/38
Feedback RegulationA few positive feedback systems operate in
the bodyPositive feedback intensifies the change taking place,
(rather than reverses) moving conditions further awayfrom homeostasis.
Although some positive feedback mechanisms arebeneficial,
they do not maintain homeostasis.
For example, a positive feedback cycle operates duringthe birth of a baby.
As the baby’s head pushes against the cervix (lower part of uterus), a reflex action causes the uterus to contract.
The contraction forces the head against the cervix again,

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 11/38

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 12/38
Comparison of Nervous and Hormonalregulation.
5. Compare nervous and hormonal regulationwith respect to structure and function of each
system.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 13/38
Nervous system vs, Endocrine
systemNervous system regulates the activities of muscles and glands via electrical impulsestransported through neurons.
Neural control is fast; its effects are short-lived
System of neurons transmits “electrical” signals& release neurotransmitters to target tissue
The magnitude of nervous system effects are
dependent upon the frequency of actionpotentials.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 14/38
Endocrine System regulates the body’s metabolic
activity via hormones that are transported in theblood.
Hormonal control is slow; its effects areprolonged
System of ductless glands secrete chemicalsignals directly into blood, chemical travels totarget tissue
slow, long-lasting response
the magnitude of endocrine effects aredependent upon the amount of hormone released.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 15/38
Nervous :Neurotransmitters released by neurons
Endocrine :Hormones release by endocrine glands
These two systems interact and regulate each other
Receptorproteins
Target cell
Endocrinegland
Receptorproteins
Hormonecarried byblood
neurotransmitter
axon

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 16/38
Nervous and hormonal regulation –
rapid and gradual control working together
6. Hormonal and neural control combined inhomeostasis, with respect to anatomy

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 17/38
The endocrine system works closely with thenervous system to maintain homeostasis, thesteady state of the body.
The nervous system helps regulate manyendocrine responses. For example, when the
body is threatened, the hypothalamus signalsthe adrenal glands to secrete the hormoneepinephrine.
Hypothalamus = “master nerve control
centre”
nervous system :receives information fromnerves around body about internal conditions
regulates release of hormones from pituitary

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 18/38
Pituitary
Hypothalamus
Anterior
Posterior

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 19/38
Managing Glucose
Levels
Insulin reduces blood glucose levelsglucose levels rise above set point, pancreas secretes
insulin
promotes transport of glucose into cells & storage of glucose (as glycogen) in liver & muscle cells
drops blood glucose levels
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels
when glucose levels drop below set point, pancreassecretes glucagon
promotes breakdown of glycogen & release of glucose

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 20/38

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 21/38
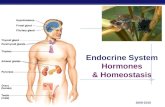
Human Endocrinesystem.
7. Using a generalized diagram of the human
body, identify the main endocrine organs inthe human body.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 22/38

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 23/38

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 24/38
The chemical nature of hormones
8. Identify the secretions of the main
endocrine organs, and the actions of thesesecretions

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 25/38
Important HormoneFunctionsReproduction
Growth and development
Immune system response
Maintenance of electrolyte, water, andnutrient balance of the blood
Regulation of cellular metabolism and energybalance

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 26/38
Major Endocrine OrgansPineal gland
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Thymus glandAdrenal glands
Pancreas
Gonads (i.e., ovaries and testes)

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 27/38
Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 28/38
Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones
Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principal Actions
Hypothalamus Releasing and inhibiting hormones Anterior lobe of pituitary Regulate secretion of hormonesby theanterior pituitary
Posteriorpituitary
Oxytocin
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
UterusMammary glands
Kidneys (collectingducts)
Stimulates contractionStimulates ejection of milk into
ducts
Stimulates re-absorption of water
Anteriorpituitary
Growth hormone (GH)
Prolactin
Melanocyte-stimulating hormones(MSH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
(ACTH)
Gonadotropic hormones
General
Mammary glands
Pigment cells in skin
Thyroid gland
Adrenal cortex
Gonads
Stimulates growth of skeleton andmuscle
Stimulates milk production
Stimulate melanin production
Stimulates secretion of thyroidhormones; helps regulate bone
remodeling
Stimulates secretion of adrenalcortical hormones
Stimulate gonad function andgrowth
Thyroid gland Thyroxine (T4) andtriiodothyronine (T3)
Calcitonin
General
Bone
Stimulate metabolic rate; regulateenergy metabolism
Lowers blood calcium level
Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principal Actions

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 29/38
g p
Pancreas Insulin
Glucagon
General
Liver, adipose tissue
Lowers blood glucoseconcentration
Raises blood glucoseconcentration
Adrenalmedulla Epinephrine andnorepinephrine Muscle; blood vessels;liver; adipose tissue Help body cope with stress;increase metabolic rate; raiseblood glucose level; increaseheart rate and blood pressure
Adrenal cortex Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Kidney tubules
General
Maintain sodium and potassiumbalance
Help body cope with long-termstress; raise blood glucose level
Pineal gland Melatonin Hypothalamus Important in biological rhythms
Ovary Estrogens
Progesterone
General; uterus
Uterus; breast
Develop and maintain sexcharacteristics in female;
stimulate growth of uterine lining
Stimulates development of uterine lining
Testis Testosterone General; reproductivestructures
Develops and maintains sexcharacteristics in males;
promotes spermatogenesis
Parathyroidglands
Parathyroidhormone
Bone, kidneys, digestivetract
Regulates blood calcium level

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 30/38
9. Describe the chemical nature of hormonesand how each main type elicits change at thecellular level

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 31/38
Hormone – A chemical substance secreted by one
cell that affects the functions of another cell.Four Classes of Hormones
1. Fatty Acid Derivatives
Prostaglandins and the juvenile hormone of insects
2. Amino acid-based hormones
Most hormones are this type
Tend to stay in the blood
3. Steroid hormones
Synthesized from cholesterol
Lipid-soluble; able to pass through the phospholipid membrane
Include the gonadal hormones and the adrenal cortical hormones(secreted by the adrenal cortex)

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 32/38
Regulation of hormone
secretion.Negative feedback
mechanisms.10. Using examples from human biology,
describe the regulation of hormone secretionby negative and positive feedback.
11. Discuss the implications of failure of aregulatory system

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 33/38
Thyroid hormones increase metabolic rate
In vertebrates, thyroid hormones are essentialfor normal growth and development. Thesehormones increase the rate of metabolism in
most body tissues.
Thyroid hormones also help regulate thesynthesis of proteins necessary for cell
differentiation.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 34/38
Thyroid secretion is regulatedby negative feedback systems
The regulation of thyroid hormone secretion depends on a negativefeedback loop between the anterior pituitary and the thyroid gland.
When the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood rises
above normal, the anterior pituitary secretes less thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Thyroid hormone concentration high inhibits anterior pituitarysecretes less TSH thyroid gland secretes less hormonehomeostasis
•
When the concentration of thyroid hormones decreases, thepituitary secretes more TSH.
Thyroid hormone concentration low anterior pituitary secretesmore TSHthyroid gland secretes more hormone homeostasis

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 35/38
Malfunction of the thyroid glandleads to specific disorders
Extreme hypothyroidism during infancy and childhood results in lowmetabolic rate and can lead to cretinism, a condition characterized byretarded mental and physical development
An adult who feels like sleeping all the time, has little energy, and ismentally slow or confused may be suffering from hypo-thyroidism.
When there is almost no thyroid function, the basal metabolic rate isreduced by about 40% the patient develops myxedema, characterized bya slowing down of physical and mental activity.
Hyperthyroidism does not cause abnormal growth but does increasemetabolic rate. This increase results in the rapid use of nutrients, causingthe individual to be hungry and to eat more. But this does not meet thedemands of the rapidly metabolizing cells, so people often lose weight. Themost common form of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease, an autoimmunedisease.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 36/38
Iodine deficiency is acommon cause of goitre,enlargement of the
thyroid gland.

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 37/38
Consequences of Endocrine MalfunctionHormone Hyposecretion Hypersecretion
Growth hormone Pituitary dwarfism Gigantism if malfunction occurs inchildhood; acromegaly in adult
Thyroid hormones Cretinism (in children); myxedema, acondition of pronounced adult
hypothyroidism; dietary iodine deficiencyleads to hyposecretion and goitre
Hyperthyroidism; increasedmetabolic rate, nervousness,
irritability; goiter; Graves’ disease
Parathyroidhormone
Spontaneous discharge of nerves;spasms; tetany; death
Weak, brittle bones; kidney stones
Insulin Diabetes mellitus Hypoglycemia
Hormones of adrenal cortex
Addison’s disease Cushing’s disease

7/27/2019 ENDOCRINE REGULATION AND CONTROL BIOLOGY HOMEOSTASIS
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/endocrine-regulation-and-control-biology-homeostasis 38/38
END