Http Cerescontrols Com Projects Eeg Electroencephalography With Labview and Mindwave Mobile
Electroencephalography (EEG) is based on synaptic currents
-
Upload
alexia-king -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Electroencephalography (EEG) is based on synaptic currents
Electroencephalography (EEG) is based on synaptic currents
http://www.brightmindsinstitute.com/blog/
http://quizlet.com/4239544/cog-sci-chapter-2-flash-cards/http://www.acm.org/conferences/sac/sac2000/Proceed/FinalPapers/BC-07/
http://apotential.wordpress.com/2012/07/11/the-neurologist-explains-eegs-to-me/
Synaptic currents create a small electrical field along a neuron
If neurons are lined up, the electric fields add together.
x
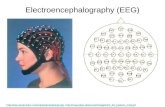
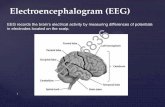
Using electrodes placed on the scalp and sensitive amplifiers…
…one can record “brain waves”!
Glial Cells
There are several different typesOligodendrocytes – make myelin for axonsAstrocytes – help to provide food and “clean up” Microglia – Undertakers and “Homeland Security”:
detect and repel invaders and get rid of the deadEpendymal cells – BBBarrier & cerebrospinal fluidRadial glia – play a big role in development
(scaffolding and producing neurons)
~120g, 8 Billion Cells~1 Billion neurons(~11:1 glia:neurons)
~150g, 85 Billion Cells~70 Billion neurons(~1:4 glia:neurons)
~1250g, 75 Billion Cells~16 Billion neurons(~4:1 glia:neurons)
~1500 g, 170 Billion Cells~86 Billion neurons(~1:1 glia:neurons)
Important properties of neurons Neurons have a negative “membrane potential” (i.e., inside has negative charge
compared to outside/CSF)
Neurons receive many signals that constantly change this “membrane potential”
Neurons will send a signal of their own if they become sufficiently “depolarized”
This signal, the Action Potential is a wave of “positivity” that propagates down the axon
Neurons can send signals quickly (~100 m/sec) to other neurons, muscles, glands etc.
Neurons have high energy demands, and low energy reserves.
Neurons do not divide and replace themselves – if damaged enough to die, they are not replaced (with few exceptions).