EKG rounds
-
Upload
clayton-ayala -
Category
Documents
-
view
61 -
download
1
description
Transcript of EKG rounds
Case
• 67y Caucasian F presents to ED c/o exertional SOB
• Worsening over last 8d
• No other assoc symptoms
• PMHx: HTN, DM, hyperlipidemia
• O/e: HR 88 BP 140/85 RR 20 sats 96%
• Nil acute on examination
Case cont’d
• Blwk:– TNT normal– D-dimer 3.27
• Investigations:– Echo: RV systolic dysfxn, mod-severe pulm
hypertension– CT confirmed PE
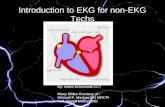
Why T inversion with PE ?
• Possible mechanisms: – Due to acute cor pulmonale from RV
enlargement and RV ischemia– Other factors such as hypoxemia and chemical
mediator release in RV may lead to T wave inversion
• T inversion occurs in 42-89% of acute PE cases
• N=80 pts hospitalized for PE
• Analysis of admission EKG’s and those during course of hospitalization
• T wave inversion is most common abnormality (68%) and best correlates to severity of PE
Chest. 1997.
• Retrospective cohort study of pts with PE and age- and sex-matched controls (n=98)
• All pts had CT PE done (no d-dimers available at that time in their institute)
• All EKG reviewed by 2 cardiologists
• ?discrete EKG findings for ED pts to rule-in vs. rule-out PE?
J Emerg Med. 2004.
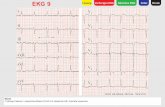
EKG and PE
• Kappa values were calculated for each EKG finding and varied from 0.14 to 1.0
• For normal T waves (k=0.17) and biphasic T waves (k=0.14)
• Conclusion: no EKG findings specific or sensitive enough to help dx PE in ED.
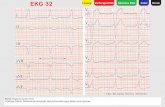
• N=40 consecutive pts with PE and 87 consecutive pts with ACS
• All pts had negative T waves >=1mm in 2+ contiguous precordial leads (V1-4)
• Exclusion criteria: ST elevation>=2mm on 2+ precordial leads, Q wave MI, conditions precluding evaluation of ST segments, hx cardiopulmonary disease
• Dx of PE made with pulm angio, V/Q, or spiral CT• Dx of ACS made with cardiac cath
Am J Cardiol. 2007.
Conclusions
• Combination of T inversion in V1 and III was more sensitive and specific for PE and rarely found in ACS (1%)
""Excuse me. ... I Excuse me. ... I
know the game's know the game's almost over; but almost over; but just for the record, just for the record, I don't think my I don't think my buzzer was buzzer was working properlyworking properly..
by Gary Larsonby Gary Larson
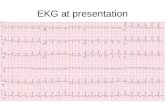
Final one…
Digoxin toxicity – T inversion, prolonged PR, diffuse ST depression with distinct scooped appearance