EKG Quiz - North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo · EKG Quiz Barry Bertolet, MD Use your Audience...
Transcript of EKG Quiz - North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo · EKG Quiz Barry Bertolet, MD Use your Audience...
Differential Diagnosis of Tachycardia
Tachycardia Narrow Complex Wide Complex
Regular ST
SVT
Atrial flutter
ST w/ BBB
SVT w/ BBB
VT
Irregular A-fib
A-flutter w/ variable conduction
MAT
A-fib w/ BBB
A-fib w/ WPW
VT
4
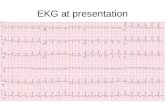
EKG #2
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. pericarditis
b. myocarditis
c. digitalis effect
d. infero postero lateral wall ST-elevation MI
EKG #2
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. pericarditis
b. myocarditis
c. digitalis effect
d. infero postero lateral wall ST-elevation MI
Ventricular Tachycardia
Rate 110 -250 bpm
Wide complex (>0.12 – 3 small blocks)
Regular
AV dissociation
Extreme Right Axis Deviation + Upright MCL-1
I III II III
MCL-1
EKG #4
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. sinus bradycardia
b. sinus tachycardia
c. 2nd degree AV block
d. complete heart block
EKG #4
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. sinus bradycardia
b. sinus tachycardia
c. 2nd degree AV block
d. complete heart block
Blocks
AV blocks
First degree block • PR interval fixed and > 0.2 sec
Second degree block, Mobitz type 1 • PR gradually lengthened, then drop QRS
Second degree block, Mobitz type 2 • PR fixed, but drop QRS randomly
Type 3 block • PR and QRS dissociated
13
EKG #5
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. V-fib
b. left bundle branch block
c. right bundle branch block
d. normal
EKG #5
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. V-fib
b. left bundle branch block
c. right bundle branch block
d. normal
EKG #6
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. V-fib
b. left bundle branch block
c. right bundle branch block
d. normal
EKG #6
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. V-fib
b. left bundle branch block
c. right bundle branch block
d. normal
Differential Diagnosis of Tachycardia
Tachycardia Narrow Complex Wide Complex
Regular ST (HR < 150)
SVT (HR > 150)
Atrial flutter (HR = 150)
ST w/ BBB
SVT w/ BBB
VT
Irregular A-fib
A-flutter w/ variable conduction
MAT
A-fib w/ BBB
A-fib w/ WPW
VT
21
EKG #8
1. What would you do next based on this EKG?
a. Reassure and discharge
b. Refer for electrophysiology study
c. Begin a beta-blocker
19 year old
male with
complaints
of
palpitations
EKG #8
1. What would you do next based on this EKG?
a. Reassure and discharge
b. Refer for electrophysiology study
c. Begin a beta-blocker
19 year old
male with
complaints
of dizziness
and
palpitations
EKG #9
1. The therapy of choice is:
a. Thrombolytics
b. Cath and PCI
c. NSAIDs and Colchicine
EKG #9
1. The therapy of choice is:
a. Thrombolytics
b. Cath and PCI
c. NSAIDs and Colchicine
Pericarditis
PR segment depression, usually in lead II
27
EKG #10
This patient is a 50 year old man who presented to the ED with chest tightness and is noted to be markedly hypotensive on exam. What is your therapy for BP restoration? A. Dopamine B. IVF bolus C. Balloon pump
EKG #10
This patient is a 50 year old man who presented to the ED with chest tightness and is noted to be markedly hypotensive on exam. What is your therapy for BP restoration? A. Dopamine B. IVF bolus C. Balloon pump
What about the right side?
RV infarcts
Move V4 to the
right side same
location
5th intercostal
space anterior
axillary
Occur in conjunction with inferior MIs
30
Acute MI with RV involvement
31
Acute MI with RV involvement
IVF to increase filling pressures
Inotropes to follow IVF loading
RV - VAD
32
EKG #11
This patient is 40 year old woman with pleuritic chest pain and breathlessness. What is the diagnostic test of choice?
a. Echo b. CTA c. CXR
EKG #11
This patient is 40 year old woman with pleuritic chest pain and breathlessness. What is the diagnostic test of choice?
a. Echo b. CTA c. CXR
EKG #13
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. V-fib
b. left bundle branch block
c. right bundle branch block
d. normal
EKG #13
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. V-fib
b. left bundle branch block
c. right bundle branch block
d. normal
EKG #14
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. Pericarditis
b. Myocardial infarction
c. Early Repolarization
EKG #14
1. What does this EKG represent?
a. Pericarditis
b. Myocardial infarction
c. Early Repolarization
Classic findings
1. J-point “notching”
2. Concave-up ST segment (smiley face)
3. ST segment elevation from baseline in V2-V5, typically <3mm
4. Large, symmetrically concordant T-waves in leads with STE
43
Classic findings
1. J-point “notching”
2. Concave-up ST segment (smiley face)
3. ST segment elevation from baseline in V2-V5, typically <3mm
4. Large, symmetrically concordant T-waves in leads with STE
44
Can we tease it out?
The degree of ST segment elevation is thought to be
indirectly proportional to the degree of sympathetic tone
In other words, the more relaxed the patient, the more
pronounced the ST segment elevation (and vice versa)
If you truly want to test your patient, get their heart rate up
and look at the ST segment
45
HR 64 HR 83
The ST segment is NOT fixed in pts w/ BER and changes from EKG to EKG and with the degree of sympathetic strain On the right, note the complete resolution of the ST elevation but maintenance of the J-point notching in V4 46