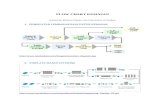
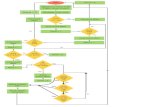
Effective Learning Flow Chart
Click here to load reader
-
Upload
franciam -
Category
Technology
-
view
5.564 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Effective Learning Flow Chart

Quality Instruction
A teacher must provide…
Incentive system that motivates students to encourage and help one another to achieve. Rewarding stu-dents based on improvement over their own past performance has also been found to be effective
Input, modeling, and checking for understanding.
Students must have independent practice that includes use of the concept or skill in the way they learned it.
One critical principal of effective use of classroom incentives is that students should generally be held accountable for what they do. For example, homework that is checked has been found to contribute more to students achievement than home-work that is assigned but not checked.
Effective Instruction in the e-Learning Environment
Incentives
Communication
Email Forums Response
Communicate high expectations for students, such as waiting for them to respond

Support Learning Basics,Stimulate Deep Thinking
Assessment—Thinking Outside the Box
Basic knowledge should be presented with illustrative examples together with tasks and their solutions.
Analytical thinking processes are stimulated when students are asked to divide elements of knowledge, to compare, to evaluate, and to explain them.
Creative thinking can be fostered when students are required to imag-ine elements of knowledge and to develop own prod-ucts of learning.
Knowledge, thinking, and problem solving should be an in-tegrated part of the achievement.
Different traditional and new ways of achievement evalua-tion (e.g., tests, ob-servations, or portfo-lios) should be used in order to get a compre-hensive and multi-faceted view of the students' knowledge, thinking, and problem solving behavior.
The strategy of documentation— a cooperative practice that helps teachers listen to and see the students with whom they work. Documen-tation is also vital for systematically following and studying the ways students develop ideas, theories, and understandings.
Interviews and questionnaires gather information about our abilities as teachers and the effectiveness of the course work.
Portfolios at key intervals and transitions. In the online set-ting, midterm and final portfo-lios shared with peers.

Allen, Tom (1998). The Madeline Hunter Elements of Effective Instruction. Retrieved April 1, 2008 from Humboldt State University Web Site: http://www.humboldt.edu/~tha1/hunter-eei.html#eei
Astleitner, Hermann (2005). Principles of effective instruction—general standards for teachers and instructional designers, Journal of Instructional Psychology. Retrieved April 13, 2008 from Find Articles at http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0FCG/is_1_32/ai_n13670698/pg_2
Clark, Don. Bloom’s Taxonomy. Retrieved February 6, 2008 from the web-site of Don Clark: http://www.nwlink.com/~Donclark/hrd/bloom.html
O’Bannon, B. (2002). Planning for Instruction, Instructional Methods. Re-trieved February 6, 2008 from The University of Tennessee Innovative Technology Center website: http://edtech.tennessee.edu/~bobannon/in_strategies.html
Slavin, Robert E. (1998). A Model of Effective Instruction. Retrieved April 13, 2008 from Success for All Web Site: http://successforall.com/_images/pdfs/modeleffect.htm
References